Abstract
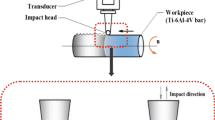
Surface properties of heat-treated Ti-6Al-4V alloy treated by heating-assisted ultrasonic rolling (HUR) were studied in this paper. The results showed that the sample treated by HUR at 140°C exhibited the better microstructure and had relatively fine grains and uniform and dense dislocations, and the highest microhardness reached to 495 HV and had an increment of 70 HV compared to UR-treated sample at 25°C. However, it showed the lower values of compressive residual stress than UR-treated sample at 25°C. The high heating temperature increased the plastic deformation capacity of the materials during UR treatment. Meanwhile, it also promoted the release of residual stress. However, its surface roughness was slightly higher than UR-treated sample at 25°C because of the lack of cold work hardening and the localized bonding behavior. Finally, HUR-treated sample at 140°C had the lower coefficient of friction and wear rate compared to UR-treated sample at 25°C. Therefore, it was deduced that the finer the grains were, the thicker the strengthening layer, and the higher mechanical properties of material surface layer had an important effect on surface friction and wear performance of the sample.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Jackson, Encyclopedia of Automotive Engineering-Automotive Applications for Titanium (ACS, Atlanta, 2014), p. 1.
O. Schauerte, Adv. Eng. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200310094 (2003).
P. Doorbar, M. Dixon, and A. Chatterjee, Mater. Sci. Forum. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.618-619.127 (2009).
N. Khanna, and J.P. Davim, Measurement. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2014.10.059 (2015).
I.V. Gorynin, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(98)01180-0 (1999).
I. Gurrappa, Mater. Charact. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2003.10.006 (2003).
M. Wen, C. Wen, P. Hodgson, and Y. Li, Colloid. Surf. B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.10.039 (2014).
Y. Luo, Y. Li, and M. Tian, Application of Biomedical-Grade Titanium Alloys in Trabecular Bone and Artificial Joints, Biomaterials and Medical Tribology (Woodhead Publishing, London, 2013), p. 181.
R. Baccino, F. Morret, F. Fellerin, D. Guichard, and G. Raisson, Mater. Des. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-3069(99)00093-X (2000).
P. Budzynski, A.A. Youssef, and J. Sielanko, Wear. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.03.008 (2006).
Y. Zhou, M. Shen, Z. Cai, J. Peng, and M. Zhu, Wear. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2016.10.027 (2017).
S.K. Vajpai, B. Sharma, M. Ota, and K. Ameyama, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.09.002 (2018).
C.H.V. Satyanarayanaraju, R. Dixit, P. Miryalkar, S. Karunanidhi, A. AshokKumar, J. NagaLakshmi, U. Ramakrishna, R. Mounika, and P. Saipavan, Mater. Today. Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.07.088 (2019).
C.L. Qiu, X.H. Wu, J.F. Mei, P. Andrews, and W. Voice, J. Alloy. Comp. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.06.045 (2013).
X.L. Xu, Q.Y. Li, J. Wang, X.P. Ren, and H.L. Hou, Mater. Charact. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111399 (2021).
L.F. Ye, H. Liu, C. Sun, X. Zhuo, J. Ju, F. Xue, J. Bai, J. Jiang, and Y. Xin, J. Alloy. Comp. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166906 (2022).
Q. Yang, J.H. Cheng, H.J. Guan, W. Tan, and Y. Zhang, Mater. Chem. Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126635 (2022).
Q. Portella, M. Chemkhi, and D. Retraint, Mater. Charact. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110463 (2020).
P. Wang, H. Guo, D.F. Wang, H. Duan, and Y. Zhang, Tribol. Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2022.107818 (2022).
F. Ghader, S.K. Hyoung, and T.K. Hessam, Severe Plastic Deformation-Methods, Processing and Properties (Elsevier, Netherlands, 2018), p. 30.
J.H. Li, R.F. Dong, H.C. Kou, J. Fan, B. Zhu, and B. Tang, Mater. Charact. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.109999 (2020).
M. Wen, G. Liu, J. Gu, W. Guan, and J. Lu, Appl. Surf. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.01.048 (2009).
X.S. Luan, W.X. Zhao, Z.Q. Lai, S. Xiao, G. Liang, Y. Chen, S. Zhou, and X. Wang, Surf. Coat. Tech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125745 (2020).
L.X. Yuan, W.K. Yuan, and G.F. Wang, J. Appl. Mech. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4046004 (2020).
H.B. Wang, G.L. Song, and G.Y. Tang, J. alloy Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.067 (2016).
J.H. Moon, S.M. Baek, S.G. Lee, Y. Seong, A. Amanov, S. Lee, and H. Kim, Mater. Res. Lett. https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2018.1560370 (2019).
Y.F. Yu, Y.H. Wei, D.Y. Zheng, X.Y. Shen, Y. Su, Y.Z. Xia, and Y.B. Liu, Tribol. Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2021.107285 (2022).
K.S. Chang, Y.J. Dong, G.M. Zheng, X. Jiang, X. Yang, X. Cheng, H. Liu, and G. Zhao, Ceram. Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.10.105 (2022).
J.Q. Dang, H. Zhang, Q.L. An, G. Lian, Y. Li, H. Wang, and M. Chen, Surf. Coat. Tech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127380 (2021).
S.G. Qu, Z.J. Ren, X.F. Hu, F. Lai, F. Sun, X. Li, and C. Yang, Surf. Coat. Tech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127408 (2021).
Y. Liu, Z.Y. Li, G.H. Li, and L. Tang, J. Mater. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-08084-w (2023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Meng, F. & Zhang, W. Effect of Heating-Assisted Ultrasonic Rolling on Surface Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. JOM 75, 1739–1749 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05776-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-023-05776-9