Abstract
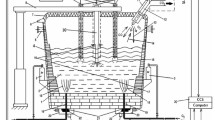
A review of the energy innovations for the electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking route is discussed. Preheating of scrap using vertical and horizontal shafts that have been commercially successful in lowering the energy consumption to as much as 90 kWh/t reaching almost the operational limit to heating input scrap materials into the EAF is discussed. Bucket-type and twin-shell preheaters have also shown to be effective in lowering the overall power consumption by 60 kWh/t, but these have been less effective than the vertical shaft-type preheaters. Beyond the scrap preheating technologies, the utilization of waste heat of the slags from the laboratory scale to the pilot scale has shown possible implementation of a granulation and subsequent heat exchange with forced air for energy recovery from the hot slags. Novel techniques to increase metal recovery have shown that laboratory-scale testing of localized Fe concentration into the primary spinel crystals was possible allowing the separation of an Fe-rich crystal from an Fe-depleted amorphous phase. A possible future process for converting the thermal energy of the CO/CO2 off-gases from the EAF into chemical energy was introduced.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Steel Association, Crude Steel Production (2012). http://www.worldsteel.org/statistics/crude-steel-production.html. Accessed 30 May 2014.
World Steel Dynamics, World Steel Dynamics Report-Scrap Outlook: A New Bundle (2012). http://www.worldsteeldynamics.com/pg/reports. Accessed 15 Sept 2013.
C.P. Manning and R.J. Fruehan, JOM 53(10), 36 (2001).
Y.N. Toulouevski and I.Y. Zinurov, Innovation in Electric Arc Furnaces (New York: Springer, 2010), pp. 1–23, 81–92.
J.P. Birat, Revue de Métall. 97, 1347 (2000).
OECD, OECD Environmental Outlook to 2030 (Paris: OECD Publishing, 2008).
L. Mathiesen and O. Maestad, Energy J. 25, 91 (2004).
A.W. Wyckoffa and J.M. Roop, Energy Policy 22, 187 (1994).
S.H. Anderson, G.E. Metius, and J.M. McClelland, 60th Electric Furnace Conference Proceedings (Warrendale, PA: ISS, 2002), pp. 175–191.
M. Atkinson and R. Kolarik, AISI Steel Industry Technology Roadmap Report (Oak Ridge, TN: American Iron and Steel Institute, 2001), pp. 23–28.
J.P. Birat, Ironmak. Steelmak. 28, 152 (2001).
N.A. Godinskii, N.N. Kushnarev, D.S. Yakhshuk, V.I. Kotenev, and E.Y. Barsukova, Metallurgist 47, 16 (2003).
C.W. Forsberg, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 32, 431 (2007).
K.S. Yoshiki-Gravelsins, J.M. Toguri, and R.T.C. Choo, JOM 45(5), 15 (1993).
O. Ostrovski and G. Zhang, AIChE J. 52, 300 (2006).
T. Emi and S. Seetharaman, Scand. J. Metall. 29, 185 (2000).
G.H. Geiger, Proc. International Symposium on Global Environment and the Iron and Steel Industry (Beijing, China: CMS, 1998), pp. 191–196.
D. Yanez, M.A. Pedroza, J. Ehle, and H. Knapp, Proc. 6th European Electric Steelmaking Conference (Dusseldorf, Germany: Verlag Stahleisen mbH, 1999), pp. 24–28.
I.A. Madugu and M. Abdulwahab, Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2, 835 (2008).
T. Wang, M. Kawakami, K. Mori, and S.H. Shahidan, Mater. Sci. Forum 449, 329 (2004).
H. Ludwig, SEAISI Q. 30, 16 (2001).
S.S. Baker, A.M.W. Briggs, P.J. Lewis, D. Capodilupo, E. Repetto, S. Gonthier, Y. Zbaczyniak, B. Kleimt, S. Kohle, M. Knoop, G. Mosel, and P.G. Oberhauser, European Commission Report—Ecological and Economical EAF Steelmaking EUR 19480, 2001, pp. 1–442.
Y. Fujiwara, Mater. World 9, 17 (2001).
R. Yamaguchi, H. Mizukami, T. Maki, and N. Ao, 58th Electric Furnace Conference Proc. (Warrendale, PA: ISS, 2000), pp. 325–336.
H. Mizukami, R. Yamaguchi, T. Nakayama, T. Maki, N. Ao, and Y. Sato, NKK Tech. Rev. 82, 14 (2000).
T. Sugasawai, H. Kato, and T. Nagai (Paper presented at the 2013 SEASI Conference and Exhibition, Dusit Thani Pattaya, Thailand, 3–6 June 2013).
J. Ehle and G. Fuchs, U.S. patent 5153,894 A (1992).
United States Environmental Protection Agency, Available and Emerging Technologies for Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions from the Iron and Steel Industry (Research Triangle Park, NC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air and Radiation, 2012). http://www.epa.gov/nsr/ghgdocs/refineries.pdf. Accessed 30 May 2014.
M.A. Pedroza, R.G. Gonzalez, and M.A. Herrera, Ironmak. Steelmak. 24, 83 (1997).
M. Haissig and W. Gebert, 56th Electric Furnace Conference Proc. (Warrendale, PA: ISS, 1998), vol. 55, pp. 391–405.
J. de Beer, Potential for Industrial Energy-Efficiency Improvement in the Long Term (Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2000), pp. 145–147.
A. Villar, J.J. Arribas, and J. Parrondo, Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 14, 29 (2012).
P. Argenta and M.B. Ferri, La Metall. Ital. 1, 41 (2005).
M.H. Adjei-Sarpong, M. Fox, B. Trumble, and J. Powers, Iron Steel Technol. 3, 65 (2006).
C. Giavani, E. Malfa, and V. Battaglia, SEAISI Q. J. 41, 16 (2012).
F. Memoli, M. Guzzon, C. Giavani, M. Zanforlin, and P. Galbiati, Iron Steel Technol. 7, 56 (2010).
J. Tang, M.B. Ferri, and P. Argenta, Ironmak. Steelmak. 32, 191 (2005).
J. Simmons, A. Manenti, and K. Shoop, 60th Electric Furnace Conference Proc. (Warrendale, PA: ISS, 2002), vol. 60, pp. 377–386.
J.A. Vallomy, Scand. J. Metall. 28, 277 (1999).
A. Michielan, A. Fior, and G. Lavaroni, 6th European Electric Steelmaking Conf. Proc. (Warrendale, PA: ISS, 1999), pp. 78–83.
K.E. Sewald, 44th Electric Furnace 957 Conf. Proc. (Warrendale, PA: ISS, 1987), pp. 243–250.
A.B. Steblov, A.V. Mateiko, and É.A. Steblova, Metallurgist 50, 571 (2006).
E. Worrell, L. Price, and N. Martin, Energy 26, 513 (2001).
V. Portanova, JOM 36, 37 (1984).
A. Michielan and A. Fior, 6th European Electric Steelmaking Conf. Proc. (Warrendale, PA: ISS, 1999), pp. 204–209.
D. Neuschutz, High Temp. Mater. Process. 4, 309 (2000).
M. Gojic, Metalurgija 43, 163 (2004).
B. Butcher, B. Laroy, K. Vanover, Y. Krotov, and S. Meyer, Iron Steel Technol. 8, 42 (2011).
H. Trenkler, ABB Rev. 9/10, 18 (1996).
M. Barati, S. Esfahani, and T.A. Utigard, Energy 36, 5440 (2011).
H. Zhang, H. Wang, X. Zhu, Y.-J. Qiu, K. Li, R. Chen, and Q. Liao, Appl. Energy 112, 956 (2013).
P. Berger, Stahl Eisen 50, 1775 (1930).
S.J. Pickering, N. Hay, T.F. Roylance, and G.H. Thomas, Ironmak. Steelmak. 12, 14 (1985).
M. Yoshinaga, K. Fujii, T. Shigematsu, and T. Nakata, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 22, 823 (1982).
J.R. Donald and C.A. Pickles, Proc. 77th Steelmaking Conf. (Warrendale, PA: ISS, 1994), pp. 681–692.
T. Akiyama, K. Oikawa, T. Shimada, E. Kasai, and J.-I. Yagi, ISIJ Int. 40, 286 (2000).
T. Shimada, V. Kochura, T. Akiyama, E. Kasai, and J. Yagi, ISIJ Int. 41, 111 (2001).
F. Sieverding, Steel Times 208, 469 (1980).
J. Ando, T. Nakahar, H. Onous, S. Tchimura, and M. Kondo, Technical Review (Japan: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, 1985), pp. 136–142.
World Steel Association, World Steel Association Yearbook and Factsheets (2012). http://www.worldsteel.org/Steel. Accessed 30 May 2014.
Verein Deutscher Eisenhuttenleute, Slag Atlas, 2nd ed. (Dusseldorf: Verlag Stahleisen, 1995), p. 597.
M. Susa, K. Nagata, and K.S. Goto, Trans. JIM 29, 133 (1998).
K. Nagata, M. Susa, and K.S. Goto, Tetsu-to-Hagané 69, 1417 (1983).
T. Akiyama, T. Shima, T. Kasai, and J. Yagi, China-Japan International Academic Symposium (2000), pp. 53–65.
D. Xie, Y. Pan, R. Flann, B. Washington, S. Sanetsis, and J. Donnelley, Proc. 1st CSRP Annual Conf. (Melbourne, Australia: CSIRO, 2007), pp. 29–30.
H. Matsuura and F. Tsukihashi, ISIJ Int. 52, 1503 (2012).
N. Maruoka, T. Mizuochi, H. Purwanto, and T. Akiyama, ISIJ Int. 44, 257 (2004).
S.-W. Joo, J.-D. Shin, D.-K. Shin, S.-H. Hong, J.-S. Ki, J.-I. Hwang, and B.-D. You, Korean J. Met. Mater. 50, 753 (2012).
Y.J. Kim and D.J. Min, Steel Res. Int. 83, 852 (2012).
H. Shen, Waste Manag. 23, 933 (2003).
D.M. Proctor, K.A. Fehling, and E.C. Shay, Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 1576 (2000).
J. Geiseler, Waste Manag. 16, 59 (1996).
S.S. Jung and I. Sohn, Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 1886 (2014).
S.S. Jung and I. Sohn, Mater. Metall. Trans. B 43B, 1530 (2012).
S.S. Jung and I. Sohn, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1309 (2013).
F.J. Weiss, M.A. Goksel, J.L. Coburn, and G.E. Metius, The Recycling of Steel Plant Waste Oxides Using the PTC (Pellet Technology Corporation) Cold Bond Carbon Bearing Pellet Technology. Disposal, Recycling and Recovery of Electric Furnace Exhaust Dust (Pittsburgh, PA: Iron and Steel Society, 1987), p. 115.
Acknowledgements
This work has been partially supported by the BK21 (Brain Korea 21) PLUS Project in the Division of the Eco-Humantronics Information Materials and Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (2014-11-070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, B., Sohn, I. Review of Innovative Energy Savings Technology for the Electric Arc Furnace. JOM 66, 1581–1594 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1092-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1092-y