Abstract
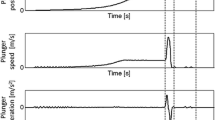
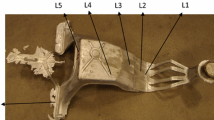
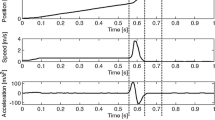
Two individual high-pressure die casting geometries were developed to study the influence of process parameters and alloy composition on the distortion behavior of aluminum alloy castings. These geometries, a stress lattice and a V-shaped lid, tend to form residual stress due to a difference in wall thickness and a deliberate massive gating system. Castings were produced from two alloys: AlSi12(Fe) and AlSi10MnMg. In the experimental castings, the influence of important process parameters such as die temperature, ejection time, and cooling regime was examined. The time evolution of process temperatures was measured using thermal imaging. Subsequent to casting, distortion was measured by means of a tactile measuring device at ambient temperatures. The measured results were compared against a numerical process and stress simulations of the casting, ejection, and cooling process using the commercial finite element method software ANSYS Workbench. The heat transfer coefficients were adapted to the temperature distributions of the die, and the castings were observed by thermal imaging. A survey of the results of the comparison between simulation and experiment is given for both alloys.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.A. El-Mahallawy, M.A. Taha, E. Pokora, and F. Klein, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 73, 125 (1998).
G.W. Liu, Y.S. Morsi, and B.R. Clayton, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 39, 582 (2000).
C. Dorum, H.I. Laukli, and O.S. Hopperstad, Comput. Mater. Sci. 46, 100 (2009).
R.W. Lewis and R.S. Ransing, Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 34, 193 (2000).
B.C. Liu, J.W. Kang, and S.M. Xiong, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2, 157 (2001).
A. Ludwig, Int. J. Thermophys. 23, 1131 (2002).
E. Kaschnitz, Gießerei-Rundschau 52, 176 (2005).
A. Fendt (Doctoral thesis, Technische Universität, Munich, Germany, 2000).
TN-503, Measurement of Residual Stresses by the Blind Hole Drilling Method (Measurement Group Inc., Wendell, NC, 1981).
E. Macherauch, Eigenspannungen, Entstehung-Messung-Bewertung, Vol. 1 (E.V.: Deutsche Gesellschaft für Metallkunde, 1983).
K.C. Mills, Recommended Values of Thermophysical Properties for Selected Commercial Alloys (Cambridge, U.K.: Woodhead Publishing, 2002).
P. Hofer and E. Kaschnitz, Gießerei-Rundschau 55, 190 (2008).
P. Hofer, E. Kaschnitz, and P. Schumacher, Gießerei-Rundschau 57, 182 (2010).
P. Hofer and E. Kaschnitz, High Temp. High Press. 40, 311 (2011).
P. Hofer (Doctoral thesis, Montanuniversität Leoben, Austria, 2012).
P. Hofer, E. Kaschnitz, and P. Schumacher, Mater. Sci. Eng. 33, 012055 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofer, P., Kaschnitz, E. & Schumacher, P. Distortion and Residual Stress in High-Pressure Die Castings: Simulation and Measurements. JOM 66, 1638–1646 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1118-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1118-5