Abstract
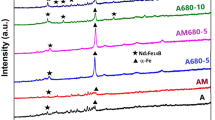
Pulse-thermal processing (PTP) based on high-density plasma arc lamp technology has been utilized to crystallize melt-spun NdFeB-based amorphous ribbons to form magnetic nanocomposites consisting of Nd2Fe14B and α-Fephases. After applying suitable pulses, the NdFeB-based ribbons were developed with hard magnetic properties. The highest coercivity can be obtained for ribbons with a thickness of 40 μm after PTP treatments consisting of a 400 A pulse for 0.25 s for ten times. The correlation between PTP parameters and magnetic properties indicates that PTP is an effective approach to control the structure and properties of nanostructured magnetic materials. Transmission-electorn microscopy analysis revealed that the observed decoupling between the hard and the soft phases is related to large grain size in the samples, which is in turn related to different heating conditions in different regions of samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Coehoom, D.B. de Mooij, and C. DeWaard, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 80 (1989), pp. 101–104.
S.D. Li et al., J. Appl. Phys., 92 (2002), pp. 7514–7518.
R. Skomski and J.M.D. Coey, Phys. Rev. B, 48 (1993), pp. 15812–15816.
R.H. Yu et al., J. Appl. Phys., 85 (1999), pp. 6034–6036.
Z.M. Chen et al., J. Appl. Phys., 89 (4) (2001), pp. 2299–2303.
V. Neu and L. Schultz, J. Appl. Phys., 90 (2001), pp. 1540–1544.
W. Liu et al., J. Appl. Phys., 93 (2003), pp. 8131–8133.
T. Schrefl, J. Fidler, and H. Kronmüller, Phys. Rev. B, 49 (9) (1994), pp. 6100–6110.
M. Yu, J. Appl. Phys., 83 (1998), pp. 6611–6613.
J.P. Liu et al., J. Appl. Phys., 85 (1999), pp. 4812–4814.
J. Zhang et al., J. Appl. Phys., 89 (2001), pp. 5601–5605.
Z.Q. Jin et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 84 (2004), pp. 4382–4384.
Z.Q. Jin et al., Acta Materialia, 52 (2004), pp. 2147–2154.
Y. Shao, M.L. Yan, and D.J. Sellmyer, J. Appl. Phys., 93 (2003), pp. 8152–8154.
K.T. Chu et al., J. Appl. Phys., 38 (2005), pp. 4009–4014.
R.D. Ott et al., JOM, 56 (10) (2004), pp. 45–47.
J.D.K. Rivard et al., Surface Engineering, 20 (2004), pp. 220–228.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Z.Q., Chakka, V.M., Wang, Z.L. et al. The pulse-thermal processing of NdFeB-based nanocomposite magnets. JOM 58, 46–49 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-006-0181-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-006-0181-y