Abstract
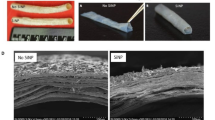
Preterm birth affects 10% of pregnancies worldwide, and the largest fraction of these untimely births is due to rupture of the amniotic sac. Biomimetic materials, such as electrospun fibrillar networks, show promise for patching the fetal membrane in cases of medical intervention, in which the tissue is transected. Here, gelatin membranes were generated in four different conditions, with and without crosslinking agents added to the electrospinning solution, plus with and without a heat treatment step to activate the crosslinkers. Drumhead puncture testing was used to measure elastic modulus and strength of electrospun materials. Stiffness was not affected by crosslinking condition, in contrast to failure strength. Results were compared with a previous study on fracture behavior of biomimetic electrospun materials, which demonstrated a third different trend in the same four material groups. Compared with natural amnion, electrospun materials were stiffer and stronger but less fracture resistant. Prior to application as a biomimetic tissue engineering scaffold, better understanding of structure-properties relationships in fibrillar materials is required.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Vidal Jr., R.C.V. Lintao, M.E.L. Severino, O.A.G. Tantengco, and R. Menon, Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 1015622 https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.1015622 (2022).
J.M. Hodek, J.M. von der Schulenburg, and T. Mittendorf, Health Econ. Rev. 1, 6 https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-1991-1-6 (2011).
J. Villar, A.T. Papageorghiou, H.E. Knight, M.G. Gravett, J. Iams, S.A. Waller, M. Kramer, J.F. Culhane, F.C. Barros, A. Conde-Agudelo, Z.A. Bhutta, and R.L. Goldenberg, Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 206, 119 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2011.10.866 (2012).
D.M. Bond, P. Middleton, K.M. Levett, D.P. van der Ham, C.A. Crowther, S.L. Buchanan, and J. Morris, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004735.pub4 (2017).
S.M. Winkler, M.R. Harrison, and P.B. Messersmith, Biomater. Sci. 7, 3092 https://doi.org/10.1039/c9bm00177h (2019).
G.L. Bourne, Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 79, 1070 https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9378(60)90512-3 (1960).
G.D. Bryant-Greenwood, Placenta 19, 1 https://doi.org/10.1016/s0143-4004(98)90092-3 (1998).
H. Oxlund, R. Helmig, J.T. Halaburt, and N. Uldbjerg, Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 34, 247 https://doi.org/10.1016/0028-2243(90)90078-f (1990).
M.L. Oyen, R.F. Cook, and S.E. Calvin, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 15, 651 https://doi.org/10.1023/b:jmsm.0000030205.62668.90 (2004).
E.M. Joyce, P. Diaz, S. Tamarkin, R. Moore, A. Strohl, B. Stetzer, D. Kumar, M.S. Sacks, and J.J. Moore, Placenta 38, 57 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2015.12.011 (2016).
M.L. Oyen, S.E. Calvin, and D.V. Landers, Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 195, 510 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2006.02.010 (2006).
K. Tonsomboon, and M.L. Oyen, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 21, 185 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.03.001 (2013).
J.M. Ludwick, and M.L. Oyen, MRS Adv. 5, 1783 https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2020.188 (2020).
Q. Jiang, H. Xu, S. Cai, and Y. Yang, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 25, 1789 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5208-2 (2014).
W. Chua, and M.L. Oyen, Cell. Molec. Bioeng. 2, 49 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-009-0049-7 (2009).
J.D. James, J.M. Ludwick, M.L. Wheeler, and M.L. Oyen, J. Mater. Res. 35, 1227 https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.114 (2020).
C.T. Koh, K. Tonsomboon, and M.L. Oyen, J. Roy. Soc. Interface Focus 9, 20190012 https://doi.org/10.1098/rsfs.2019.0012 (2019).
A.L. Butcher, C.T. Koh, and M.L. Oyen, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 69, 412 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.02.007 (2017).
S. Guessasma, and M.L. Oyen, Soft Matter 12, 602 https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SM02342D (2015).
E.A. Schober, R.P. Kusy, and D.A. Savitz, Ann. Biomed. Eng. 22, 540 https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02367090 (1994).
E.K. Pressman, J.L. Cavanaugh, and J.R. Woods, Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 187, 672 https://doi.org/10.1067/mob.2002.125742 (2002).
D. Kumar, R.M. Moore, B.M. Mercer, J.M. Mansour, R.W. Redline, and J.J. Moore, Placenta 42, 59 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2016.03.015 (2016).
A. Grémare, S. Jean-Gilles, P. Musqui, L. Magnan, Y. Torres, M. Fénelon, S. Brun, J.-C. Fricain, and N. L’Heureux, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 99, 18 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.07.007 (2019).
M.D. Shoulders, and R.T. Raines, Ann. Rev. Biochem. 78, 929 https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.032207.120833 (2009).
R.S. Rivlin, and A.G. Thomas, J. Polym. Sci. 10, 291 https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1953.120100303 (1953).
P.P. Purslow, J. Mater. Sci. 18, 3591 https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00540731 (1983).
P.P. Purslow, J. Biomech. 16, 947 https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9290(83)90058-1 (1983).
J.P. Gong, Soft Matter 6, 2583 (2010).
J.Y. Sun, X. Zhao, W.R. Illeperuma, O. Chaudhuri, K.H. Oh, D.J. Mooney, J.J. Vlassak, and Z. Suo, Nature 489, 133 (2012).
R.F. Cook, and M.L. Oyen, J. Phys. Mater. 4, 021001 https://doi.org/10.1088/2515-7639/abdb39 (2021).
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by the East Carolina University (ECU) Department of Engineering via graduate assistantship funding to MLW and by the ECU Division of Research, Economic Development and Engagement (REDE) via start-up funds to MLO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wheeler, M.L., Oyen, M.L. Physical Properties of Biomimetic Fibrous Gelatin Networks. JOM 75, 2149–2157 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05888-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05888-2