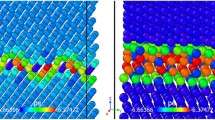
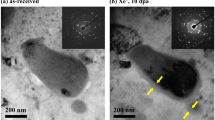
Abstract
Nanocrystalline materials containing amorphous intergranular films (AIFs) exhibit excellent mechanical properties, radiation resistance, and thermal stability and may serve as promising candidate materials for use in advanced nuclear energy systems. The aim of this work is to reveal the effect of mechanical stress on the radiation damage behavior of AIF systems. Based on a bicrystal Cu system with Zr-doped AIFs, molecular dynamics is used to simulate the radiation process and examine the AIF sink efficiency, defect propensity, defect size distribution, and Zr mixing under uniaxial and hydrostatic strain conditions. The results show that the sink efficiency of the glue-like AIFs is not compromised under applied strains. The anisotropy resulting from the intrinsic microstructure and elastic deformation leads to a distinct radiation response, where extension (contraction) of the structure perpendicular to the AIFs increases (decreases) the vacancy density. The strain-dependent defect density, along with the cluster size distributions, can be interpreted based on the variations in the defect formation energy and anisotropic defect diffusion. Finally, the Zr mixing induced by collision cascades is found to be insensitive to the mechanical strains. These findings provide meaningful information towards understanding the stress effect on the radiation response of AIF systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.S. Was, Fundamentals of Radiation Materials Science: Metals and Alloys (Berlin: Springer, 2016).
D. Kaoumi, A. Motta, and R. Birtcher, J. Appl. Phys. 104, 073525 (2008).
M. Jin, P. Cao, and M.P. Short, Scr. Mater. 163, 66 (2019).
A. Khalajhedayati, Z. Pan, and T.J. Rupert, Nat. Commun. 7, 10802 (2016).
Y. Wang, J. Li, A.V. Hamza, and T.W. Barbee, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 104, 11155 (2007).
P. Dubuisson, A. Maillard, C. Delalande, D. Gilbon, and J.L. Seran, Effects of Radiation on Materials the 15th International Symposium, STP 1125 (Philadelphia, PA: American Society for Testing and Materials, 1992), pp. 995–1014.
K. Kasama, F. Toyokawa, M. Tsukiji, M. Sakamoto, and K. Kobayashi, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 33, 1210 (1986).
C. Xu and G.S. Was, J. Nucl. Mater. 454, 255 (2014).
M. Cui, N. Gao, D. Wang, X. Gao, and Z. Wang, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 460, 60 (2019).
A. Brailsford and R. Bullough, J. Nucl. Mater. 48, 87 (1973).
B. Beeler, M. Asta, P. Hosemann, and N. Grønbech-Jensen, J. Nucl. Mater. 459, 159 (2015).
S. Miyashiro, S. Fujita, and T. Okita, J. Nucl. Mater. 415, 1 (2011).
F. Gao, D. Bacon, P. Flewitt, and T. Lewis, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 180, 187 (2001).
S. Di, Z. Yao, M.R. Daymond, and F. Gao, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 303, 95 (2013).
B. Beeler, M. Asta, P. Hosemann, and N. Grønbech-Jensen, J. Nucl. Mater. 474, 113 (2016).
M.J. Banisalman and T. Oda, Comput. Mater. Sci. 158, 346 (2019).
N. Gao, W. Setyawan, R.J. Kurtz, and Z. Wang, J. Nucl. Mater. 493, 62 (2017).
C. Kang, Q. Wang, and L. Shao, J. Nucl. Mater. 485, 159 (2017).
S. Plimpton, P. Crozier, and A. Thompson, LAMMPS-Large-Scale Atomic/Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator, Vol. 18 (Sandia National Laboratories, 2007), p. 43.
V. Borovikov, M.I. Mendelev, and A.H. King, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 24, 085017 (2016).
J.F. Ziegler, J.P. Biersack, and U. Littmark, The Stopping and Range of Ions in Solids (Oxford: Pergamon, 1985).
K. Nordlund, M. Ghaly, R. Averback, M. Caturla, T.D. de La Rubia, and J. Tarus, Phys. Rev. B 57, 7556 (1998).
A. Stukowski, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 18, 015012 (2009).
G. Henkelman, B.P. Uberuaga, and H. Jónsson, J. Chem. Phys. 113, 9901 (2000).
S.J. Dillon, M. Tang, W.C. Carter, and M.P. Harmer, Acta Mater. 55, 6208 (2007).
R. Averback, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 15, 675 (1986).
H.A. Atwater, C.V. Thompson, and H.I. Smith, J. Appl. Phys. 64, 2337 (1988).
P. Shewmon, Diffusion in Solids (Berlin: Springer, 2016).
D. Wang, N. Gao, Z. Wang, X. Gao, W. He, M. Cui, L. Pang, and Y. Zhu, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 384, 68 (2016).
W. Johnson, Y. Cheng, M. Van Rossum, and M. Nicolet, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 7, 657 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, M., Cao, P. Revealing the Strain Effect on Radiation Response of Amorphous–Crystalline Cu-Zr Laminate. JOM 72, 868–876 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03932-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03932-8