Abstract
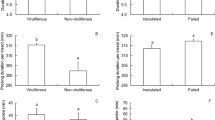
Laodelphax striatellus is an important vector of rice stripe virus (RSV). In this study, electrical penetration graph technology was applied to investigate the feeding behavior of L. striatellus associated with virus transmission. The effects of a disease-resistant variety Yandao No. 8 on the feeding behavior and subsequent virus transmission efficiency of L. striatellus were examined. The results indicate that in addition to the phloem sap ingestion phase, which was previously reported as a behavior associated with virus acquisition, phases of salivation and stylet movement were relevant to RSV acquisition by naïve L. striatellus. The duration of the non-penetration phase of naïve L. striatellus on healthy Yandao No. 8 plants was significantly longer, and the duration of sap ingestion was significantly shorter compared to those on a susceptible control. RSV acquisition rate of naïve L. striatellus on Yandao No. 8 was only 28 % of that on the susceptible control. Virus inoculation by viruliferous L. striatellus could occur during the salivation, stylet movement, and phloem sap ingestion phases. Yandao No. 8 significantly prolonged the duration of the non-penetration phase and significantly shortened the duration of sap ingestion in viruliferous L. striatellus. Virus inoculation rate of viruliferous L. striatellus feeding on healthy Yandao No. 8 was significantly lower, decreasing by 27 %, than that of the control. The mechanisms of varietal effects on the feeding behavior and virus transmission of L. striatellus are discussed. The varietal effect on virus transmission should have significance for viral disease control.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng JH, Li S, Hong J, Ji YH, Zhou YJ (2013) Investigation on subcellular localization of rice stripe virus in its vector small brown planthopper by electron microscopy. Virus J 10:310. http://www.virologyj.com/content/10/1/310
Fraser RSS (1992) The genetics of plant-virus interactions: implications for plant breeding. Euphytica 63:175–185
Hibino H (1996) Biology and epidemiology of rice viruses. Annu Rev Phytopathol 34:249–274
Ise K, Ishikawa K, Li CY, Ye CR (2002) Inheritance of resistance to rice stripe virus in rice line ‘BL 1’. Euphytica 127:185–191
Jahan SMH, Lee GS, Lee S, Lee KY (2014) Acquisition of Tomato yellow leaf curl virus enhances attraction of Bemisia tabaci to green light emitting diodes. J Asia–Pacific Entomol 17:79–82
Ji CQ, Zhong H, Zhong PY, Liang GH (2005) Detecting rice stripe virus (RSV) in infected rice plant by RT-PCR. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Agric Sci) 23(2):188–191
Jiang YX, De Blas C, Barrios L, Fereres A (2000) Correlation between whitefly (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) feeding behavior and transmission of tomato yellow leaf curl virus. Ann Entomol Soc Am 93:573–579
Jimenez-Martinez ES, Bosque-Perez NA, Berger PH, Zemetra R, Ding HJ, Eigenbrode SD (2004) Volatile cues influence the response of Rhopalosiphum padi (Homoptera: Aphididae) to barley yellow dwarf virus-infected transgenic and untransformed wheat. Environ Entomol 33:1207–1216
Jing P, Bai SF, Liu F (2013) Preliminary research on electrical penetration graph (EPG) waveforms in relation to feeding behavior of Laodelphax striatellus. Chin J Appl Entomol 50(3):758–763
Johnson DD, Walker GP, Creamer R (2002) Stylet penetration behavior resulting in inoculation of a semipersistently transmitted closterovirus by the whitefly Bemisia argentifolii. Entomol Exp Appl 102:115–123
Khan ZR, Saxena RC (1984) Electronically recorded waveforms associated with the feeding behavior of Sogatella furcifera (Homoptera: Delphacidae) on susceptible and resistant rice varieties. J Econ Entomol 77:1479–1482
Khan ZR, Saxena RC (1986) Effect of steam distillate extracts of resistant and susceptible rice cultivars on behavior of Sogatella furcifera (Homoptera: Delphacidae). J Econ Entomo 79:928–935
Kimmins FM (1989) Electrical penetration graphs from Nilaparvata lugens on resistant and susceptible rice varieties. Entoml Exp Appl 50:69–79
Liang D, Qu Z, Ma X, Hull R (2005) Detection and localization of rice stripe virus gene products in vivo. Virus Genes 31:211–221
Limburg DD, Mauk PA, Godfrey LD (1997) Characteristics of Beet yellows closterovirus transmission to sugar beets by Aphis fabae. Phytopathology 87:766–771
Lin QY, Xie LH, Zhou ZJ, Xie LY, Wu ZJ (1990) Studies on rice stripe. I. Distribution and losses caused by the disease. J Fujian Agric Univ 19:421–425
Lin QY, Xie LH, Xie LY, Zhou ZJ, Song XG (1991) Study on rice stripe II: symptoms and transmission of the disease. Jof Fujian Agric Coll 20(1):24–28
Liu F, Song Y, Bao SW, Lu HY, Zhu SD, LiangG H (2007a) Resistance to small brown planthopper and its mechanism in rice varieties. Acta Phytophy Sin 34(5):449–454
Liu HJ, Cheng ZB, Wang Y, Wei BQ, Ren CM, Zhou YJ, Fan YJ (2007b) Preliminary study on transmission of rice stripe virus by small brown plangthopper. Jiangsu J Agr Sci 23(5):492–494
Lu BG, Fang ZW, Liu HQ, Fan JW, Ren LK, Wang XH, Pan QM (2006) Surveys of resistance of some japonica rice varieties to rice stripe virus. Chin Rice 26(1):22–24
McLean DL, Kinsey MG (1964) A technique for electronically recording aphid feeding and salivation. Nature 202:1358–1359
Pirone TP, Perry KL (2002) Aphids: non-persistent transmission. Adv Bot Res 36:1–19
Powell G (1991) Cell membrane punctures during epidermal penetrations by aphids: consequences for the transmission of two potyvirus. Ann Appl Biol 119:313–321
Prado E, Tjallingii WF (1994) Aphid activities during sieve element punctures. Entomol Exp Appl 72:157–165
Ramirez BC, Haenni AL (1994) Molecular biology of tenuiviruses: a remarkable group of plant viruses. J Gen Virol 75:467–475
Seo BY, Kwon YH, Jung JK, Kim GH (2009) Electrical penetration graphic waveforms in relation to the actual positions of the stylet tips of Nilaparvata lugens in rice tissue. J Asia–Pacific Entomol 12:89–95
Sogawa K (1982) The rice planthopper: feeding physiological and host plant interactions. Ann Rev Entomo 27:49–73
Sun DZ, Jiang L, Zhang YX, Cheng XN, Wang CM, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2006) Resistance to rice stripe in eight rice varieties. Chin J Rice Sci 20(2):219–222
Tjallingii WF (1978) Electronic recording of penetration behaviour by aphids. Entomol Exp Appl 24:721–730
Tjallingii WF (2006) Salivary secretions by aphids interacting with proteins of phloem wound responses. J Exp Bot 57:739–745
Toriyama S (1986) Rice stripe virus: prototype of a new group of viruses that replicate in plants and insects. Microbiol Sci 3(11):347–351
Toriyama S, Tomaru K (1995) Genus tenuivirus. In: Murphy FA, Fauquet CM, Bishop DHL, Ghabrial SA, Jarvis AW, Martelli GP, Mayo MA, Summers MD (eds) Virus taxonomy classification and nomenclature of viruses, sixth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. Springer, Wien
Walker G (2000) A beginners guide to electronic monitoring of homopteran feeding behavior. In: Walker GP, Backus EA (eds) Principles and applications of electronic monitoring and other techniques in the study of Homopteran feeding behavior. Thomas Say Publications, The Entomological Society of America, USA, pp 14–40
Yang JG, Fang ZX, Zhang MQ, Xu F, Wang WT, Xie LY, Lin QY, Wu ZJ, Xie LH (2008) Detection on different resistance of two rice varieties against rice stripe virus in real-time RT-PCR. J South China Agric Univ 29(3):25–28
Yao LS, Sun MF, Yan GH, Tang HS (2007) Resistance to rice stripe virus and popularization and application effect in Yandao No. 8. Jiangsu Agric Sci 27(4):40–42
Zhang PF, Chen JQ, Zhang X, Wang B, Jiang QF (2001) The feeding behavior and the acquisition of CMV by the cotton aphid Aphis gossypii. Acta Entomol Sin 44(4):395–401
Zhang SX, Li L, Wang XF, Zhou GH (2007) Transmission of rice stripe virus acquired form frozen infected leaves by the small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus Fallen). J Virol Methods 146:359–362
Zhou YJ, Liu HJ, Wang GZ, Huang X, Cheng ZB, Chen ZX, Zhou XP (2004) Immuno-detection of rice stripe virus carried by small brown planthopper. Jiangsu Agric Sci 1:50–51
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30971914, 31171842) and Jiangsu Agricultural Scientific Self-innovation Fund (No. cx [14]2030). We thank the two anonymous referees and the editor for helpful comments and revision suggestions on an early version of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Joe Louis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, P., Huang, L., Bai, S. et al. Effects of rice resistance on the feeding behavior and subsequent virus transmission efficiency of Laodelphax striatellus . Arthropod-Plant Interactions 9, 97–105 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-014-9354-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-014-9354-8