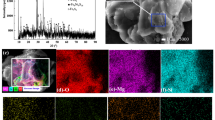
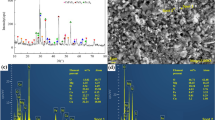
Abstract
We investigated the effects of ilmenite roasting temperature on the efficiency of iron oxide removal from the obtained residue by selective chlorination. Roasting-induced phase transformations were analyzed by x-ray diffraction measurements, and the phase composition of roasted residue was shown to be determined by process conditions. The highest iron oxide removal efficiency was observed for non-roasted samples, which was ascribed to the fact that roasted samples contained hematite (Fe2O3), whereas non-roasted ones contained wustite (FeO). The kinetics of selective chlorination was fitted by two models, and the obtained results indicated that the rate-controlling step corresponded to diffusion through the TiO2 layer between the interface and ilmenite core.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.M. Lakshmanan, H.E. Hoelscher and B. Chennakesvan, Chem. Eng. Sci. 20, 1107. (1965).
A.S. Athavale and V.A. Altekar, Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 10, 523. (1971).
J.S.J. Van Deventer, Thermochim. Acta 124, 205. (1988).
J. Kim, M.S. Lee and E.J. Jung, Mater. Chem. Phys. 241, 122433. (2020).
L. Zhou and H.Y. Sohn, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 35, 954. (1996).
H.Y. Sohn and L. Zhou, Chem. Eng. J. 72, 37. (1999).
G.G. Fouga, D.M. Pasquevich and A.E. Bohe, Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. C 116, 230. (2007).
J. Kang and T.H. Okabe, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 44, 516. (2013).
J. Kang and T.H. Okabe, Mater. Trans. 55, 591. (2014).
J. Kang and T.H. Okabe, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45, 1260. (2014).
J. Kang and T.H. Okabe, Int. J. Miner. Process. 149, 111. (2016).
A.W. Schlechten, V.D. Benedetto, K.B. Higble, L.K. Hudson, C.A. Klatt, C.L. Lo, D.F. Othmer, F.A. Peters, M.E. Wadsworth and S.T. Weng, Processes for rutile substitutes, 81–87, NMAB-293, Washington DC, USA.
J.H. Chen, Beneficiation of titaniferous ores, US Patent 3,825,419.
A.W. Schlechten, V.D. Benedetto, K.B. Higble, L.K. Hudson, C.A. Klatt, C.L. Lo, D.F. Othmer, F.A. Peters, M.E. Wadsworth and S.T. Weng, Processes for rutile substitutes, pp. 130–132, NMAB-293, Washington DC, USA.
W. Hoecker, Process for the production of synthetic rutile, US Patent 5,601,630.
R.G. Auger and E.F. Restelli Jr. Process for producing a synthetic rutile from ilmenite, US Patent 4,097,574.
H.N. Sinha, Murso process for producing rutile substitute (Plenum Press, New York - London, Titanium Science and Technology, 1973), pp 233–244
A.W. Schlechten, V.D. Benedetto, K.B. Higble, L.K. Hudson, C.A. Klatt, C.L. Lo, D.F. Othmer, F.A. Peters, M.E. Wadsworth and S.T. Weng, Processes for rutile substitutes, pp. 145–149, NMAB-293, Washington DC, USA.
S.K. Gupta, V. Rajakumar and P. Grieveson, Metall. Trans. B 22, 711. (1991).
V. Tathavadkar, C. Kari, S.M. Rao, Proceed. Int. Seminar Mineral Processing Tech., Chennai, India, 553 (2006).
G. Zhang and O. Ostrovski, Int. J. Miner. Process. 64, 201. (2002).
D.B. Rao and M. Rigaud, Oxid. Met. 9, 99. (1975).
P.L. Vijay, R. Venugopalan and D. Sathiyamoorthy, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 27, 731. (1996).
H.Y. Lin, Y.W. Chen and C. Li, Thermochim. Acta 400, 61. (2003).
R.J. Fruehan, Metall. Trans. B 8, 279. (1977).
W.K. Jozwiak, E. Kaczmarek, T.P. Maniecki, W. Ignaczak and W. Maniukiewicz, Appl. Catal. A:General 326, 17. (2007).
Y.K. Rao, Metall. Trans. 2, 1439. (1971).
C.E. Seaton, J.S. Foster and J. Velasco, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 23, 497. (1983).
P.C. Hayes and P. Grieveson, Metall. Trans. B 12, 579. (1981).
J. Yu, Y. Han, Y. Li, P. Gao and W. Li,Minerals 7, 209. (2017).
N.V. Manukyan and V.H. Martirosyan, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 142, 145. (2003).
I. Bertoti, I.S. Pap, T. Szekely and I.Z. Babievskaya,J. Therm. Anal. 32, 281. (1987).
A. Fuwa, E. Kimura and S. Fukushima, Metall. Trans. B 9, 643. (1978).
K.I. Rhee and H.Y. Sohn, Metall. Trans. B 21, 341. (1990).
O. Levenspiel, Chemical Reaction Engineering, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1972)
D.M. Pasquevich, J.P. Gaviria, M. Esquivel and A.E. Bohe, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 37, 589. (2006).
A.M. Ramadan, M. Farghaly, W.M. Fathy and M.M. Ahmed, IRJET 3, 46. (2016).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Technology Innovation Program (10052751) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Lee, Y.R. & Jung, E.J. A Study on the Roasting Process for Efficient Selective Chlorination of Ilmenite Ores. JOM 73, 1495–1502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04620-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04620-2