Abstract
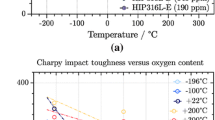
Oxide inclusions introduced by oxygen on the raw powder surface play an important role in the material performance of powder metallurgy products. In this study, we report the effect of oxygen content in the powder on the microstructure and mechanical properties of hot isostatically pressed (HIPed) 30CrMnSiNi2A ultra-high strength steel (UHSS). The results indicate that, when there is more oxygen in—powder, the size of the oxide inclusions increases, and the prior particle boundaries (PPBs) become clearly visible. In addition, the main constituents of—inclusions in—PPBs changes from Al-rich oxide to Si-rich oxide. When the oxygen content increases from 200 ppm to 650 ppm, the tensile strength maintains a value about 1300 MPa, while with further increases in the oxygen content to 1700 ppm, it decreases to 1200 MPa. The impact toughness of steel is sensitive to the oxygen content in the powder, and it deteriorates as the oxygen content goes above 365 ppm. Our findings not only clarify the influence of the oxygen content in raw powders on the mechanical properties of HIPed UHSS but also shed light on the formation mechanism of PPBs and their evolution, such as oxide size, morphology, species, etc., during sintering.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Wang, D. Wen, J. Li, Z. Zheng, and Y. Xiong, Mater. Today. Commun. 26, 102009 (2021).
Y. Duan, W. Liu, Y. Ma, Q. Cai, W. Zhu, and J. Li, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 15192 (2020).
H.V. Atkinson and S. Davies, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 31, 2981 (2000).
W.X. Yuan, J. Mei, V. Samarov, D. Seliverstov, and X. Wu, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 182, 39 (2007).
K. Kallip, N.K. Babu, K.A. AlOgab, L. Kollo, X. Maeder, Y. Arroyo, and M. Leparoux, J. Alloys Compd. 714, 133 (2017).
S. Irukuvarghula, H. Hassanin, C. Cayron, M.M. Attallah, D. Stewart, and M. Preuss, Acta Mater. 133, 269 (2017).
C.L. Qiu, M.M. Attallah, X.H. Wu, and P. Andrews, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 564, 176 (2013).
J.E. MacDonald, R.H.U. Khan, M. Aristizabal, K.E.A. Essa, M.J. Lunt, and M.M. Attallah, Mater. Design 174, 107796 (2019).
Q. Teng, Q. Wei, P. Xue, C. Cai, H. Chen, H. Chen, and Y. Shi, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 739, 118 (2019).
M. Higashi and N. Kanno, Mater. Design 194, 108926 (2020).
G.A. Rao, M. Srinivas, and D.S. Sarma, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 435, 84 (2006).
A. Sergi, R.H.U. Khan, and M.M. Attallah, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 808, 140950 (2021).
S. Irukuvarghula, H. Hassanin, C. Cayron, M. Aristizabal, M.M. Attallah, and M. Preuss, Acta Mater. 172, 6 (2019).
W. Ding, Z. Wang, G. Chen, W. Cai, C. Zhang, Q. Tao, X. Qu, and M. Qin, Corros. Sci. 178, 109080 (2021).
K. Zumsande, A. Weddeling, E. Hryha, S. Huth, L. Nyborg, S. Weber, N. Krasokha, and W. Theisen, Mater. Charact. 71, 66 (2012).
T. Yamashita and P. Hayes, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 2441 (2008).
I. Olefjord and L. Nyborg, Powder Metall. 28, 237 (1985).
G. Hultquist and C. Leygraf, Corros. Sci. 22, 331 (1982).
E. Gil, J. Cortés, I. Iturriza, and N. Ordás, Appl. Surf. Sci. 427, 182 (2018).
D.H. Shim, T. Lee, J. Lee, H.J. Lee, J.Y. Yoo, and C.S. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 700, 473 (2017).
Z.X. Qiao, Y.C. Liu, L.M. Yu, and Z.M. Gao, J. Alloys Compd. 475, 560 (2009).
Y. Zhou, T. Jia, X. Zhang, Z. Liu, and R.D.K. Misra, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 626, 352 (2015).
D. Chasoglou, E. Hryha, and L. Nyborg, Mater. Chem. Phys. 138, 405 (2013).
A. Pineau, A.A. Benzerga, and T. Pardoen, Acta Mater. 107, 424 (2016).
X. He, M. Wang, C. Hu, and L. Xu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 827, 141999 (2021).
D.R. Eo, S.H. Park, and J.W. Cho, Addit. Manuf. 33, 101119 (2020).
A.J. Cooper, W.J. Brayshaw, and A.H. Sherry, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 49, 1579 (2018).
A.J. Cooper, N.I. Cooper, J. Dhers, and A.H. Sherry, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47, 4467 (2016).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51701242, 51931012), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (Grant No. 2018JJ3648).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Ma, Y., Cai, Q. et al. Influence of Oxygen Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hot Isostatically Pressed 30CrMnSiNi2A Ultra-High Strength Steel. JOM 74, 3595–3606 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05336-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05336-7