Abstract
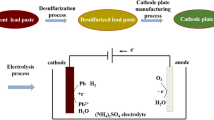
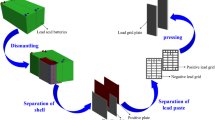
Metal lead was first prepared from waste lead paste by direct electrochemical reduction in NH3-NH4Cl solution. Cyclic voltammetry of waste lead paste powders indicated that waste lead paste could be directly electrochemically reduced to metal lead. After constant cell voltage electrolysis for 3 h, waste lead paste pellets were almost completely converted into metal containing 98.3% lead, and the current efficiency and energy consumption were approximately 86.3% and 689.4 kW h/t, respectively. In addition, an empirical model of direct electrochemical reduction of waste lead paste pellets in NH3-NH4Cl solution has been proposed. Metal lead was initially formed at a three-phase interface of the current collector, waste lead paste and electrolyte; then, the newly formed three-phase interface of the metal lead, waste lead paste and electrolyte quickly expanded along the surface of the pellets and eventually extended into the interior of the pellets.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Tian, Y. Gong, Y.F. Wu, A. Agyeiwaa, and T.Y. Zuo, Res. Conserv. Recycl. 93, 75 (2014).
E.R. Cole, A.Y. Lee, and D.L. Paulson, JOM 35, 42 (1983).
E.R. Cole, A.Y. Lee, and D.L. Paulson, JOM 37, 79 (1985).
C.S. Chen, Y.J. Shi, and Y.H. Huang, Waste Manag. 52, 212 (2016).
D. Andrews, A. Raychaudhuri, and C. Frias, J. Power Sources 88, 124 (2000).
N.K. Lyakov, D.A. Atanasova, V.S. Vassilev, and G.A. Haralampiev, J. Power Sources 171, 960 (2007).
Y.J. Ma and K.Q. Qiu, Waste Manag. 40, 151 (2015).
J.Q. Pan, C. Zhang, Y.Z. Sun, Z.H. Wang, and Y.S. Yang, Electrochem. Commun. 19, 70 (2012).
J.K. Yang, X.F. Zhu, and R. Vasant Kumar, Mater. Chem. Phys. 131, 336 (2011).
X.F. Zhu, X. He, J.K. Yang, L.X. Gao, J.W. Liu, D.N. Yang, X.J. Sun, W. Zhang, Q. Wang, and R. Vasant Kumar, J. Hazard. Mater. 250–251, 387 (2013).
R.D. Prengaman, JOM 47, 31 (1995).
M. Olper, and P. Fracchia, US Patent, 4769116 (1998).
G. Díaz and D. Andrews, JOM 48, 29 (1996).
D. Andrews, A. Raychaudhuri, and C. Frias, J. Power Sources 88, 124 (2000).
J. Yang, J.F. Ma, Y.Y. Liu, J.C. Ma, and S.R. Batten, Inorgan. Chem. 46, 42 (2007).
R. V. Kumar, M. S. Sonmez, and V. P. Kotzeva, UK Patent, 0622249.1 (2006).
J.J. Ru, Y.X. Hua, C.Y. Xu, J. Li, Y. Li, D. Wang, Z.R. Zhou, and K. Gong, Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 2094 (2015).
E. Shangguan, J. Li, D. Guo, L.T. Guo, M.Z. Nie, Z.R. Chang, X.Z. Yuan, and H.J. Wang, J. Power Sources 282, 158 (2015).
X.Y. Zhang, Y.X. Hua, C.Y. Xua, N. Xu, and H. Xue, Electrochim. Acta 63, 197 (2012).
Y.Y. Chen, U.T. Hong, H.C. Shih, J.W. Yeh, and T. Duval, Corros. Sci. 47, 2679 (2005).
G. Díaz and D. Andrews, JOM 48, 29 (1996).
W. Xiao, X.B. Jin, Y. Deng, D.H. Wang, and G.Z. Chen, J. Electroanal. Chem. 639, 130 (2010).
J.J. Ru, Y.X. Hua, D. Wang, C.Y. Xu, J. Li, Y. Li, Z.R. Zhou, and K. Gong, Electrochim. Acta 186, 455 (2015).
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers U1760120, 51504059); the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant Numbers 2017YFC0210403-04, 2017YFC0210404); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Numbers N162504016, N182504018); the Fund of Liaoning S&T Project (Grant Number 20180551008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Liu, Y., Niu, L. et al. Preparation of Metal Lead from Waste Lead Paste by Direct Electrochemical Reduction in NH3-NH4Cl Solution. JOM 71, 4518–4527 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03797-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03797-x