Abstract
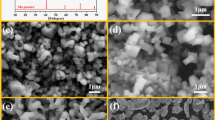
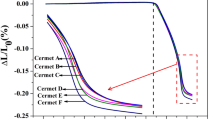
TiCN-Ni based cermets were prepared by pre-solid solubilizing Ti in Ni to adjust the composition of the binder in advance. The composition, morphology, microstructure and effects on TiCN cermets of Ni-Ti powder were tested and analyzed by XRD, SEM, EDS and TEM. The mechanical properties such as transverse rupture strength, fracture toughness and hardness were tested. The results showed that the wettability of Ni to ceramic particles can be improved, and the particles could be refined by pre-solution treatment. The reasons for the improvement of wettability were as follows: the content of alloy elements in the binder phase during sintering was adjusted, the complete and uniform rim-shaped phase was formed, and a nanometer thickness transition zone was formed between the metal binder phase and the rim-shaped phase. In addition, a high density of dislocation in the transition zone could inhibit grain growth. The fracture mode of cermets was mixed fracture mode composed of intergranular fracture and transgranular fracture. When 3 wt.% Ti was fore-solid solubilized in Ni, the performance of the cermets was the best. The transverse rupture strength, fracture toughness and the hardness of the cermets reached 2356.8 Mpa, 14.33 MPa·m1/2 and 88.9 HRA, respectively.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Peng, H. Miao, and Z. Peng, Int. J. Refract. Metal. Hard Mater. 39, 78 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2012.07.001 (2013).
H. Xiong, Y. Wu, Z. Li, X. Gan, K. Zhou, and L. Chai, Ceram. Int. 44, 805 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.003 (2018).
W. Lengauer and F. Scagnetto, Solid State Phenom. 274, 53 https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.274.53 (2018).
S. Xiao and S. Wu, Key Eng. Mater. 633, 82 https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.633.82 (2015).
M. Chen, X. Xiao, X. Zhang, and C. Zhao, JOM J. Miner. Metal. Mater. Soc. 72, 385 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03850-9 (2019).
N. Wu, F. Xue, H. Yang, H. Zhou, and F. Luo, Mater. Today Comm. 25, 101311 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101311 (2020).
H. Yu, L. Ying, Y. Jin, and J. Ye, Int. J. Refract. Metal. Hard Mater. 29, 586 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2011.03.013 (2011).
M. Chen, X. Xiao, X. Zhang, and C. Zhao, Mater. Res. Express https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aafbd5 (2019).
G. Zhang, Y. Zheng, J. Zhang, K. Zheng, X. Xu, H. Wu, and X. Lu, Ceram. Int. 46, 9698 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.237 (2020).
Q. Wang, W. Wang, H. Zhang, and G. Li, J. Northeastern Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 17(5), 490. (1996).
Q. Li, N. Liu, A. Liu, and H. Zhang, Int. J. Refract. Metal. Hard Mater. 40, 43 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2013.04.003 (2013).
B. Li, Y. Jing, B. Huang, and W. Xiong, Cemented Carbide 33(03), 147–153. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-7292.2016.03.001 (2016).
M. Zhang, N. Lin, Y. He, and X. Kang, J. Alloys Compd. 799, 462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.159 (2019).
Z. Li, X. Liu, K. Guo, H. Wang, B. Cai, F. Chang, C. Hong, and P. Dai, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 767, 138427 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138427 (2019).
X. Chen, Y. Zhou, J. Tao, and X. Sun, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32(2), 177–181 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2015.11.007 (2016).
C. Shuai, C. He, S. Peng, F. Qi, G. Wang, A. Min, W. Yang, and W. Wang, Adv. Eng. Mater. 23, 2001098 https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.202001098 (2021).
H. Chikwanda, and L. Mahlatji, Key Eng. Mater. 770, 95 https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.770.95 (2018).
A. Rostami, G.A. Bagheri, and S.K. Sadrnezhaad, Physica B 552, 214 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.10.015 (2018).
C. Suryanarayana, Prog. Mater. Sci. 46, 1–184 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6425(99)00010-9 (2002).
X. Xu, Y. Zheng, J. Zhang, Z. Ke, and C. Xue, Ceram. Int. 47(10), 14482 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.027 (2021).
G. Zhang, Y. Zheng, Z. Ke, J. Zhang, Y. Zhao, and X. Lu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 761, 138024 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138024 (2019).
K.W. Chae, D.I. Chun, D.Y. Kim, Y.J. Baik, and K.Y. Eun, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 1979 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1990.tb05255.x (2010).
H. Xiong, Y. Wu, X. Gan, Z. Li, and K. Zhou, Ceram. Int. 44(16), 19113 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.06.080 (2018).
W. Zhou, Y. Zheng, Y. Zhao, G. Zhang, and J. Zhang, Int. J. Refract. Metal. Hard Mater. 74, 70–77 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.03.004 (2018).
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out with financial support from Natural Science Foundation of China (51801140). This work was also supported by the Analytical and Testing Center in Wuhan University of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Xu, G., Yao, Z. et al. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TiCN-Ni Based Cermets Strengthened by Fore-Solid Solubilizing Ti in Ni. JOM 74, 4317–4325 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05343-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05343-8