Abstract
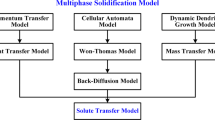
A three-dimensional mathematic model based on segmentation that joins the electromagnetic field, melt flow, heat transfer, solidification and solute transport in the whole casting domain has been established to study the solute transport at the final stage of solidification in a bloom continuous casting process. The effects of the final electromagnetic stirring (F-EMS) positions on the macrosegregation degree of the as-cast bloom are compared and analyzed. The results show that the maximum carbon segregation degree, the ratio of the local carbon concentration to the initial carbon concentration, is reduced from 1.292 to 1.254 with the application of F-EMS. In addition, the position of F-EMS is also an important factor. The maximum carbon segregation degrees are 1.254, 1.237 and 1.269 when the installation location of F-EMS is 14 m, 16 m and 18 m away from the meniscus, respectively. The optimal center solid fraction is about 0.1 at the F-EMS center for this study.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Ghosh, Sadhana 26, 5 (2001).
G. Lesoult, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 413, 19 (2005).
J. Verhoeven, Metall. Trans. 2, 2673 (1971).
M.C. Schneider and C. Beckermann, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 38, 3455 (1995).
A. Scholes, Ironmak. Steelmak. 32, 10 (2005).
S.K. Choudhary and S. Ganguly, ISIJ Int. 47, 1759 (2007).
K. Ayata, T. Mori, T. Fujimot, T. Ohnishi, and I. Wakasugi, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 24, 931 (1984).
T. Ohnishi, K. Shiwaku, S. Kawaski, S. Okushima, Y. Suzuki, and K. Doi, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 73, 513 (1987).
J. Li, B. Wang, Y. Ma, and J. Cui, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 425, 201 (2006).
H. Sun, L. Li, X. Cheng, W. Qiu, Z. Liu, and L. Zeng, Ironmak. Steelmak. 42, 439 (2015).
M. Long and D. Chen, Steel Res. Int. 82, 847 (2011).
H. Mizukami, M. Komatsu, T. Kitagawa, and K. Kawakami, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 70, 194 (1984).
K.S. Oh and Y.W. Chang, ISIJ Int. 35, 866 (1995).
W. Jiang, M. Long, T. Liu, D. Chen, H. Chen, J. Cao, H. Fan, S. Yu, and H. Duan, JOM 70, 2059 (2018).
H. Sun and J. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45, 1133 (2014).
H. Sun, L. Li, D. Ye, and X. Wu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49, 1909 (2018).
D. Jiang and M. Zhu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 3446 (2016).
P.A. Davidson, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 31, 273 (1999).
S. Li, H. Xiao, P. Wang, H. Liu, and J. Zhang, Metals 9, 946 (2019).
W.P. Jones and B.E. Launder, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 16, 1119 (1973).
S. Li, P. Lan, H. Tang, Z. Tie, and J. Zhang, Steel Res. Int. 89, 1800071 (2018).
H. Sun and J. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45, 936 (2014).
Q. Dong, J. Zhang, L. Qian, and Y. Yin, ISIJ Int. 57, 814 (2017).
M.C. Schneider and C. Beckermann, ISIJ Int. 33, 665 (1995).
Y.M. Won and B.G. Thomas, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32, 1755 (2001).
H. Yang, X. Zhang, K. Deng, W. Li, Y. Gan, and L. Zhao, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 29, 1345 (1998).
M.R. Aboutalebi, M. Hasan, and R.I.L. Guthrie, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 26, 731 (1995).
M. Long, D. Chen, Q. Wang, D. Luo, Z. Han, Q. Liu, and W. Gao, Ironmak. Steelmak. 39, 370 (2012).
T. Takahashi, K. Ichikawa, M. Kudou, and K. Shimahara, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 16, 283 (1976).
M.R. Bridge and G.D. Rogers, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 15, 581 (1984).
Acknowledgement
The first author Shaoxiang Li thanks the National Science and Technology Major Project of China under Grant Number 2019ZX04029001 as his further study after receiving the PhD is partially financed by this Project. The authors are also grateful to Yuqi Zhang from Beijing Forestry University for editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Han, Z. & Zhang, J. Numerical Modeling of the Macrosegregation Improvement in Continuous Casting Blooms by Using F-EMS. JOM 72, 4117–4126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04363-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04363-6