Abstract
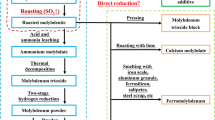
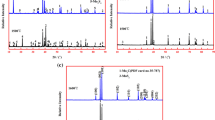
Molybdenite (MoS2) is the most commonly used mineral for molybdenum extraction. In this work, molybdenum (Mo) powder was directly synthesized via CaO-assisted carbothermic reduction of MoS2. The experimental results showed that MoS2 first reacted with CaO to form CaMoO4, Mo and CaS, and then carbon black reduced the CaMoO4 to yield Mo. Almost all the sulfur as MoS2 was fixed in CaS, and the main gaseous product was CO. In addition, it was observed that MoS2 can be almost fully converted to Mo at a MoS2:CaO:C molar ratio of 1:4:1.7 after reacting at 1200°C for 60 min. After removing by-product CaS, the prepared Mo powder has a carbon content of 0.18% and a sulfur content of 0.46%.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.A. Lasheen, M.E. El-Ahmady, H.B. Hassib, and A.S. Helal, Min. Proc. Ext. Met. Rev. 36, 145. (2015).
L. Wang, G.H. Zhang, J. Dang, and K.C. Chou, Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 25, 4167. (2015).
D.H. Wang, G.D. Sun, and G.H. Zhang, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 75, 70. (2018).
A.G. Kholmogorov, O.N. Kononova, G.L. Pashkov, S.V. Kachin, O.N. Panchenko, and O.P. Kalyakina, Euro. J. Miner. Environ. Proc. 2, 82. (2002).
E. Blanco, H.Y. Sohn, G. Han, and K.Y. Hakobyan, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 38, 689. (2007).
Q.S. Zhou, W.T. Yun, J.T. Xi, X.B. Li, T.G. Qi, G.H. Liu, and Z.H. Peng, Trans. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 27, 1618. (2017).
P.V. Aleksandrov, A.S. Medvedev, M.F. Milovanov, V.A. Imideev, S.A. Kotova, and D.O. Moskovskikh, Int. J. Miner. Process. 161, 13. (2017).
Z.F. Cao, H. Zhong, Z.H. Qiu, G.Y. Liu, and W.X. Zhang, Hydrometallurgy 99, 2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2009.05.001 (2009).
L. Wang, P. Guo, J. Pang, L. Luo, and P. Zhao, Vacuum 116, 77. (2015).
G.H. Zhang, H.Q. Chang, L. Wang, and K.C. Chou, Int. J. Min. Metal. Mater. 25, 405. (2018).
L. Wang, P.M. Guo, P. Zhao, L.B. Kong, and Z.L. Tian, Vacuum 152, 330. (2018).
M. Kumar, T.R. Mankhand, D.S.R. Murthy, R. Mukhpadhyay, and P.M. Prasad, Hydrometallurgy 86, 56. (2007).
F. Habashi, and R. Dugdale, Metall. Trans. 4, 1865. (1973).
P.M. Prasad, T.R. Mankhand, and P. Suryaprakash Rao, Miner. Eng. 6, 857. (1993).
M.M. Afsahi, M. Sohrabi, R.V. Kumar, and H.A. Ebrahim, Thermochim. Acta 473, 61. (2008).
M.M. Afsahi, R.V. Kumar, M. Sohrabi, and Y.J. Park, Chem. Eng. Process 75, 1. (2014).
T.R. Mankhand, and P.M. Prasad, Metall. Trans. B 13, 275. (1982).
P.S. Rao, and P.M. Prasad, Mater. Trans. JIM 34, 1229. (1993).
P.M. Prasad, T.R. Mankhand, P.S.P. Rao, S.N. Singh, and A.J.K. Prasad, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 33, 345. (2002).
R. Padilla, M.C. Ruiz, and H.Y. Sohn, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 28, 265. (1997).
P.K. Tripathy, and R.H. Rakhasia, Min. Proc. Ext. Metall. Rev. 115, 8. (2006).
S. Ghasemi, M.H. Abbasi, A. Saidi, J.Y. Kim, and J.S. Lee, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 50(23), 13340. (2011).
S.G. Najafabadi, M.H. Abbasi, and A. Saidi, Thermochim. Acta 503, 46. (2010).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy, University of Science and Technology Beijing, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, HQ., Zhang, GH. & Chou, KC. CaO-Assisted Carbothermal Reduction of MoS2 to Synthesize Molybdenum Powder. JOM 73, 2540–2548 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04719-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04719-6