Abstract
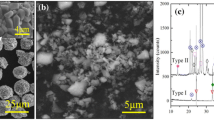
Via micro- and nano-structure design of a coating layer on the bottom of ceramic pots with copper powders and low melting point glass powders, a simple and low-cost solution for fabricating high-efficiency induction heating ceramic pots without changing the induction cookers has been provided. The influences of sintering temperature and glass content on the heating efficiency of the copper layer were studied. The hysteresis loop, resistivity, and microstructure of the copper layer were investigated using a vibrating sample magnetometer, a field-emission scanning electron microscope, and a high-resolution transmission electron microscope, respectively. Microstructure observation revealed that an insulating glass film with 1.06 nm width was formed between the adjacent copper particles in the sintered copper layer. The experimental results showed that the sintered layer made with copper powder slurry had a resistivity of 22.67 × 10–8 Ωm, which is 12.95 times that of a pure copper plate. The saturation magnetization of the sintered layer under the static magnetic field was about 3.55 × 10–2 emu/g, which is 3.38 times that of a copper plate. A ceramic pot with a sintered copper layer takes about 510 s to heat 500 mL of water from room temperature to 100°C under the power of 500 W. Its heating efficiency is comparable to that of a ferromagnetic stainless-steel pot.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Lucia, P. Maussion, E.J. Dede, and J.M. Burdio, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61, 2509 (2013).
B. Thomas, D. Miro, M. Peter, and B. Debes, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 57, 27 (2014).
P.D. Agarwal, IEEE Trans. Commun. 78, 169 (1959).
Z.T. Yong, S.P. Chandrakant, J.S.T. Ang, and W.C. Jia, J. Membr. Sci. 606, 118150 (2020).
K. Vladimir, O. Elena, M. Olga, F. Marina, Z. Andrey, P. Sergey, and F. Aleksandr, Ceram. Int. 49, 2034 (2023).
A. Fomin, Ceram. Int. 45, 8258 (2019).
Y.Y. Lian, L. Wang, J.Y. Cao, T.T. Liu, Z.J. Xu, B.W. Yang, T.Q. Huang, X.D. Jiang, and N.N. Wu, Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 4, 925 (2021).
N. Kakuta, K. Nishijima, K. Kondo, and Y. Yamada, J. Appl. Phys. 122, 044901 (2017).
B.R. Anupam, U.C. Sahoo, and A.K. Chandrappa, Constr. Build. Mater. 321, 126395 (2022).
B.H. Dinh, D.W. Park, and T.H.M. Le, Constr. Build. Mater. 164, 246 (2018).
V.Y. Skeeba, V.V. Ivancivsky, and N.V. Martyushev, Metals 11, 1354 (2021).
Z.M. Liu, T.D. Wang, Y.F. Meng, Z.C. Han, and T. Jin, Int. J. Pavement Eng. 23, 3838 (2022).
P.B. Kharat, S.B. Somvanshi, P.P. Khirade, and K.M. Jadhav, ACS Omega 5, 23378 (2020).
O. Lucia, J. Acero, C. Carretero, and J. Burdio, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 7, 35 (2013).
M.K. Kazimierczuk, T. Nandakumar, and S. Wang, IEEE Trans. Aeros. Elec. Syst. 29, 88 (1992).
M. Kamli, S. Yamamoto, and M. Abe, IEEE Trans. Ind. Elec. 43, 163 (1996).
H.M. El-Mashad, and Z.L. Pan, Food Eng. Rev. 9, 82 (2017).
E. Jang, S.M. Park, D. Joo, H.M. Ahn, and K. Lee, J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 14, 2399 (2019).
F.P. Dawson, and P. Jain, IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 6, 430 (1991).
F.G. Alvear, R. Carlos, and P. Joe, JOM. 72, 11 (2020).
C.S. Chen, China patent CN201310450752.3, 18 May 2016
A. Pan, H. Lan, Y. Huang, C. Peng, and S. Wang, Appl. Sci. 9, 970 (2019).
X.P. Qu, D.H. Cao, and Y.H. Huang, China patent CN110386758A, 29 Oct 2019
K. Pashova, E. Dhaouadi, I. Hinkov, O. Brinza, Y. Roussigné, M. Abderrabba, and S. Farhat, Coatings 10, 305 (2020).
M.S. Huang, C.C. Liao, Z.F. Li, Z.R. Shih, and H.W. Hsueh, IEEE Access 9, 5105 (2021).
A. Ahlbom, and M. Feychting, Br. Med. Bull. 68, 157 (2003).
S. Yao, J. Xing, J. Zhang, S. Xiong, Y. Yang, X. Yuan, H. Li, and H. Tong, J. Mater. Sci. 29, 18540 (2018).
Q. Ma, S. Ma, J. Bai, and H. Wang, RSC Adv. 7, 47500 (2017).
H. Zhang, H. Bai, Q. Jia, W. Guo, L. Liu, and G. Zou, Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 33, 1543 (2020).
A. Sahu, R.S. Maurya, S. Ram, L.K. Singh, and T. Laha, Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 35, 1043 (2022).
W. Han, K.T. Chau, and Z. Zhang, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64, 1982 (2017).
P. Cui, W.B. Zhu, H.J. Ji, H.T. Chen, C.J. Hang, and M.Y. Li, Appl. Energy. 321, 119316 (2022).
M. Runde, and N. Magnusson, Physica C 372, 1339 (2002).
W. Chen, Z. Sun, Z. Wang, L. Gu, X. Xu, S. Wu, and C. Gao, Science 366, 983 (2020).
H. Bishara, S. Lee, T. Brink, M. Ghidelli, and G. Dehm, ACS Nano 15, 16607 (2021).
J.C. Fisher, and I. Giaever, J. Appl. Phys. 32, 172 (1961).
D. Gatteschi, and R. Sessoli, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 268 (2003).
G.R. Ruschau, S. Yoshikawa, and R.E. Newnham, J. Appl. Phys. 72, 953 (1992).
P. Zhang, Y. Bin, R. Zhang, and M. Matsuo, Polym. J. 49, 839 (2017).
J.G. Simmons, J. Appl. Phys. 34, 1793 (1963).
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by key research project of education department of Guangdong Province, China [No. 2020ZDZX2026].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that influenced the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Wei, J., Zheng, H. et al. Investigation of the Induction Heating Phenomenon of Sintered Coatings with Copper Powders. JOM 75, 1800–1809 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05782-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05782-x