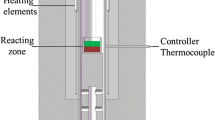
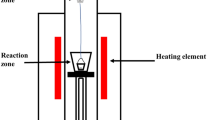
Abstract
A bath smelting furnace is a clean technology replacing sinter machines to simultaneously produce lead-rich slag and lead metal. Lead-rich slag can be used as a feedstock for blast furnaces or smelting reduction furnaces to produce lead metal. Understanding the reduction mechanism of lead-rich slag by carbon provides useful information for the complete reduction of the lead oxide. Kinetic studies on the reduction of lead-rich slags with CaO/SiO2 ratios of 0.38, 0.56, and 0.80 were carried out in the temperature range 1073–1473 K. The volume of the product gas was measured continuously to represent the extent of lead-rich slag reduction. It was found that the reduction was initially chemically controlled and then diffusion controlled. At the chemically-controlled stage, the activation energy of the reduction was higher at lower CaO/SiO2 ratios. An increase of the CaO/SiO2 ratio from 0.38 to 0.56 can decrease the activation energy from 273 kJ/mol to 95 kJ/mol. At the diffusion-controlled stage, the activation energy was determined to be 392 kJ/mol, 294 kJ/mol, and 280 kJ/mol for the slags with CaO/SiO2 ratios of 0.38, 0.56, and 0.80, respectively. Formation of liquid plays an important role in the reduction of the lead-rich slag. The reduction mechanism has been analyzed by experimental results and thermodynamic calculations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.Y. Chen, A.J. Li, and D.E. Finlow, J. Power Sources 191(1), 22–27. (2009).
X. Zhu, L. Li, X. Sun, D. Yang, L. Gao, J. Liu, and J. Yang, Hydrometallurgy 117, 24–31. (2012).
U.S. Geological Survey. “Mineral commodity summaries 2021” (U.S. Geological Survey, 2021) https://doi.org/10.3133/mcs2021
L. Chen, T. Yang, S. Bin, W. Liu, D. Zhang, W. Bin, and Li. Zhang, JOM 66, 1664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1057-1 (2014).
W. Gao, C. Wang, F. Yin, Y. Chen, and W. Yang, AMR 581, 904. (2012).
W. Wu, P. Xin, and J. Wang, The latest development of oxygen bottom blowing lead smelting technology, in PbZn 2020: 9th International Symposium on Lead and Zinc Processing. (Springer, Cham, 2020), pp. 327–336.
W. Li, J. Zhan, Y. Fan, C. Wei, C. Zhang, and J.-Y. Hwang, JOM 69, 784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-2236-z (2017).
L. Chen, Z. Hao, T. Yang, W. Liu, D. Zhang, Li. Zhang, S. Bin, and W. Bin, JOM 67, 1123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1375-y (2015).
K. Upadhya, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 17, 271. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02655074 (1986).
N.N. Kinaev, E. Jak, and P.C. Hayes, Scand. J. Metall 34, 150. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0692.2005.00733.x (2005).
B. Zhao, B. Errington, E. Jak, and P. Hayes, Can. Metall. Quart 49, 241. https://doi.org/10.1179/cmq.2010.49.3.241 (2010).
X. Hou, K.C. Chou, and B. Zhao, J. Min. Metall., Sect. B: Metall. 49(2), 201–206. (2013).
J. Liao, and B. Zhao, Calphad 74, 102282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.calphad.2021.102282 (2021).
C. Feng, M. Chu, J. Tang, Y. Tang, and Z. Liu, Steel. Res. Int 87, 1274. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201500355 (2016).
C.W. Bale, E. Bélisle, P. Chartrand, S.A. Decterov, G. Eriksson, A.E. Gheribi, K. Hack, I.-H. Jung, Y.-B. Kang, J. Melançon, A.D. Pelton, S. Petersen, C. Robelin, J. Sangster, P. Spencer, and M.-A. Van Ende, Calphad 54, 35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.calphad.2016.05.002 (2016).
C.F. Dickinson, and G.R. Heal, Thermochim. Acta 340, 89. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(99)00256-7 (1999).
E. Bidari, and V. Aghazadeh, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46(5), 2305–2314. (2015).
F. Vegliò, M. Trifoni, F. Pagnanelli, and L. Toro, Hydrometallurgy 60, 167. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(00)00197-3 (2001).
Mark Pritzker, Chem. Eng. Sci 58, 473. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(02)00554-7 (2003).
S. He, J. Wang, X. Zhang, and Y. Li, Nonferrous Metals. 3, 13–16. (2010).
L. Yanting, Y. Tianzu, and L. Mingzhou, Chinese J. Nonferrous Metals 30(5), 1110–1118. (2020).
G. Pi, and Z. Jia, Nonferrous Metals. 6, 17–19. (2009).
J. Wang, Y. Dong, and G. Feng, Eng. Sci. 7, 256–259. (2005).
H. Kim, H. Matsuura, F. Tsukihashi, W. Wang, D.J. Min, and I. Sohn, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 44(1), 5–12. (2013).
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, S., Liao, C. & Zhao, B. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies on Lead-Rich Slag Reduction at Various CaO/SiO2 Ratios. JOM 74, 3625–3633 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05413-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05413-x