Abstract
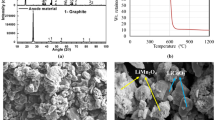
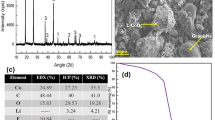
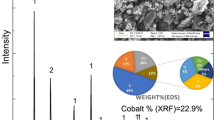
Lithium-ion batteries have a limited lifespan and ever-growing demand and the presence of critical metals such as lithium and cobalt make their recycling inevitable. In this study, discarded mixed mobile batteries were discharged, dismantled, and separated into cathode and anode sheets, followed by attritor crushing. The cathode material comprises LiCoO2 and LiMn2O4, while graphite is present in the anode material. The cathode material was indigenously reduced with purified graphite in a muffle furnace at different times and dosages. A Taguchi statistical design is employed for the optimization of reduction parameters and the obtained magnetic fraction contains cobalt and manganese oxide, whereas graphite and lithium carbonate were found in a nonmagnetic fraction and dried solution. The composition, saturation magnetization and product phases obtained in optimum conditions (900°C, 7.5% graphite, 45 min and 800°C, 7.5% graphite, 45 min) are: Co: ~ 80 to 84%; Mn: 6–10%; and saturation magnetization: 105–114 emu/g with Co, CoO and MnO phases, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Meshram, B.D. Pandey, and T.R. Mankhand, Hydrometallurgy 150, 192 (2014).
Indian Bureau of Mines, Indian Minerals Yearbook, (Part-II: Metals & Alloys) 52 Cobalt.
J. Li, G. Wang, and Z. Xu, J. Hazard. Mater. 302, 97 (2016).
S.R. Sunil, S. Vishvakarma, A. Barnwal, and N. Dhawan, JOM (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03540-6.
T. Georgi-Maschler, B. Friedrich, R. Weyhe, H. Heegn, and M. Rutz, J. Power Sources 207, 173 (2012).
J. Hu, J. Zhang, H. Li, Y. Chen, and C. Wang, J. Power Sources 351, 192 (2017).
F. Wang, T. Zhang, Y. He, Y. Zhao, S. Wang, G. Zhang, and Y. Feng, J. Clean. Prod. 185, 646 (2018).
W. Gao, J. Song, H. Cao, X. Lin, X. Zhang, X. Zheng, and Z. Sun, J. Clean. Prod. 178, 833 (2018).
Q. Meng, Y. Zhang, and P. Dong, J. Clean. Prod. 180, 64 (2018).
Y. Chen, N. Liu, F. Hu, L. Ye, Y. Xi, and S. Yang, Waste Manag. 75, 469 (2018).
L. Li, W. Qu, X. Zhang, J. Lu, R. Chen, F. Wu, and K. Amine, J. Power Sources 282, 544 (2015).
L. Li, Y. Bian, X. Zhang, Y. Guan, E. Fan, F. Wu, and R. Chen, Waste Manag. 71, 362 (2018).
X. Chen, H. Ma, C. Luo, and T. Zhou, J. Hazard. Mater. 326, 77 (2017).
P. Meshram, B.D. Pandey, and T.R. Mankhand, Chem. Eng. J. 281, 418 (2015).
X. Zeng, J. Li, and B. Shen, J. Hazard. Mater. 295, 112 (2015).
W. Lv, Z. Wang, H. Cao, X. Zheng, W. Jin, Y. Zhang, and Z. Sun, Waste Manag. 79, 545 (2018).
P. Meshram, B.D. Pandey, T.R. Mankhand, and H. Deveci, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 43, 117 (2016).
L. Yun, D. Linh, L. Shui, X. Peng, A. Garg, M.L.P. Le, and J. Sandoval, Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 136, 198 (2018).
G.P. Nayaka, K.V. Pai, G. Santhosh, and J. Manjanna, Hydrometallurgy 161, 54 (2016).
E.G. Pinna, M.C. Ruiz, M.W. Ojeda, and M.H. Rodriguez, Hydrometallurgy 167, 66 (2017).
P. Liu, L. Xiao, Y. Tang, Y. Chen, L. Ye, and Y. Zhu, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 136, 1323 (2018).
S.P. Barik, G. Prabaharan, and B. Kumar, Waste Manag. 51, 222 (2016).
X. Zheng, Z. Zhu, X. Lin, Y. Zhang, Y. He, H. CaO, and Z. Sun, Engineering 4, 361 (2018).
Z. Huang, J. Zhu, R. Qiu, J. Ruan, and R. Qui, J. Clean. Prod. 229, 1148 (2019).
J. Xiao, J. Li, and Z. Xu, Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 11960 (2017).
D. Wang, X. Zhang, H. Chen, and J. Sun, Miner. Eng. 126, 28 (2018).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank and acknowledge the funding received from the Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee under Faculty Initiation Grant; FIG-100714, and Rahul Singh for meaningful discussions and raw material preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pindar, S., Dhawan, N. Carbothermal Reduction of Spent Mobile Phones Batteries for the Recovery of Lithium, Cobalt, and Manganese Values. JOM 71, 4483–4491 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03799-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03799-9