Abstract
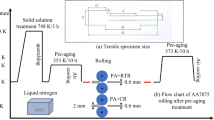
To explore the effect of deformation temperature and subsequent heat treatment on the materials’ formability, AA7075 sheets were prepared by cryorolling (− 196°C) and room-temperature rolling, associated with subsequent peak aging treatment at 100°C for 40 h. Erichsen tests were carried out on samples with different thicknesses. At the same reduction rate, the Erichsen height of cryorolled samples was obviously higher than that of room-temperature rolled samples. As the reduction rate reached 80%, the Erichsen value of cryorolled samples was 0.87 mm higher than room-temperature rolled samples. After peak aging treatment, the Erichsen height values of cryorolled + peak aged and room-temperature rolled + peak aged samples increased greatly. Specially, the Erichsen value of cryorolled + peak aged samples with the same reduction was 0.3–0.6 mm higher than that of room-temperature rolled + peak aged samples. In addition, for the samples of cryorolled, room-temperature rolled, cryorolled + peak aged and room-temperature rolled + peak aged, their cryogenic Erichsen heights are all higher than room-temperature Erichsen heights. Compared to room-temperature Erichsen heights of room-temperature rolled samples, the increasing rates of cryogenic Erichsen heights of cryorolled samples are in the range of 13–117%.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
B. Zhou, B. Liu, S.G. Zhang, R. Lin, Y. Jiang, and X.Y. Lan, J. Alloys Compd. 879, 160407 (2021).
Y.X. Feng, J. Liu, and C. An, Mater. Guide 18(8A), 196 (2004).
B. Liu, C.Q. Peng, R.C. Wang, X.F. Wang, and T.T. Li, Chin. J. Nonferr. Met. 20, 1705 (2010).
Y.S. Lee, D.H. Kou, H.W. Kin, and Y.S. Ahn, Scr. Mater. 147, 45 (2018).
M.M. Shahzamanian, M. Parsazadeh, and P.D. Wu, Int. J. Solid Struct. 286–287, 112558 (2024).
Z.H. Du, Z.S. Deng, A. Xiao, X.H. Cui, H.L. Yu, and Z.Z. Feng, J. Manuf. Process. 70, 15 (2021).
H. Li, P. Chen, Z.X. Wang, F. Zhu, R.G. Song, and Z.Q. Zheng, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 742, 798 (2019).
S. Zhang, X. Luo, G.Y. Zheng, N.Z. Zhai, Y.Q. Yang, and P.T. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 832, 142482 (2022).
L.H. Su, C. Lu, G.Y. Deng, and K. Tieu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45, 515 (2014).
N. Nie, L.H. Su, G.Y. Deng, H.J. Li, H.L. Yu, and K. Tieu, J. Mater. Res. Tech. 15, 6574 (2021).
H.L. Li, A.H. Guo, C. Kong, and H.LYu. Mater, Sci. Eng. A 891, 146007 (2024).
L.H. Su, G.Y. Deng, V. Luzin, H. Wang, Z.Y. Wang, H.L. Yu, H.J. Li, and A.K. Tieu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 780, 139190 (2020).
G.Y. Deng, C. Lu, A.K. Tieu, L.H. Su, N.N. Huynh, and X.H. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. 45, 4711 (2010).
G.Y. Deng, C. Lu, L.H. Su, A.K. Tieu, J.T. Li, M. Liu, H.T. Zhu, and X.H. Liu, Comp. Mater. Sci. 81, 79 (2014).
P.T. Wei, C. Lu, K. Tieu, L.H. Su, G.Y. Deng, and W.B. Huang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 684, 239 (2017).
H. Kim, H. Ha, J. Lee, S. Son, H.S. Kim, H. Sung, J.B. Seol, and J.G. Kim, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 810, 141020 (2021).
K. Lu, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 55, 1 (2024).
Z.D. Li, H. Gu, K.G. Luo, C. Kong, and H.L. Yu, Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.01.019 (2023).
H.Q. Xiong, L.H. Su, C. Kong, and H.LYu. Adv. Eng. Mater. 23, 2001533 (2021).
S.S. Yang, Z.D. Li, Y.X. Zhou, C. Kong, and H.L. Yu, J. Alloys Compd. 931, 167556 (2023).
H.L. Yu, C. Lu, A.K. Tieu, and S.H. Zhang, Adv. Eng. Mater. 18, 754–769 (2016).
Y.H. Zhao, J.F. Bingert, X.Z. Liao, B.Z. Cui, K. Han, A.V. Sergueeva, A.K. Mukherjee, R.Z. Valiev, T.G. Langdon, and Y.T. Zhu, Adv. Mater. 18, 2949 (2006).
H. Gu, L. Bhatta, H.T. Gao, Z.D. Li, C. Kong, and H.LYu. Mater, Sci. Eng. A 843, 143141 (2022).
F.L. Yu, C. Kong, and H.L. Yu, Tungsten 5, 522 (2023).
L. Wang, D.L. Tang, C. Kong, and H.L. Yu, Materialia 21, 101283 (2022).
H.L. Yu, L. Wang, L.J. Chai, J.T. Li, C. Lu, A. Godbole, H. Wang, and C. Kong, Mater Charact 153, 34 (2019).
H.L. Yu, C. Lu, K. Tieu, H.J. Li, A. Godbole, X. Liu, and C. Kong, J. Mater. Res. 32, 3761 (2017).
H.L. Yu, China Mech. Eng. 31(1), 89 (2020).
S.K. Panigrahi, and R. Jayaganthan, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 9609–9616 (2011).
J. Luo, H. Lou, S. Li, R. Wang, and Y. Ma, Mater. Des. 187, 108402 (2020).
D. Jia, K.T. Ramesh, and E. Ma, Acta Mater. 51, 3495–3509 (2003).
C. Zhou, L. Zhan, and C. Liu, M. Huang. iScience 26, 106870 (2023).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the High-tech Industry Technology Innovation Leading Plan of Hunan Province (Grant No. 2022GK4032), the Innovation Driven Program of CSU (no. 2019CX006), and the Research Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Precision Manufacturing for Extreme Service Performance at Central South University for the financial support. The authors also thank to Mr. Shisen Yang at Central South University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that will affect the reporting in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Gao, H., Huang, Y. et al. Effect of Cryorolling and Aging Treatment on Erichsen Formability of AA7075 Sheets at Room and Cryogenic Temperatures. JOM (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-024-06613-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-024-06613-3