Abstract
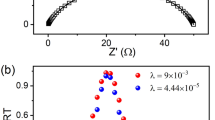
The distribution function of the relaxation times (DRT) technique is a powerful tool for the interpretation of impedance spectra of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) because it enables direct identification of rate-limiting processes through mathematical calculations. Selection of an appropriate regularization parameter (λreg) is critical for obtaining meaningful deconvolution solutions in DRT analysis. Herein, we introduce an L-curve criterion as a reliable graphical tool for determination of the λreg value. In a parametric plot of log(solution norm) versus log(misfit norm), the λreg value at the corner of the L curve provides an optimum balance between the regularization error and perturbation error. In a case study on La0.6Sr0.4CoO3−δ-based cathodes, the DRT technique guided by the L-curve criterion enabled identification of rate-limiting processes and clarification of reaction pathways. The analytical methodology presented in this article provides guidelines for the effective use of the DRT technique for the impedance analysis of SOFCs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.C. Singhal, Solid State Ionics 135, 305 (2000).
S. McIntosh and R.J. Gorte, Chem. Rev. 104, 4845 (2004).
S.M. Haile, Acta Mater. 51, 5981 (2003).
G.M. Rupp, A.K. Opitz, A. Nenning, A. Limbeck, and J. Fleig, Nat. Mater. 16, 640 (2017).
J.J. Kim, S.R. Bishop, D. Chen, and H.L. Tuller, Chem. Mat. 29, 1999 (2017).
C. Nicollet, A. Flura, V. Vibhu, A. Rougier, J.M. Bassat, and J.C. Grenier, J. Power Sources 294, 473 (2015).
R. Antunes, J. Jewulski, and T. Golec, J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 11, 7 (2014).
B. Liu, H. Muroyama, T. Matsui, K. Tomida, T. Kabata, and K. Eguchi, J. Electrochem. Soc. 157, B1858 (2010).
H. Sumi, T. Yamaguchi, K. Hamamoto, T. Suzuki, Y. Fujishiro, T. Matsui, and K. Eguchi, Electrochim. Acta 67, 159 (2012).
H. Schichlein, A.C. Müller, M. Voigts, A. Krügel, and E. Ivers-Tiffée, J. Appl. Electrochem. 32, 875 (2002).
G. Jeschke and S. Schlick, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 8, 4095 (2006).
G. Jeschke, G. Panek, A. Godt, A. Bender, and H. Paulsen, Appl. Magn. Reson. 26, 223 (2004).
M.K. Bowman, A.G. Maryasov, N. Kim, and V.J. DeRose, Appl. Magn. Reson. 26, 23 (2004).
M. Saccoccio, T.H. Wan, C. Chen, and F. Ciucci, Electrochim. Acta 147, 470 (2014).
J.P. Tomba, M. de la Paz Miguel, and C.J. Perez, J. Raman Spectrosc. 42, 1330 (2011).
T.M. Correia, A.P. Gibson, M. Schweiger, and J.C. Hebden, J. Biomed. Opt. 14, 11 (2009).
J. Weese, Comput. Phys. Commun. 69, 99 (1992).
Y. Takeda, R. Kanno, M. Noda, Y. Tomida, and O. Yamamoto, J. Electrochem. Soc. 134, 2656 (1987).
E. Siebert, A. Hammouche, and M. Kleitz, Electrochim. Acta 40, 1741 (1995).
J.E. Bauerle, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 30, 2657 (1969).
V. Sonn, A. Leonide, and E. Ivers-Tiffee, J. Electrochem. Soc. 155, B675 (2008).
A. Leonide, B. Ruger, A. Weber, W.A. Meulenberg, and E. Ivers-Tiffee, J. Electrochem. Soc. 157, B234 (2010).
Y.W. Chiang, P.P. Borbat, and J.H. Freed, J. Magn. Reson. 172, 279 (2005).
P.C. Hansen, SIAM Rev. 34, 561 (1992).
D. Klotz, M. Schonleber, J.P. Schmidt, and E. Ivers-Tiffee, Electrochim. Acta 56, 8763 (2011).
B.A. Boukamp, Electrochim. Acta 154, 35 (2015).
S.-W. Baek, J. Bae, and Y.-S. Yoo, J. Power Sources 193, 431 (2009).
H.N. Im, M.B. Choi, B. Singh, D.K. Lim, and S.J. Song, J. Electrochem. Soc. 162, F728 (2015).
A. Grimaud, F. Mauvy, J.M. Bassat, S. Fourcade, L. Rocheron, M. Marrony, and J.C. Grenier, J. Electrochem. Soc. 159, B683 (2012).
M.J. Escudero, A. Aguadero, J.A. Alonso, and L. Daza, J. Electroanal. Chem. 611, 107 (2007).
B. Philippeau, F. Mauvy, C. Nicollet, S. Fourcade, and J.C. Grenier, J. Solid State Electrochem. 19, 871 (2014).
V. Dusastre and J.A. Kilner, Solid State Ionics 126, 163 (1999).
F.S. Baumann, J. Fleig, H.-U. Habermeier, and J. Maier, Solid State Ionics 177, 1071 (2006).
R. Amin, B. Kenney, and K. Karan, J. Electrochem. Soc. 158, B1076 (2011).
Y.L. Yang, C.L. Chen, S.Y. Chen, C.W. Chu, and A.J. Jacobson, J. Electrochem. Soc. 147, 4001 (2000).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT (NRF-2016M1A2A2940148) and the institutional research program of Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, MB., Shin, J., Ji, HI. et al. Interpretation of Impedance Spectra of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: L-Curve Criterion for Determination of Regularization Parameter in Distribution Function of Relaxation Times Technique. JOM 71, 3825–3834 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03762-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03762-8