Abstract
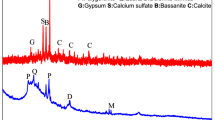
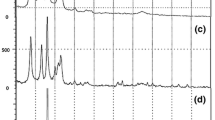
Electric-arc furnace (EAF) slag, the by-product of steel fabricated at the EAF, is in most cases still sent to dumps, with serious environmental consequences. This work shows an innovative, economically convenient application for EAF slag: its use as reinforcing filler for polypropylene. Composites based on polypropylene containing 10–40 wt.% of EAF slag particles were prepared by melt compounding followed by injection molding. A physical–chemical analysis of the EAF slag was performed to determine microstructural features and main component phases. Leaching tests demonstrated that, although EAF slag can release small amounts of toxic elements, such as heavy metals, incorporating such material into the polymeric matrix immobilizes the heavy metals inside that matrix. The mechanical characterization of the polymer-based composites was performed. Incorporating EAF slag particles raises the Young’s modulus and the tensile strength at yield, whereas elongation at break and the impact strength of the polymer-based composite are significantly reduced only when large amounts of filler are added, i.e., 30% or more.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.M. Proctor, K.A. Fehling, E.C. Shay, J.L. Wittenborn, J.J. Green, C. Avent, R.D. Bigham, M. Connolly, B. Lee, T.O. Shepker, and M.A. Zak, Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 1576 (2000).
H. Motz and J. Geiseler, Waste Manag. 21, 285 (2001).
P. Ahmedzade and B. Sengoz, J. Hazard. Mater. 165, 300 (2009).
P. Ahmedzade, M. Tigdemir, and S.F. Kalyoncuoglu, Construct. Build. Mater. 21, 626 (2007).
I.M. Asi, H.Y. Qasrawi, and F.I. Shalabi, Can. J. Civil Eng. 34, 902 (2007).
J.J. Emery, Slag Utilization in Pavement Construction (Extending Aggregate Resources (West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International, 1982), pp. 95.
M. Kara, E. Gunay, B. Kavakli, S. Tayfur, K. Eren, and G. Karadag, Key Eng. Mater. 264–268, 2493 (2004).
N.L. Nemerow, F.J. Agardy, and J.A. Salvato, Environmental Engineering: Environmental Health and Safety for Municipal Infrastructure, Land Use and Planning, and Industry, 6th ed. (New York: Wiely, 2009), p. 58.
W. Shena, M. Zhoua, W. Mab, J. Hub, and Z. Caib, J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 99 (2009).
P. Chaurand, J. Rose, V. Briois, L. Olivi, J.L. Hazemann, O. Proux, J. Domas, and J.Y. Bottero, J. Hazard. Mater. B139, 537 (2007).
G. Wanga, Y. Wanga, and Z. Gaob, J. Hazard. Mater. 184, 555 (2010).
S. Wu, Y. Xue, Q. Ye, and Y. Chen, Build. Environ. 42, 2580 (2007).
S.I. Abu-Eishaha, A.S. El-Diebb, and M.S. Bedir, Const. Build. Mater. 34, 249 (2012).
M. Frıas, Rojas and M.I. Sanchez de Rojas. Cement Concrete Res. 34, 1881 (2004).
M. Luckman, V. Satish, and D. Venkateswaran, Cement Concrete Res. 39, 102 (2009).
C. Shi and J. Qian, Resourc. Conserv. Recycl. 29, 195 (2000).
P.E. Tsakiridis, G.D. Papadimitrou, S. Tsivilis, and C. Koroneos, J. Hazard. Mater. 152, 805 (2008).
D. Venkateswaran, D. Sharma, L. Muhmood, and S. Witta, Global Slag Magazine, pp. 21 (2007).
T. Zhang, F. Liu, and S. Liu, Adv. Cement Res. 20, 145 (2008).
M. Arm, P. Suer, H. Arvidsson, and J.E. Lindqvist, Waste Manage. 31, 101 (2011).
J.M. Manso, J.A. Polanco, M. Losanez, and J.J. Gonzalez, Cement Concrete Compos. 28, 528 (2006).
C. Pellegrino and V. Gaddo, Cement Concrete Compos. 31, 663 (2009).
P. Suer, J.E. Lindqvist, M. Arm, and P. Frogner-Kockum, Sci. Total Environ. 407, 5110 (2009).
T. Zhang, Q. Yu, J. Wei, and J. Li, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 110, 633 (2012).
D.R. Reinhart, Waste Manage. Res. 11, 257 (1993).
M.A. Ozaki, H. Watanabe, and B. Wiebusch, Wat. Sci. Tech. 36, 267 (1997).
M. Tossavainen, F. Engstrom, Q. Yang, N. Menad, and M. Lidstrom, Larsson, and B. Bjorkman, Waste Manage. 27, 1335 (2007).
M. Wahlstrom, Sci. Total Environ. 178, 95 (1996).
M. Gelfi, G. Cornacchia, and R. Roberti (Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 6th Euroslag 2010 Conference, Madrid, Spain, 2010), pp. 157–169.
J.F.P. Gomes and C.G. Pinto, Rev. Metal. 42, 409 (2006).
Y. Lee and C.L. Nassarella, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 29B, 405 (1988).
E.R. Plunkett, Handbook of Industrial Toxicology (New York: Chemical Publishing Co., 1976), pp. 108–109.
J.-Z. Liang, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 83, 1547 (2002).
A.L.N. Da Silva, M.C.G. Rocha, M.A.R. Moraes, C.A.R. Valente, and F.M.B. Coutinho, Polym. Test. 21, 57 (2002).
M.Y.A. Fuad, H. Hani., R. Zarina, Z.A. Mohd Ishak, and A. Hassan, eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 4 (10), 611 (2010), 611–620.
L.E. Nielsen, Mechanical Properties of Polymers and Composites (New York: Marcel Dekker, 1974).
R. Roberti, Italian patent BS2008A000143 (2008).
CEN, prEN 12457-2, Characterization of Waste-Leaching-Compliance Test of Leaching of Granular Waste Material and Sludges–Part 2: One-Stage Batch Test at a Liquid to Solid Ration of 10 l/kg for Materials with Particle Size Below 4 mm (With or Without Particle Reduction), (2002a).
ISO 527-1:2012, Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 1: General Principles (2012).
ISO 179-2:1997, Plastics—Determination of Charpy Impact Properties—Part 2: Instrumented Impact Test (1997).
K.E. Daugherty, B. Saad, C. Weirich, and A. Eberendu, Silic. Indust. 4, 107 (1983).
L. Nicolais and M. Narkis, Polym. Eng. Sci. 11, 194 (1971).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ing. Massimo Svanera and ASO Siderurgica srl for their collaboration in carrying out the experiments. Also, the contributions of Valentina Ferrari, Isabella Peroni, and Gloria Spagnoli in the experimental testing is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cornacchia, G., Agnelli, S., Gelfi, M. et al. Reuse of EAF Slag as Reinforcing Filler for Polypropylene Matrix Composites. JOM 67, 1370–1378 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1396-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1396-6