Abstract
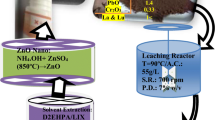
Herein, a novel solvent-assisted approach is being proposed to recover Zn as nano-ZnO.powders from zinc slag oxidation dust (ZSOD). Choline chloride–urea–butyl alcohol deep eutectic solvent (ChCl–urea–BA DES) was used as an efficient solvent for selective leaching of Zn from the ZSOD, coupled with water precipitation and calcination, to produce highly porous nano-ZnO powders. The ChCl–urea–BA DES exhibits a high selectivity for Zn and Pb from ZSOD, achieving extraction efficiencies of 78.2% and 91.6%, respectively, after leaching at 80°C for 36 h under a liquid/solid ratio of 50 mL g−1. Afterward, the dissolved Pb was efficiently removed with a residual concentration of 8.6 mg L−1 by cementation with Zn powders at an optimal Zn/Pb2+ molar ratio of 2:1 at 75°C for 2 h. A mixture of ZnO and Zn4(OH)6(CO3)⋅H2O was obtained by adding deionized water to precipitate the purified leaching solvent. The resulting mixtures were then calcined at high temperature to produce nano-ZnO powders, the purity of which was greater than 99.71 wt%. As a novel synthesis method of high value-added functional materials, the ZnO powders exhibited a flower spherical structure packed with ultrathin mesoporous nanosheets, having a thickness of around 10 nm and pore size of 20–40 nm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Ju, H. Yao, H. Ma, R. Mao, J. Qiu, and C. Chen, Inorg. Chem. Commun. 127, 108496. (2021).
Y.M. Su, W.C. Huang, Y.C. Liu, C.K. Chang, and Y.L. Kuo, Ceram. Int. 43, S694. (2017).
J. Wang, Y. Zhang, K. Cui, T. Fu, J. Gao, S. Hussain, and T.S. AlGarni, J. Cleaner Prod. 298, 126788. (2021).
A. Dutra, P. Paiva, and L. Tavares, Miner. Eng. 19, 478. (2006).
F. Kukurugya, T. Vindt, and T. Havlík, Hydrometallurgy 154, 20. (2015).
Š Langová, J. Riplová, and S. Vallová, Hydrometallurgy 87, 157. (2007).
A.P. Abbott, K.J. Edler, and A.J. Page, J. Chem. Phys. 155, 150401. (2021).
B.B. Hansen, S. Spittle, B. Chen, D. Poe, Y. Zhang, J.M. Klein, A. Horton, L. Adhikari, T. Zelovich, and B.W. Doherty, Chem. Rev. 121, 1232. (2020).
Y. Hou, C. Yao, and W. Wu, Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin. 34, 873. (2018).
A.A. Elgharbawy, M. Hayyan, A. Hayyan, W.J. Basirun, H.M. Salleh, and M.E. Mirghani, Biomass Bioenergy 137, 105550. (2020).
J. Huang, X. Guo, T. Xu, L. Fan, X. Zhou, and S. Wu, J. Chromatogr. A 1598, 1. (2019).
Y. Nahar and S.C. Thickett, Polymers 13, 447. (2021).
H. Qin, X. Hu, J. Wang, H. Cheng, L. Chen, and Z. Qi, Green Energy Environ. 5, 8. (2020).
B. Tang, H. Zhang, and K.H. Row, J. Sep. Sci. 38, 1053. (2015).
D.V. Wagle, H. Zhao, and G.A. Baker, Acc. Chem. Res. 47, 2299. (2014).
A.P. Abbott, G. Capper, D.L. Davies, K.J. McKenzie, and S.U. Obi, J. Chem. Eng. Data 51, 1280. (2006).
A. Bakkar and V. Neubert, J. Alloys Compd. 771, 424. (2019).
S. Wang, C. Xu, Z. Lei, J. Li, J. Lu, Q. Xiang, X. Chen, Y. Hua, and Y. Li, Miner. Eng. 175, 107295. (2022).
H. Gong, J. Hu, J. Wang, C. Ong, and F. Zhu, Sens. Actuators B 115, 247. (2006).
R.V. Kumar, Y. Diamant, and A. Gedanken, Chem. Mater. 12, 2301. (2000).
Z.L. Wang and J. Song, Science 312, 242. (2006).
A.P. Abbott, G. Frisch, J. Hartley, and K.S. Ryder, Green Chem. 13, 471. (2011).
O. Ruiz, C. Clemente, M. Alonso, and F.J. Alguacil, J. Hazard. Mater. 141, 33. (2007).
A.P. Abbott, J. Collins, and I. Dalrymple, Aust. J. Chem. 62, 341. (2009).
R. Hong, T. Pan, J. Qian, and H. Li, Chem. Eng. J. 119, 71. (2006).
M.K. Jha, V. Kumar, and R. Singh, Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 33, 1. (2001).
D. Mondelaers, G. Vanhoyland, H. Van den Rul, J. D’haen, M. Van Bael, J. Mullens, and L. Van Poucke, Mater. Res. Bull. 37, 901. (2002).
A. Moulahi, F. Sediri, and N. Gharbi, Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 667. (2012).
J. Moghaddam, R. Sarraf-Mamoory, M. Abdollahy, and Y. Yamini, Sep. Purif. Technol. 51, 157. (2006).
S. Sharma, G.K. Agarwal, and N.N. Dutta, J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manage. 22, 1509. (2020).
F. Yusubov, Tribol. Ind. 43, 489. (2021).
A. Kalyon, M. Günay, and D. Özyürek, Adv. Manuf. 6, 419. (2018).
L. Qiang, I.S. Pinto, and Z. Youcai, J. Cleaner Prod. 84, 663. (2014).
F. Yu, Y. Wu, J. Ma, and C. Zhang, J. Environ. Sci. 25, 195. (2013).
J. Kasperek, D. Verchere, D. Jacquet, and N. Phillips, Mater. Chem. Phys. 56, 205. (1998).
N.M. Al-Hada, E.B. Saion, A.H. Shaari, M.A. Kamarudin, M.H. Flaifel, S.H. Ahmad, and S.A. Gene, PLoS ONE 9, e103134. (2014).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51764027) and Independent Project of the State Key Laboratory of Complex Nonferrous Metal Resources Cleaning Utilization (CNMRCUKF1901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Xu, C., Wang, S. et al. Preparation of Nano-ZnO Powders from Zinc Slag Oxidation Dust Using a Deep Eutectic Solvent. JOM 74, 4746–4754 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05536-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05536-1