Abstract
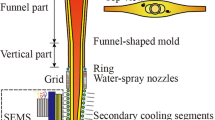
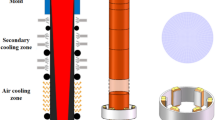
The effect of a helical electromagnetic stirring on the magnetic field, liquid steel flow, and heat transfer in 800-mm-diameter vertical round billets has been studied by numerical simulation, and its effectiveness in improving the internal defects has been verified by industrial experiments. The results show that the electromagnetic force drives the liquid steel to produce tangential rotating flow, which is concentrated in the liquid core. The X-velocity value increases first and then decreases at frequencies in the range 1–9 Hz, reaching its maximum value when f = 7 Hz. The higher the current intensity, the stronger the liquid steel flow. The flow range increases and the gradient of X-velocity decreases with the increase of current intensity. The heat transfer of the liquid core interacts with the flow of liquid steel and the effect is limited by the helical F-EMS current parameters. When F-EMS is not applied, the central porosity is porphyritic and dense, gradually dispersing outwards. After applying the helical F-EMS (I = 600 A, f = 7 Hz), the center porosity is dispersed into small pieces and the stirring traces appear in the mushy zone. The center porosity level was significantly reduced, and the center crack range was decreased on average by 26 mm.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.P. Cherukuri and R.E. Johnson, Int. J. Mech. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7403(00)00059-X (2001).
L.W. Zhang, Z.L. Wang, C.J. Xu, S.L. Li, X.G. Ai and J. Li, Ironmak. Steelmak. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2017.1408244 (2019).
P. Pennerstorfe, H. Thöne and F. Wimmer, Chernye Metally 11, 60. ((in Russian)) (2014).
H.P. Liu, Z.Y. Wang and H. Qiu, ISIJ Int. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2019-738 (2020).
K.J. Brimacombe and K. Sorimachi, Metall. Trans. B. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02696937 (1977).
N. Zong, H. Zhang, Y. Liu and Lu. Zhifang, Ironmak. Steelmak. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02696937 (2019).
Y. Kong, D. Chen, Q. Liu and M. Long, Metals. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9050587 (2019).
C.H.O. Seong-Mook and G. Brian Thomas, JOM. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04329-8 (2020).
H. Ma, J. Zhang, R. Cheng and S. Wang, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1538-y (2019).
Y. Zheng, M. Wu, A. Kharicha and A. Ludwig, Comp. Mater. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2016.07.017 (2016).
Q.-P. Dong, J.-M. Zhang and X.-K. Zhao, Metall. Res. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1051/metal/2017004 (2017).
B. Rogberg and E.K. Lina, ISIJ Int. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2017-534 (2018).
B. Willers, M. Barna, J. Reiter and S. Eckert, ISIJ Int. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2016-495 (2017).
R. Pardeshi, A.K. Singh and P. Dutta, Numer. Heat Trans. A-Appl. https://doi.org/10.1080/10407780802553961 (2009).
T.T. Natarajan and N. El-Kaddah, Appl. Math. Model. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0307-904X(03)00114-8 (2004).
J.T. Huang, E.G. Wang and J.C. He, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-003-0111-1 (2003).
M. Barna, Magnetohydrodynamics 53, 571. (2017).
Q. Zhao, X.G. Zhang, C.F. Fang, N. Zhang, Y.B. Han, J.S. Guo and X.G. Hou, Adv. Mater. Res. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.482-484.1447 (2012).
B.Z. Ren, D.F. Chen, W.T. Xia, H.D. Wang and Z.W. Han, Metals. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110903 (2018).
Q.T. Guo, T.M. Wang, J.X. Jia, X.F. Wan, D. Cao and G. Zhao, Int. J. Cast Metal Res. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743133612Y.0000000031 (2013).
G. Qing-Tao, L. Xiang-Wei, J. Ji-Xiang, H. Yu-Ping and Z. Huan, Research of helical magnetic field stirring in bloom continuous casting. Paper presented at the 6th International Steelmaking Technology Conference, Beijing, 12–14 May 2015
H.J. Wu, C.J. Xu, H.Y. Jin, Y.L. Gao, X.B. Zhang and Y.K. Jin, Appl. Phys. A-Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05257-x (2022).
D.B. Jiang and M.Y. Zhu, Steel Res. Int. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201400281 (2015).
W.I. Middleton and E.W. Davis, J. Am. Inst. Elec. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/JoAIEE.1921.6594011 (2013).
T.T. Natarajan and N. El-Kaddah, ISIJ Int. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.38.680 (2007).
S.X. Li, P. Lan, H.Y. Tang, Z.P. Tie and J.Q. Zhang, Steel Res. Int. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201800071 (2018).
M. Reza, M. Aboutalebi, R. Hasan and I.L. Guthrie, Metall Mater. Trans. B. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02651719 (1995).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 51504130) and Henan Province Key S&T Special Projects (151100212700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Xu, C., Lei, C. et al. Numerical Simulation and Industrial Experiment of the Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Large Vertical Round Billets with Helical Final Electromagnetic Stirring. JOM 75, 1439–1449 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05511-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05511-w