Abstract
Introduction
Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen (DMC) syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive type of skeletal dysplasia. It is characterized by the association of progressive spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia (SEMD), microcephaly, mental retardation (MR), and coarse facies. The radiographic appearance of generalized platyspondyly with double-humped end plates and the lace-like appearance of iliac crests are pathognomonic and distinctive of DMC syndrome. The disorder results from mutations in the DYM gene mapped in the 18q12-12.1 chromosomal region.
Materials and methods
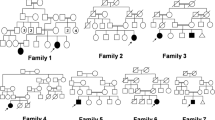
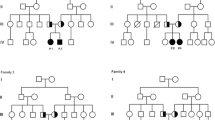
In this report, we studied 15 Egyptian cases with DMC syndrome from nine unrelated families. We aimed to emphasize the characteristic clinical and radiological features in order to differentiate the condition from other SEMDs and mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS). Patients were subjected to detailed history taking, three-generation family pedigree analysis, complete physical examination, anthropometric measurements, quantitative estimation, and two-dimensional electrophoresis of glycosaminoglycans in the urine and measurement of α-l-iduronidase and galactose-6-sulfatase enzyme activities to exclude Hurler and Morquio diseases (MPS type I and MPS type IVA), respectively. Other investigations were carried out whenever indicated. All patients were the offspring of consanguineous apparently normal parents. Positive family history and similarly affected sibs were noted, confirming the autosomal recessive inheritance pattern of the syndrome. Short stature, microcephaly, variable degree of MR, and coarse facies were constant features. The frequency of characteristic orthopedic and radiological findings was reported. Orthopedic surgical intervention was carried out for two patients.
Conclusions
The study concluded that DMC syndrome may be more frequent in Egypt than previously thought, especially due to misdiagnosis. Characteristic facial dysmorphism, body habitus, and pathognomonic radiological signs suggest the diagnosis and differentiate it from other types of SEMDs and MPS for proper genetic counseling and management.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dyggve HV, Melchior JC, Clausen J (1962) Morquio-Ullrich’s disease: an inborn error of metabolism? Arch Dis Child 37:525–534
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM). McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, and the National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Library of Medicine, Bethesda, MD. Home page at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/
Schorr S, Legum C, Ochshorn M, Hirsch M, Moses S, Lasch EE, El-Masri M (1977) The Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome. Am J Roentgenol 128:107–113
Beighton P (1990) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome. J Med Genet 27:512–515
Thauvin-Robinet C, El Ghouzzi V, Chemaitilly W, Dagoneau N, Boute O, Viot G, Mégarbané A, Sefiani A, Munnich A, Le Merrer M, Cormier-Daire V (2002) Homozygosity mapping of a Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome gene to chromosome 18q21.1. J Med Genet 39:714–717
Spranger J, Bierbaum B, Herrmann J (1976) Heterogeneity of Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen dwarfism. Hum Genet 33:279–287
Ehtesham N, Cantor RM, King LM, Reinker K, Powell BR, Shanske A, Unger S, Rimoin DL, Cohn DH (2002) Evidence that Smith–McCort dysplasia and Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen dysplasia are allelic disorders that result from mutations in a gene on chromosome 18q12. Am J Hum Genet 71:947–951
Neumann LM, El Ghouzzi V, Paupe V, Weber HP, Fastnacht E, Leenen A, Lyding S, Klusmann A, Mayatepek E, Pelz J, Cormier-Daire V (2006) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome and Smith–McCort dysplasia: clinical and molecular findings in three families supporting genetic heterogeneity in Smith–McCort dysplasia. Am J Med Genet A 140:421–426
Whitley CB, Draper KA, Dutton CM, Brown PA, Severson SL, France LA (1989) Diagnostic test for mucopolysaccharidosis. II. Rapid quantification of glycosaminoglycan in urine samples collected on a paper matrix. Clin Chem 35:2074–2081
Meikle PJ, Ranieri E, Ravenscroft EM, Hua CT, Brooks DA, Hopwood JJ (1999) Newborn screening for lysosomal storage disorders. JAMA 281:249–254
Kresse H, von Figura K, Klein U, Glössl J, Paschke E, Pohlmann R (1982) Enzymic diagnosis of the genetic mucopolysaccharide storage disorders. Methods Enzymol 83:559–572
Toledo SP, Saldanha PH, Lamego C, Mourão PA, Dietrich CP, Mattar E (1979) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome: genetic studies and report of affected sibs. Am J Med Genet 4:255–261
Galasso C, Fabbri F, Pagnotta G, Palusci A, Sanna ML, Serrao Arnone D, Scirè G (1995) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome: description of 2 further cases. Pediatr Med Chir 17:573–576
Naffah J (1976) The Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 28:607–614
Spranger JW, Maroteaux P, Der Kaloustian VM (1975) The Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome. Radiology 114:415–421
Nakamura K, Kurokawa T, Nagano A, Nakamura S, Taniguchi K, Hamazaki M (1997) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome without mental retardation (Smith–McCort dysplasia): morphological findings in the growth plate of the iliac crest. Am J Med Genet 72:11–17
Carbonell PG, Fernández PD, Vicente-Franqueira JR (2005) MRI findings in Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome, a rare spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:572–576
Horton WA, Scott CI (1982) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome a histochemical study of the growth plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am 64:408–415
Engfeldt B, Bui TH, Eklöf O, Hjerpe A, Reinholt FP, Ritzen EM, Wikström B (1983) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen dysplasia. Morphological and biochemical findings in cartilage growth zones. Acta Paediatr Scand 72:269–274
Beck M, Lücke R, Kresse H (1984) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome: normal degradation of proteodermatan sulfate, proteokeratan sulfate and heparan sulfate. Clin Chim Acta 141:7–15
Roesel RA, Carroll JE, Rizzo WB, van der Zalm T, Hahn DA (1991) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome with increased pipecolic acid in plasma and urine. J Inherit Metab Dis 14:876–880
Burns C, Powell BR, Hsia YE, Reinker K (2003) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome: report of seven patients with the Smith–McCort variant and review of the literature. J Pediatr Orthop 23:88–93
Paupe V, Gilbert T, Le Merrer M, Munnich A, Cormier-Daire V, El Ghouzzi V (2004) Recent advances in Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome. Mol Genet Metab 83:51–59
Cohn DH, Ehtesham N, Krakow D, Unger S, Shanske A, Reinker K, Powell BR, Rimoin DL (2003) Mental retardation and abnormal skeletal development (Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen dysplasia) due to mutations in a novel, evolutionarily conserved gene. Am J Hum Genet 72:419–428
El Ghouzzi V, Dagoneau N, Kinning E, Thauvin-Robinet C, Chemaitilly W, Prost-Squarcioni C, Al-Gazali LI, Verloes A, Le Merrer M, Munnich A, Trembath RC, Cormier-Daire V (2003) Mutations in a novel gene dymeclin (FLJ20071) are responsible for Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 12:357–364
Osipovich AB, Jennings JL, Lin Q, Link AJ, Ruley HE (2008) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome: chondrodysplasia resulting from defects in intracellular vesicle traffic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:16171–16176
Dimitrov A, Paupe V, Gueudry C, Sibarita JB, Raposo G, Vielemeyer O, Gilbert T, Csaba Z, Attie-Bitach T, Cormier-Daire V, Gressens P, Rustin P, Perez F, El Ghouzzi V (2009) The gene responsible for Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome encodes a novel peripheral membrane protein dynamically associated with the Golgi apparatus. Hum Mol Genet 18:440–453
Bonafede RP, Beighton P (1978) The Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome in adult siblings. Clin Genet 14:24–30
Elsayed SM (2005) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome: case report. Egypt J Med Hum Genet 6:67–72
Temtamy SA, Aglan MS, El-Gammal MA, Hosny LA, Ashour AM, El-Badry TH, Awad SA, Fateen E (2007) Genetic heterogeneity in spondylo-epi-metaphyseal dysplasias: a clinical and radiological study. Egypt J Med Hum Genet 8:147–171
Teebi AS (1997) Introduction. In: Teebi AS, Farag TI (eds) Genetic disorders among Arab populations. Oxford University Press, New York, p 11
Rodríguez Rodríguez CM, Pineda Marfa M, Duque R, Cormier-Daire V (2007) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome, diagnostic difficulty due to it similarity to Morquio disease. Neurologia 22:126–129
Coëslier A, Boute-Bénéjean O, Moerman A, Fron D, Manouvrier-Hanu S (2001) Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome: differential diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidosis type IV or Morquio disease. Arch Pediatr 8:838–842
Bieganski T, Dawydzik B, Kozlowski K (1999) Spondylo-epimetaphyseal dysplasia: a new X-linked variant with mental retardation. Eur J Pediat 158:809–814
Geneviève D, Héron D, El Ghouzzi V, Prost-Squarcioni C, Le Merrer M, Jacquette A, Sanlaville D, Pinton F, Villeneuve N, Kalifa G, Munnich A, Cormier-Daire V (2005) Exclusion of the dymeclin and PAPSS2 genes in a novel form of spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia and mental retardation. Eur J Hum Genet 13:541–546
Khosravi M, Weaver DD, Bull MJ, Lachman R, Rimoin DL (1998) Lethal syndrome of skeletal dysplasia and progressive central nervous system degeneration. Am J Med Genet 77:63–71
Kandziora F, Neumann L, Schnake KJ, Khodadadyan-Klostermann C, Rehart S, Haas NP, Mittlmeier T (2002) Atlantoaxial instability in Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 96:112–117
Hosny GA, Fabry G (1998) Treatment of hip subluxation in Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome. J Pediatr Orthop B 7:32–34
Eguchi M, Kadota Y, Yoshida Y, Masuda M, Masuyama T, Kammura Y (2001) Anesthetic management of a patient with Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome. Masui 50:1116–1117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Aglan, M.S., Temtamy, S.A., Fateen, E. et al. Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome: clinical, genetic, and radiological study of 15 Egyptian patients from nine unrelated families. J Child Orthop 3, 451–458 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-009-0211-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-009-0211-8