Abstract
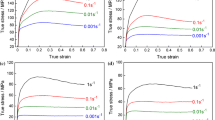
ZK60 alloys are known to have high mechanical strength relative to other Mg alloys. Composition variations in precipitate and solute content of ZK60 Mg alloys, with Zn variations and Ce substitutions, allow for the formation of higher melting point precipitates and impact dynamic recrystallization (DRX) behavior, microstructure, and mechanical properties. Creating constitutive models of the DRX process in various Mg alloys can help guide processing to efficiently create products with desirable microstructures. In this work, hot compression testing at various strain rates and temperatures was carried out. It has been shown that greater peak true stresses are required for DRX in alloys processed at lower temperatures and higher strain rates. Moreover, increases in Zn and Ce content increase the stress that the microstructure can absorb before DRX starts. Finally, electron backscattered diffraction mapping shows how texture is decreased by DRX compared to the as-received conditions and how DRX was more advanced for low Zr and low strain rate conditions, consistently with the developed model. Based on these experimental results, a constitutive model to quantify the relationship between the Zener–Hollomon parameter and peak stress was developed. The model was shown to reflect the experimentally obtained results accurately.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.M. Avedesian, and H. Baker, ASM specialty handbook: magnesium and magnesium alloys (ASM International, 1999).
A. Hadadzadeh, S.K. Shaha, M.A. Wells, H. Jahed, and B.W. Williams, Magnesium Technology 2017 (Springer, 2017), pp513–519.
Z. Zhu, and A.D. Pelton, J. Alloy. Compd. 652, 426 (2015).
H. Yu, Y.M. Kim, B.S. You, H.S. Yu, and S.H. Park, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 559, 798 (2013).
E. Silva, R.H. Buzolin, F. Marques, F. Soldera, U. Alfaro, and H.C. Pinto, J. Magnes. Alloys 9, 995 (2021).
S.R. Agnew, and Ö. Duygulu, Int. J. Plast. 21, 1161 (2005).
R. Verma, L.G. Hector, P.E. Krajewski, and E.M. Taleff, JOM 61, 29 (2009).
T. Sakai, and J.J. Jonas, Acta Metall. 32, 189 (1984).
S. Fatemi, and H. Paul, Mater. Chem. Phys. 257, 123726 (2021).
A. Galiyev, R. Kaibyshev, and G. Gottstein, Acta Mater. 49, 1199 (2001).
J. Dong, J. Sun, L. Jin, Z. Zhang, and W. Ding, in Proceedings of 135h International Conference on Fracture 1 (2013)
L. Fu, Q. Le, W. Hu, J. Zhang, and J. Wang, J. Market. Res. 9, 6834 (2020).
P. Xu, J. Yu, and Z. Zhang, Materials 12, 2773 (2019).
J. Liu, Z. Cui, and C. Li, Comput. Mater. Sci. 41, 375 (2008).
L. Li, Y. Wang, H. Li, W. Jiang, T. Wang, C.-C. Zhang, F. Wang, and H. Garmestani, Comput. Mater. Sci. 166, 221 (2019).
H. Mirzadeh, M. Roostaei, M.H. Parsa, and R. Mahmudi, Mater. Des. 68, 228 (2015).
A. Najafizadeh, and J.J. Jonas, ISIJ Int. 46, 1679 (2006).
N. Safara Nosar, F. Sandberg, and G. Engberg, Mater. Sci. Forum 941, 458–467 (2018).
J. Duan, Y. Tan, L. Ji, W. Liu, J. Zhang, and R. Liu, Progr. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 25, 34 (2015).
T. Lin, J.-X. Zhou, C.-N. Jing, Y.-T. Liu, L.-L. Zhang, and X.-B. Meng, High Temp. Mater. Process. (London) 39, 200 (2020).
H. Mecking, and U. Kocks, Acta Metall. 29, 1865 (1981).
H. Mirzadeh, Mater. Chem. Phys. 152, 123 (2015).
Y.-J. Qin, Q.-L. Pan, Y.-B. He, W.-B. Li, X.-Y. Liu, and X. Fan, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527, 2790 (2010).
H. Yu, H. Yu, G. Min, S.S. Park, B.S. You, and Y.M. Kim, Met. Mater. Int. 19, 651 (2013).
M. Nienaber, G. Kurz, D. Letzig, K.U. Kainer, and J. Bohlen, Crystals 12, 1307 (2022).
I. Dillamore, P. Hadden, and D. Stratford, in (Hindawi, 1970)
Y. Li, P. Hou, Z. Wu, Z. Feng, Y. Ren, and H. Choo, Mater. Des. 202, 109562 (2021).
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge support by the Center for Advanced Non-Ferrous Structural Alloys (CANFSA), a National Science Foundation Industry/University Cooperative Research Center (I/UCRC) (Award No. 1624836) at the Colorado School of Mines. Mag Specialties, Inc. supplied and designed all alloys evaluated during the project duration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Storey, G.K., Eres-Castellanos, A., Sutton, S. et al. Modeling of Dynamic Recrystallization Kinetics in Ce Containing Mg Alloys. JOM 75, 2397–2405 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05809-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05809-3