Abstract
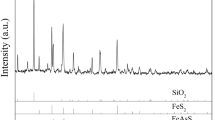
The process optimization and mechanism of microwave pyrolysis in a nitrogen atmosphere were studied to improve the gold leaching rate for high-arsenic-refractory gold sulfide resources, mainly containing minerals of elemental sulfur, dense pyrite, and arsenopyrite. The decomposability was evaluated using thermodynamic and thermogravimetric analyses. Faster microwave heating characteristics were confirmed under a nitrogen atmosphere. The main factors affecting microwave pyrolysis were pyrolysis temperature, time, and protective nitrogen temperature. The optimum conditions for the four variables were determined to remove 97.96% of As and 50.43% of S. The arsenopyrite first formed pyrite through a shrinking nuclear process in the presence of sulfur. The decomposition of pyrite and pyrrhotite is random. Many pores and cracks are formed to expose the locked gold for leaching. The gold leaching rate reached 95.36% with sodium cyanide and a small amount of lead nitrate; this rate was much higher than that observed before pretreatment (38.65%).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.T. Konadu, R.J. Huddy, S. Harrison, K. Osseo-Asare, and K. Sasaki, Miner. Eng. 138, 86. (2019).
X. Guo, Y. Xin, H. Wang, and Q. Tian, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27, 1888. (2017).
T. Chen, L.J. Cabri, and J.E. Dutrizac, JOM 54, 20. (2002).
J.P. Vaughan, JOM 56, 46. (2004).
J. Jin, Y. Han, H. Li, Y. Huai, Y. Peng, X. Gu, and W. Yang, Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 27, 1184. (2019).
K.A. Richmond, S. William, and A.M. Jonas, Hydrometallurgy 179, 79. (2018).
H. Abdollahi, P. Karimi, A. Amini, and A. Akcil, Miner. Metall. Proc. 32, 161. (2015).
I.J. Corrans, and J.E. Angove, Miner. Eng. 4, 763. (1991).
S. Ruan, C. Wang, X. Jie, F. Yin, Y. Zhang, Z. Yao, and Y. Chen, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2021).
M.N. Lehmann, S.O. Leary, and J.G. Dunn, Miner. Eng. 13, 1. (2000).
K.S. Pak, T. Zhang, C.S. Kim, and G.H. Kim, Hydrometallurgy 194,105325 (2020).
N. Marchevsky, M.M.B. Quitoga, A. Giaveno, and E. Donati, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27, 1143. (2017).
N.V. Fomchenko, M.I. Muravyov, and T.F. Kondrat’eva, Hydrometallurgy 101, 28. (2010).
E. Jorjani, and A. Ghahreman, Hydrometallurgy 171, 333. (2017).
A.D. Bas, E. Ghali, and Y. Choi, Hydrometallurgy 172, 30. (2017).
Q. Wang, X. Hu, F. Zi, X. Qin, Y. Nie, and Y. Zhang, Miner Eng. 136, 89. (2019).
S.L.M. Espitia, and G.T. Lapidus, Hydrometallurgy 153, 106. (2015).
H. Qin, X. Guo, Q. Tian, D. Yu,and L. Zhang, Miner. Eng. 164,106822 (2021).
X. Liu, Q. Li, Y. Zhang, T. Jiang, Y. Yang, B. Xu, and Y. He, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 50, 1588. (2019).
R.K. Amankwah, and C.A. Pickles, Miner. Eng. 22, 1095. (2009).
H. Zhang, Safety Technology Complete Book of Hazardous Chemicals, 2nd ed. ((Beijing, NY: Chemical Industry Press, 2008), pp. 450.
J.G. Dunn, A.S. Ibrado, and J. Graham, Miner. Eng. 8, 459. (1995).
W. Xu, P. Jin, S. Xu, S. Zhang, and X. Wu, Central South Pharmacy 17, 899. (2019).
G. Zhou, Q. Huang, B. Yu, H. Tong, Y. Chi, and J. Yan, Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 26, 1171. (2018).
S.S. Rath, N. Dhawan, D.S. Rao, B. Das, and B.K. Mishra, Powder Technol. 301, 1016. (2016).
K.E. Haque, Int. J. Miner. Proc. 57, 1. (1999).
Z. Xu, H. Shao, Q. Zhao, and Z. Liang, JOM 73, 2104. (2021).
P. Zhao, C. Liu, C. Srinivasakannan, L. Zhang, F. Wang, and J. Gao, Powder Technol. 379, 630. (2021).
Y. Liu, W. Yao, C. Lei, Q. Zhang, S. Zhong, and Z. Yan, J. Electrochem. Soc. 166, A1300. (2019).
Y. Liu, J. Zhang, X. Yang, W. Yang, Y. Chen, and C. Wang, Chinese. J. Chem. Eng. (2020).
C.A. Pickles, Miner. Eng. 22, 1112. (2009).
R.K. Amankwah, and G. O. Sarpong, Miner. Eng. 151, 106312, (2020).
R.K. Amankwah, and G.O. Sarpong, Miner. Eng. 24, 541. (2011).
X. Zhang, C. Sun, Y. Xing, J. Kou, and M. Su, Hydrometallurgy 180, 210. (2018).
X. Zhang, J. Kou, and C. Sun, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 138, 41. (2019).
R. K. Amankwah, and G. Ofori-Sarpong, Miner. Eng. 151,106312 (2020).
S. Ma, W. Luo, W. Mo, X. Su, P. Liu, and J. Yang, Miner. Eng. 23, 61. (2010).
X. Zhang, J. Kou, and C. Sun, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 138, 41. (2019).
S. Zhang, Y. Li, R. Wang, Z. Xu, B. Wang, S. Chen, and M. Chen, J. Clean. Prod. 152, 1. (2017).
Y. Zhang, C. Wang, B. Ma, X. Jie, and P. Xing, Hydrometallurgy 186, 284. (2019).
F. Soltani, M. Marzban, H. Darabi, M. Aazami, and M.H. Chegeni, JOM 72, 774. (2020).
S. Ruan, P. Xing, C. Wang, Y. Chen, F. Yin, X. Jie, B. Ma, and Y. Zhang, Thermochim. Acta 690, 178666 (2020).
G. Hu, K.D. Johansen, S. Wedel, and J.P. Hansen, Prog. Energy. Combust. Sci. 32, 295. (2006).
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51604030), National Key R&D Program of China (Nos. 2019YFC1908301, 2018YFC1900303, and 2019YFC1908305), and the Research Fund of the BGRIMM Group (No. 02-1915).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruan, S., Qiu, D., Wang, C. et al. Microwave Pyrolysis Pretreatment of High Arsenic Refractory Gold Sulfide Concentrates in Nitrogen Atmosphere: Process Optimization and Mechanism Study. JOM 74, 167–177 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-05000-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-05000-6