Abstract
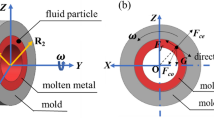
True centrifugal casting is a standard casting technique for the manufacture of hollow, intricate and sound castings without the use of cores. The molten metal or alloy poured into the rotating mold forms a hollow casting as the centrifugal forces lift the liquid along the mold inner surface. When a mold is rotated at low and very high speeds defects are found in the final castings. Obtaining the critical speed for sound castings should not be a matter of guess or based on experience. The defects in the casting are mainly due to the behavior of the molten metal during the teeming and solidification process. Motion of molten metal at various speeds and its effect during casting are addressed in this paper. Eutectic Al-12Si alloy is taken as an experiment fluid and its performance during various rotational speeds is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yogesh Jaluria, J. Fluid Engineering, 123 (June 2001), pp. 173–210.
G. Bergeles and J. Anagnostopoulos, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 30B (1999), pp. 1095–1105.
Nathan Janco, Centrifugal Casting (Schaumburg, IL: Americal Foundrymen’s Society, 1988).
Wu Shi Ping et al., Mater. Sci. and Eng. A, 426 (2006), pp. 240–249.
S.R. Chang, ISIJ International, 41(7) (2001), pp. 738–747.
B.G. Thomas and R.M. McDavid, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 27B (1996), pp. 672–685.
H. Fredriksson and C.M. Raihle, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 25B (1994), pp. 123–133.
I.V. Samarasekara and J.K. Brimacombe, Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 18 (1979), pp. 251–266.
I.V. Samarasekara et al., ISS Transaction, 5 (1984), pp. 71–77.
I.V. Samarasekara et al., Metall. Trans. B, 22B (1991), pp. 861–873.
S.T. Thoroddsen and L. Mahadevan, Experiments in Fluids (New York: Springer-Verlag, 1997), pp. 1–13.
S.K. Wilson, R. Hunt, and B.R. Duffy, Q.J. Mech. Appl. Math., 55(3) (2002), pp. 357–383.
J.M. Lopez et al., J. Fluid Mech., 502 (2004), pp. 99–126.
P.G. Mukunda et al., “Understanding Fluid Flow Behaviour in Cetrifugal Casting” (Presented at AFI/TFI-2007, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan, 14–15 December 2007).
P.G. Mukunda, Shailesh Rao A., A.S. Kiran, and Shrikantha S. Rao, J. Appl. Fluid Mech., 2(1) (2009), pp. 47–51.
Shailesh Rao A., P.G. Mukunda, and Shrikantha S. Rao, Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 48(2) (2009), pp. 157–163.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agari, S.R., Mukunda, P.G., Rao, S.S. et al. Inference of optimal speed for sound centrifugal casting of Al-12Si alloys. JOM 63, 25–29 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-011-0071-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-011-0071-9