Abstract
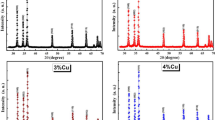
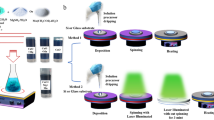
In this study, CuO, ZnO, and (1 − x)ZnO − xCuO (CZO) powders were synthesized through the aqueous solution method. Sintering (separate) and direct synthesis were conducted at 500°C and 700°C, respectively, to produce CuO, ZnO, and CZO powders in different proportions. Various proportions of (1 − x)ZnO−xCuO (x = 0.33, 0.5, 0.67) powders were analyzed and compared under various temperature and process conditions. The morphology, phase structure, and photoelectromagnetic properties of CZO were analyzed to determine the influence of ZnO, CuO, and their mutual doping on the photoelectromagnetic properties. The results revealed that direct synthesis was the most effective process and that CZO powder exhibited the best electromagnetic properties when the Cu doping ratio was high—when Cu:Zn was close to 1:1. When Cu was doped excessively (x = 0.67), it resulted in the formation of the cuprous oxide phase, which is detrimental to the electrical and magnetic properties of CZO powder.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Cai, A. Shui, X. Wang, C. He, J. Qian and B. Du, J. Alloys Compd., vol. 842, Article ID 155638 (2020).
H. Qin, Z. Zhang, X. Liu, Y. Zhang, and J. Hu, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 1994–1998 (2010).
Y. Keriti, R. Brahimi, Y. Gabes, S. Kaci, and M. Trari, Sol. Energy 206, 787–792 (2020).
J. Wang, N. Du, H. Zhang, J. Yu, and D. Yang, J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 11302–11305 (2011).
H.G. Na, D.S. Kwak, and H.W. Kim, Cryst. Res. Technol. 47, 79–86 (2012).
L.C. Chen, C.M. Huang, C.S. Gao, G.W. Wang, and M.C. Hsiao, Chem. Eng. J. 175, 49–55 (2011).
J.P. Li, F.Q. Sun, K.Y. Gu, T.X. Wu, W. Zhai, W.S. Li, and S.F. Huang, Appl. Catal. A 406, 51–58 (2011).
S. Yun, T. Guo, Y. Li, X. Gao, A. Huang and L. Kang, Mater. Res. Bull., vol. 130, Article ID 110935 (2020).
H.T. Hsueh, S.J. Chang, W.Y. Weng, C.L. Hsu, T.J. Hsueh, F.Y. Hung, S.L. Wu, and B.T. Dai, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 11, 127–133 (2012).
T.H. Liu, F.Y. Hung, T. Chien, and K.J. Chen, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 144–153 (2020).
S. Sivasakthi and K. Gurunathan, Renew. Energy 159, 786–800 (2020).
C.S. Dandeneau, Y.H. Jeon, C.T. Shelton, T.K. Plant, D.P. Cann, and B.J. Gibbons, Thin Solid Films 517, 4448–4454 (2009).
T. Ghosh, M. Dutta, S. Mridha, and D. Basak, J. Electrochem. Soc. 156, 285–289 (2009).
H. Liu, J. Yang, Z. Hua, Y. Zhang, L. Yang, L. Xiao, and Z. Xie, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 4162–4165 (2010).
S.Y. Zhuo, X.C. Liu, Z. Xiong, J.H. Yang, and E.W. Shi, Solid State Commun. 152, 257–260 (2012).
J.V. Bellini, M.R. Morelli, and R.H.G.A. Kiminami, Mater. Lett. 57, 3775–3778 (2003).
S. Choopun, N. Hongsith and E. Wongrat, IntechOpen, 39506 (2010).
K.J. Chen, F.Y. Hung, T.S. Lui, S.P. Chang, and W.L. Wang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 273, 598–602 (2013).
R. Al-Gaashani, S. Radiman, N. Tabet, and A.R. Daud, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 8761–8769 (2011).
L. Li, J.G. Lei, and T.H. Ji, Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 2084–2089 (2011).
H. Kim, B. K. Lee, K. S. An and S. Ju, Nanotechnology, vol. 23, Article ID 045604 (2012).
M.H. Chou, S.B. Liu, C.Y. Huang, S.Y. Wu, and C.L. Cheng, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 7539–7543 (2008).
H.A. Weakliem, J. Chem. Phys. 36, 2117 (1962).
T.R.N. Kutty and N. Raghu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 54, 1796–1798 (1989).
N.Y. Garces, L. Wang, L. Bai, N.C. Giles, L.E. Halliburton, and G. Cantwell, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 622 (2002).
X. Chen, Z. Zhou, K. Wang, X. Fan, S. Hu, Y. Wang, and Y. Huang, Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 799–802 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, TH., Hung, FY., Chen, CH. et al. Optical, Microstructure, and Electromagnetic Properties of (1 − x)ZnO − xCuO Powders Prepared Using Two-Stage Sintering and Direct Synthesis. JOM 73, 815–822 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04532-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04532-7