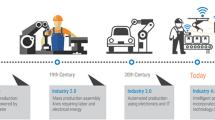
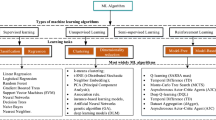
Abstract
In recent years, computer-based graphic knowledge has evolved and become the most common trend. The computer-aided design would be used by the designers to generate design concepts and draft documents (CAD). Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) is the use of computer-based software tools to assist engineers in the production of goods. The designers would use computer-aided design (CAD) to create a product. The concept would then be converted into hardware using computer-aided manufacturing on the same computer (CAM). These two technologies are merged into unified CAD/CAM systems, in which a specification is created in a CAD system and the production process is managed in a single system from start to finish in CAM. CAD/CAM systems are often used in computer-aided design, which is the use of a computer to create, modify, and analyze a design. This article aims to provide an overview of the computer-aided design and manufacturing processes in various sectors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmidt DC, Stal M, Rohnert H, Buschmann F (2013) Pattern-oriented software architecture, patterns for concurrent and networked objects, vol 2. Wiley
Shim JP, Warkentin M, Courtney JF, Power DJ, Sharda R, Carlsson C (2002) Past, present, and future of decision support technology. Decis Supp Syst 33(2):111–126
Sarcar MMM, Rao KM, Narayan KL (2008) Computer-aided design and manufacturing. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.
Kalay YE (2004) Architecture’s new media: Principles, theories, and methods of computer-aided design. MIT press
Kalogirou SA (2003) Artificial intelligence for the modeling and control of combustion processes: a review. Prog Energy Combust Sci 29(6):515–566
Allen E, Iano J (2019) Fundamentals of building construction: materials and methods. Wiley
Kibert CJ (2016) Sustainable construction: green building design and delivery. Wiley
Lumsdaine E, Shelnutt JW, Lumsdaine M (1999) Integrating creative problem solving and engineering design. Age 4:1
Naboni R, Paoletti I (2015) Advanced customization in architectural design and construction. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Ertas A (2018) Transdisciplinary engineering design process. Wiley
Agoki GS, Ng BC, Johnson RL (2007) Development of communication skills and teamwork amongst undergraduate engineering students. In: 2007 37th annual frontiers in education conference-global engineering: knowledge without borders, opportunities without passports. IEEE, pp. F3B-13
Malamas EN, Petrakis EG, Zervakis M, Petit L, Legat JD (2003) A survey on industrial vision systems, applications, and tools. Image Vis Comput 21(2):171–188
Horváth I, Vroom RW (2015) Ubiquitous computer-aided design: A broken promise or a Sleeping Beauty? Comput Aided Des 59:161–175
Bi Z, Wang X (2020) Computer aided design and manufacturing. Wiley
Oh JH (2018) Recent advances in the reconstruction of cranio-maxillofacial defects using computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 40(1):1–7
Yu JC, Krizan S, Ishii K (1993) Computer-aided design for manufacturing process selection. J Intell Manuf 4(3):199–208
Pedro Company-Calleja Departamento de Tecnología, Universitat Jaume I Campus Penyeta Roja - E12071 Castellón, Spain
Quintana V, Rivest L, Pellerin R, Venne F, Kheddouci F (2010) Will Model-based Definition replace engineering drawings throughout the product lifecycle? A global perspective from aerospace industry. Comput Ind 61(5):497–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2010.01.005
Wang L, Shen W, Xie H, Neelamkavil J, Pardasani A (2002) Collaborative conceptual design—state of the art and future trends. Comput Aided Des 34(13):981–996
Gujarathi GP, Ma YS (2011) Parametric CAD/CAE integration using a common data model. J Manuf Syst 30(3):118–132
Hirz M, Dietrich W, Gfrerrer A, Lang J (2013) Integrated computer-aided design in automotive development. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg
Culler DE, Burd W (2007) A framework for extending computer aided process planning to include business activities and computer aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) data retrieval. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 23(3):339–350
Chang KH (2014) Product design modeling using CAD/CAE: The computer aided engineering design series. Academic Press
Elanchezhian C, Sundar GS (2007) Computer aided manufacturing. Firewall Media
Spur G, Wentz W (1972) A system for direct numerical control of machine tool. In: Proceedings of the twelfth international machine tool design and research conference. Palgrave: London, pp. 421–428
Liu T, Yu T, Wang W (2005) INC: a new type of computer numerical control. In: Proceedings of the ninth international conference on computer supported cooperative work in design, IEEE 2:787–792
Kiritsis D (1995) A review of knowledge-based expert systems for process planning. Methods and problems. The Int J Adv Manuf Technol 10(4):240–262
Gupta SK, Regli WC, Das D, Nau DS (1997) Automated manufacturability analysis: a survey. Res Eng Des 9(3):168–190
Groover M, Zimmers EWJR (1983) CAD/CAM: computer-aided design and manufacturing. Pearson Education
Yin L, Song XF, Song YL, Huang T, Li J (2006) An overview of in vitro abrasive finishing & CAD/CAM of bioceramics in restorative dentistry. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 46(9):1013–1026
Suh NP (1990) The principles of design. Oxford university press: New York, Oxford
Kohler E, Handley M, Floyd S (2006) Designing DCCP: congestion control without reliability. ACM SIGCOMM Comput Commun Rev 36(4):27–38
Steward DV (1981) The design structure system: a method for managing the design of complex systems. IEEE Trans Eng Manage 3:71–74
Shaw M, DeLine R, Klein DV, Ross TL, Young DM, Zelesnik G (1995) Abstractions for software architecture and tools to support them. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 21(4):314–335
Jacob RJ, Deligiannidis L, Morrison S (1999) A software model and specification language for non-WIMP user interfaces. ACM Trans Comput Human Interact (TOCHI) 6(1):1–46
Encarnação JL, Lindner R, Schlechtendahl EG (1990) CAD application examples. Computer Aided Design. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 375–397
Lwin KK, Murayama Y (2011) Web-based GIS system for real-time field data collection using a personal mobile phone. J Geogr Inf Syst 3(4):382
Saleh B, Sadoun B (2006) Design and implementation of a GIS system for planning. Int J Digit Libr 6(2):210–218
Langford M, Unwin DJ (1994) Generating and mapping population density surfaces within a geographical information system. Cartogr J 31(1):21–26
Golledge RG, Klatzky RL, Loomis JM, Speigle J, Tietz J (1998) A geographical information system for a GPS based personal guidance system. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 12(7):727–749
Burrough PA (1992) Development of intelligent geographical information systems. Int J Geogr Inf Syst 6(1):1–11
Ray N (2005) PATHMATRIX: a geographical information system tool to compute effective distances among samples. Mol Ecol Notes 5(1):177–180
Babiker IS, Mohamed MA, Terao H, Kato K, Ohta K (2004) Assessment of groundwater contamination by nitrate leaching from intensive vegetable cultivation using geographical information system. Environ Int 29(8):1009–1017
Myers S, Marquis DG (1969) Successful industrial innovations: a study of factors underlying innovation in selected firms. National Science Foundation
Eb R, Al F (1988) Strategies for improving research utilization. Technol Rev 3(4):554
Azar FD (2014) Use of CAAD tools on conceptual stage of design (Doctoral dissertation, Eastern Mediterranean University (EMU)-Doğu Akdeniz Üniversitesi (DAÜ))
Belhadj TA.(1989) Computer aided architectural evaluation and design: a cost modelling experiment (Doctoral dissertation, University of Sheffield)
Mitchell WJ (1975) The theoretical foundation of computer-aided architectural design. Environ Plann B Plann Des 2(2):127–150
Guney D (2015) The importance of computer-aided courses in architectural education. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 176:757–765
Jeong SK, Ban YU (2011) Computational algorithms to evaluate design solutions using Space Syntax. Comput Aided Des 43(6):664–676
Radford AD, Gero JS (1980) On optimization in computer aided architectural design. Build Environ 15(2):73–80
Das S, Fan A, Chen KN, Tan CS, Checka N, Reif R (2004).Technology, performance, and computer-aided design of three-dimensional integrated circuits. In: Proceedings of the 2004 international symposium on Physical design, pp. 108–115
Duggal V (2000) Cadd Primer: a general guide to computer aided design and drafting-cadd, CAD. Mailmax Publishing
Klein KJ, Hall RJ, Laliberte M (1990) Training and the organizational consequences of technological change: a case study of computer-aided design and drafting. End-user training, 7
Ault HK (2009) 3-D geometric modeling for the 21st century. Eng Des Graph J 63(1999):33–42
Staneva NN (2008) Approaches for generating 3D solid models in AutoCAD and solid works. J Eng 3:28–31
Koo B, Fischer M (2000) Feasibility study of 4D CAD in commercial construction. J Constr Eng Manag 126(4):251–260
Heesom D, Mahdjoubi L (2004) Trends of 4D CAD applications for construction planning. Constr Manag Econ 22(2):171–182
Xu X, Wang L, Newman ST (2011) Computer-aided process planning–a critical review of recent developments and future trends. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 24(1):1–31
Ford S, Minshall T (2019) Invited review article: where and how 3D printing is used in teaching and education. Addit Manuf 25:131–150
Field DA (2004) Education and training for CAD in the auto industry. Comput Aided Des 36(14):1431–1437
Dubovska R, Jambor J, Majerik J (2014) Implementation of CAD/CAM system CATIA V5 in simulation of CNC machining process. Proc Eng 69:638–645
Meinders T, Burchitz IA, Bonté MH, Lingbeek RA (2008) Numerical product design: springback prediction, compensation and optimization. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48(5):499–514
Xu XY, Wang YY (2002) Multi-model technology and its application in the integration of CAD/CAM/CAE. J Mater Process Technol 129(1–3):563–567
Coley DA, Schukat S (2002) Low-energy design: combining computer-based optimisation and human judgement. Build Environ 37(12):1241–1247
Szykman S, Racz JW, Sriram RD (1999) The representation of function in computer-based design. In: ASME design engineering technical conferences, 11th international conference on design theory and methodology
Brown P (2009) CAD: Do computers aid the design process after all? Intersect The Stanford J Sci Technol Soc 2(1):52–66
Liker JK, Fleischer M, Arnsdorf D (1992) Fulfilling the promises of CAD. MIT Sloan Manag Rev 33(3):74
Chang KH (2014) Design theory and methods using CAD/CAE: the computer aided engineering design series. Academic Press
Ullman DG, Wood S, Craig D (1990) The importance of drawing in the mechanical design process. Comput Graph 14(2):263–274
Guney D, Aydin E (2012) The nonlinear effect of infill walls stiffness to prevent soft story collapse of RC structures. The Open Constr Build Technol J, 6(1)
Moseng B, Nes BH (1984) Integration of CAD/CAM as seen from the production planners point of view. Comput Ind 5(4):341–350
Moseng B, Hygen J (1986) Interactive production planning CAM. Advances in Computer Graphics I. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 381–418
Gerwin D (1988) A theory of innovation processes for computer-aided manufacturing technology. IEEE Trans Eng Manage 35(2):90–100
He Y, Liu F, Wu T, Zhong FP, Peng B (2012) Analysis and estimation of energy consumption for numerical control machining. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 226(2):255–266
Shah J, Sreevalsan P, Mathew A (1991) Survey of CAD/feature-based process planning and NC programming techniques. Comput Aided Eng J 8(1):25–33
Yoshikawa H, Uehara K (1985) Design theory for CAD/CAM integration. CIRP Ann 34(1):173–178
Hoque ASM, Halder PK, Parvez MS, Szecsi T (2013) Integrated manufacturing features and Design-for-manufacture guidelines for reducing product cost under CAD/CAM environment. Comput Ind Eng 66(4):988–1003
Henderson MR, Anderson DC (1984) Computer recognition and extraction of form features: a CAD/CAM link. Comput Ind 5(4):329–339
Wang X, Bi Z (2019) New CAD/CAM course framework in digital manufacturing. Comput Appl Eng Educ 27(1):128–144
Harrington J Jr (2020) Understanding the manufacturing process: key to successful CAD/CAM implementation. Crc Press
Alghazzawi TF (2016) Advancements in CAD/CAM technology: options for practical implementation. J Prosthodont Res 60(2):72–84
Wang HF, Zhang YL (2002) CAD/CAM integrated system in collaborative development environment. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 18(2):135–145
Shah JJ, Mäntylä M (1995) Parametric and feature-based CAD/CAM: concepts, techniques, and applications. John Wiley & Sons
Beatty CA, Gordon JR (1988) Barriers to the implementation of CAD/CAM systems. MIT Sloan Manag Rev 29(4):25
Yixian D, Qihua T, Xuan D, Kongde H (2014) CAD/CAM courses integration of theoretical teaching and practical training. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 116:4297–4300
Rao PN (2004) CAD/CAM: principles and applications. Tata McGraw-Hill Education
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by King Mongkut's University of Technology North Bangkok with Contract no. KMUTNB-65-KNOW-06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shivegowda, M.D., Boonyasopon, P., Rangappa, S.M. et al. A Review on Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing Processes in Design and Architecture. Arch Computat Methods Eng 29, 3973–3980 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-022-09723-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-022-09723-w