Abstract
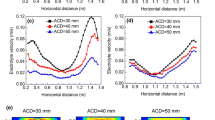
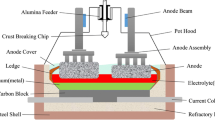
Numerical simulations of the effects of different anode slot configurations on the gas–liquid multiscale flow characteristics in an aluminum electrolysis cell have been conducted based on a recently developed mathematical model. The results clearly showed that use of anode slots can significantly promote the bubble evacuation behavior and thus affect the overall flow pattern. Both the gas volume fraction and bubble size decreased obviously when transversal or especially longitudinal slots were used. Moreover, the greater the number of both kinds of slot, the lower the mentioned parameters. With increasing anode slot width, the gas volume fraction decreased slightly while there was almost no effect on the bubble size distribution (BSD). Reducing the anode slot height caused a higher gas volume fraction. Both the overall gas volume fraction and BSD in industrial-scale cells are apparently influenced by two large circulation vortices caused by electromagnetic forces (EMFs).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.E. Einarsrud, I. Eick, W. Bai, Y.Q. Feng, J.S. Hua, and P.J. Witt, Appl. Math. Model. 44, 3 (2017).
B.J. Moxnes, B.E. Aga, and H. Skaar, Light Metals 1998, ed. H. Kvande (San Francisco, : TMS, 1998), pp. 247–255.
X.W. Wang, Light Metals 2007, ed. M. Sørlie (Orlando: TMS, 2007), pp. 539–544.
K.A. Rye, E. Myrvold, and I. Solberg, Light Metals 2007, ed. M. Sørlie (Orlando: TMS, 1998), pp. 293–298.
K. Vekony and L.I. Kiss, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 41, 1006 (2010).
M.A. Cooksey and W. Yang, Light Metals 2006, ed. T.J. Galloway (San Antonio: TMS, 2006), pp. 359–365.
Y.Q. Xue, N.J. Zhou, and S.Z. Bao, Chin. J. Nonferrous Metals 16, 1823 (2006).
M. Alam, W. Yang, K. Mohanarangam, G. Brooks, and Y.S. Morsi, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 44, 1155 (2013).
R.G. Aaberg, V. Ranum, and K. Williamson, Light Metals 1997, ed. R. Huglen (Orlando: TMS, 1997), pp. 341–346.
Z.B. Zhao, Z.W. Wang, B.L. Gao, Y.Q. Feng, Z.N. Shi, and X.W. Hu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 1962 (2016).
Y.Q. Feng, M.A. Cooksey, and M.P. Schwarz, Light Metals 2007, ed. M. Sørlie (Orlando: TMS, 2007), pp. 339–344.
J. Li, Y.J. Xu, H.L. Zhang, and Y.Q. Lai, Int. J. Multiph. Flow 37, 46 (2011).
Y.Q. Feng, M.P. Schwarz, W. Yang, and M.A. Cooksey, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46, 1959 (2015).
Q. Wang, B.K. Li, and N.X. Feng, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45, 272 (2014).
S.Q. Zhan, Z.T. Wang, J.H. Yang, R.J. Zhao, C.F. Li, J.F. Wang, and J.M. Zhou, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 56, 8649 (2017).
W. Yang and M.A. Cooksey, Light Metals 2007, ed. M. Sørlie (Orlando: TMS, 2007), pp. 451–456.
D.S. Severo, V. Gusberti, E.C.V. Pinto, and R.R. Moura, Light Metals, ed. M. Sørlie (Orlando: TMS, 2007), pp. 287–292.
S. Yang, H.L. Zhang, Y.J. Xu, H.H. Zhang, Z. Zou, J. Li, and Y.Q. Lai, J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. (Chinese) 43, 4617 (2012).
S.Q. Zhan, M. Li, J.M. Zhou, J.H. Yang, and Y.W. Zhou, J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 22, 2482 (2015).
S.Q. Zhan, J.H. Yang, Z.T. Wang, R.J. Zhao, J. Zheng, and J.F. Wang, JOM 69, 1589 (2017).
S.Q. Zhan, J.F. Wang, Z.T. Wang, and J.H. Yang, JOM 70, 229 (2018).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51704126), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20170551, BK20171301), Natural Science Foundation of Higher Education Institutions of Jiangsu Province (17KJB450001), Foundation of Senior Talent of Jiangsu University (2015JDG158), and “Qing Lan” Project Foundation of Jiangsu Province. Our special thanks are due to the anonymous reviewers for insightful suggestions on this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, S., Huang, Y., Wang, Z. et al. CFD Simulations of Gas–Liquid Multiscale Flow Characteristics in an Aluminum Electrolysis Cell with Population Balance Model: Effect of Anode Slot Configuration. JOM 71, 23–33 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-3191-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-018-3191-7