Abstract
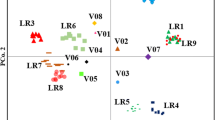
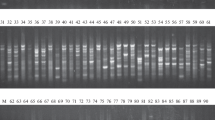
Lentil is an important annual food legume crop, nitrogen fixer and provides a substantial amount of protein, carbohydrate, minerals, and vitamin content. The use of molecular markers to assess genetic diversity is crucial for crop improvement, efficient management, and conservation of plant genetic resources. The current study aimed to determine the genetic diversity among lentil genotypes using sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers. Therefore, we evaluated a collection of 36 lentil genotypes, including 20 from Yemen, Saudi Arabia (7), Egypt (4), and Bangladesh (3), and (2) genotypes from the International Center for Research in Dry Area (ICARDA) using 21 SRAP primer combinations. The amplified fragments showed a high level of useful polymorphic amplified fragments (775 out of 782) indicating a higher degree of variation. The polymorphic information content (PIC) ranged from 0.31 to 0.39 with an average of 0.33 for each primer. The UPGMA trees, based on Jaccard similarity index matrices, separated the genotypes into four main clusters according to their geographical origin. The population structure supported the major groups and attested to their great degree of differentiation. The highest lentil population was found at K = 3, K = 5, and K = 7 levels, showing purity and admixture ancestry among the lentil population. This study highlighted the wide genetic diversity among the studied lentil genotypes and demonstrated the effectiveness of the SRAP technique in determining the genetic variability of lentil. Furthermore, it could be used to establish the genetic peculiarity of ecotypes when applying for the obtainment of origin and agro-morphological characteristics.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not available.
References
Abo-elwafa A, Murai K, Shimada T (1995) Intra- and inter-specific variations in Lens revealed by RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 90(3):335–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00221974
Abuzayed M, El-Dabba N, Frary A, Doganlar S (2017) GDdom: an online tool for calculation of dominant marker gene diversity. Biochem Genet 55(2):155–157
Ahmad M, McNeil DL (1996) Comparison of crossability, RAPD, SDS-PAGE and morphological markers for revealing genetic relationships within and among Lens species. Theor Appl Genet 93(5):788–793
Alghamdi SS, Migdadi HM, Ammar MH, Paull JG, Siddique K (2012) Faba bean genomics: current status and future prospects. Euphytica 186:609–624
Alghamdi SS, Khan AM, Ammar MH, El-Harty EH, Migdadi HM, El-Khalik SMA, Al-Shameri AM, Javed MM, Al-Faifi SA (2013) Phenological, nutritional and molecular diversity assessment among 35 introduced lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) genotypes grown in Saudi Arabia. Int J Mol Sci 15(1):277–295
Alvarez M, Garcia P, Perez M, Perez de la Vega M (1997) RAPD polymorphism in Spanish lentil landraces and cultivars [random amplified polymorphic DNA-Lens culinaris]. J Genet Breed (Italy) 2(4):538–544
Aneja B, Yadav NR, Yadav RC, Kumar R (2013) Sequence related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) analysis for genetic diversity and micronutrient content among gene pools in mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]. Physiol Mol Biol Plant 19:399–407
Babayeva S, Akparov Z, Abbasov M, Mammadov A, Zaifizadeh M, Street K (2009) Diversity analysis of central Asia and Caucasian lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) germplasm using SSR fingerprinting. Genet Res Crop Evolut 56(3):293–298
Bermejo C, Gatti I, Caballero N, Cravero V, Martin E, Cointry E (2014) Study of diversity in a set of lentil RILs using morphological and molecular markers. Aust J Crop Sci 8(5):689
Cubero J, Perez De La Vega M, Fratini R (2009) Origin phylogeny domestication and spread. The lentil: botany, production and uses. CABI, Wallingford, pp 13–33
Datta S, Prasoonpal G, Mayank K, Kumar S (2016) Genetic diversity analysis of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik) cultivars using inter imple sequence epeats arkers. Mol Plant Breed. https://doi.org/10.5376/mpb.2016.07.0023
de la Vega MP, Vinagre MYD (2004) Assessment of genetic variation and species relationships in a collection of “Lens” using RAPD and ISSR. Span J Agric Res 4:538–544
Durán Y, de la Vega MP (2004) Assessment of genetic variation and species relationships in a collection of Lens using RAPD and ISSR [Inter-simple sequence repeats]. Span J Agric Res 2(4):538–544
El-Nahas A, El-Shazly H, Ahmed SM, Omran A (2011) Molecular and biochemical markers in some lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) genotypes. Annal Agricu Sci 56(2):105–112
Erskine W, Muehlbauer F (1991) Allozyme and morphological variability, outcrossing rate and core collection formation in lentil germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 83(1):119–125
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14(8):2611–2620
Fikiru E, Tesfaye K, Bekele E (2007) Genetic diversity and population structure of Ethiopian lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus) landraces as revealed by ISSR marker. Afr J Biotechnol 6(12):1460–1468
Ford R, Pang E, Taylor P (1997) Diversity analysis and species identification in Lens using PCR generated markers. Euphytica 96(2):247–255
Gupta M, Verma B, Kumar N, Chahota RK, Rathour R, Sharma SK, Bhatia S, Sharma TR (2012) Construction of intersubspecific molecular genetic map of lentil based on ISSR, RAPD and SSR markers. J Genet 91(3):279–287
Hammer H, Harper D, Ryan P (2001) Paleontological statistics software: package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 1 (4): 4-9.
Hamwieh A, Udupa SM, Sarker A, Jung C, Baum M (2009) Development of new microsatellite markers and their application in the analysis of genetic diversity in lentils. Breed Sci 59(1):77–86
Hoelzel AR (1998) Molecular genetic analysis of populations: a practical approach, vol 187. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Idrissi O, Udupa SM, Houasli C, De Keyser E, Van Damme P, De Riek J (2015) Genetic diversity analysis of Moroccan lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) landraces using simple sequence repeat and amplified fragment length polymorphisms reveals functional adaptation towards agro-environmental origins. Plant Breed 134(3):322–332
Idrissi O, Piergiovanni AR, Toklu F, Houasli C, Udupa SM, De Keyser E, Van Damme P, De Riek J (2018) Molecular variance and population structure of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) landraces from Mediterranean countries as revealed by simple sequence repeat DNA markers: implications for conservation and use. Plant Genet Res 16(3):249–259
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles researches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaud Sci Nat 44:223–270
Jin L, Jian-Ping G, Dong-Xu X, Zhang X-Y, Jing G, Xu-Xiao Z (2008) Genetic diversity and population structure in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) germplasm detected by SSR markers. Acta Agron Sin 34(11):1901–1909
Kahraman BTSOA, Muehlbauer F (2010) Linkage mapping of lentil (Lens culinaris L.) genome using recombinant inbred lines revealed by AFLP, ISSR, RAPD and some morphologic markers. J Agric Biotechnol Sustain Dev 2(1):1–6
Kaur S, Cogan NO, Pembleton LW, Shinozuka M, Savin KW, Materne M, Forster JW (2011) Transcriptome sequencing of lentil based on second-generation technology permits large-scale unigene assembly and SSR marker discovery. BMC Genom 12(1):1
Khan MA, Ammar MH, Migdadi HM, El-Harty EH, Alfaifi SA, Farooq M, Alghamdi SS (2016) Field performance and genetic diversity of chickpea genotypes. Int J Agric Biol 18(4):683–688
Khazaei H, Caron CT, Fedoruk M, Diapari M, Vandenberg A, Coyne CJ, McGee R, Bett KE (2016) Genetic diversity of cultivated lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) and its relation to the world’s agro-ecological zones. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01093
Kole PR, Sharma MK, Kumar S, Kumar R (2015) Genetic diversity assessment in Indian cultivated pea (Pisum sativum L.) varieties using RAPD markers. J Appl Nat Sci 7(1):316–323
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103(2–3):455–461
Mbasani-Mansi J, Ennami M, Briache FZ, Gaboun F, Benbrahim N, Triqui ZEA, Mentag R (2019) Characterization of genetic diversity and population structure of Moroccan lentil cultivars and landraces using molecular markers. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 25(4):965–974
Mekonnen F, Mekbib F, Kumar S, Ahmed S, Sharma T (2016) Molecular diversity and population structure of the Ethiopian lentil (Lens Culinaris Medikus) genotype assessment using SSR markers. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 19(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-015-0046-4
Mohammed NA, Refay YA, Migdadi HM, Al-Somain BH, Muharram AA, Al-Selwey WA, Abdela KA, Alghamdi SS, Farooq M (2019) Agro-morphological characterization of lentil genotypes in dry environments. Int J Agric Biol 22(6):1320–1330
Pavan S, Bardaro N, Fanelli V, Marcotrigiano AR, Mangini G, Taranto F, Catalano D, Montemurro C, De Giovanni C, Lotti C (2019) Genotyping by sequencing of cultivated lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) highlights population structure in the Mediterranean gene pool associated with geographic patterns and phenotypic variables. Front Genet 10:872
Pinkas R, Zamir D, Ladizinsky G (1985) Allozyme divergence and evolution in the genusLens. Plant Syst Evol 151(1):131–140
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959
Rana MK, Kumari R, Singh S, Bhat KV (2007) Genetic analysis of Indian Lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus) cultivars and landraces using RAPD and STMS markers. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 16(1):53–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03321929
Roldan-Ruiz I, Calsyn E, Gilliland T, Coll R, Van Eijk M, De Loose M (2000) Estimating genetic conformity between related ryegrass (Lolium) varieties. 2. AFLP characterization. Mol Breed 6:593–602
Ruisi P, Longo M, Martinelli F, Di Miceli G, Frenda A, Saia S, Carimi F, Giambalvo D, Amato G (2015) morpho-agronomic and genetic diversity among twelve sicilian agro-ecotypes of lentil (Lens culinaris). JAPS J Anim Plant Sci 25(3):716–728
Sarker A, Erskine W (2006) Recent progress in the ancient lentil. J Agric Sci 144(1):19–29
Sharma SK, Dawson IK, Waugh R (1995) Relationships among cultivated and wild lentils revealed by RAPD analysis. Theor Appl Genet 91(4):647–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00223292
Sharma S, Knox M, Ellis TN (1996) AFLP analysis of the diversity and phylogeny of Lens and its comparison with RAPD analysis. Theor Appl Genet 93(5–6):751–758
Sonnante G, Pignone D (2001) Assessment of genetic variation in a collection of lentil using molecular tools. Euphytica 120(2):301–307
Sonnante G, Pignone D (2007) The major Italian landraces of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.): their molecular diversity and possible origin. Genet Resourc Crop Evolut 54(5):1023–1031
Tewari K, Dikshit H, Kumari J, Jain N, Singh D, Singh A (2015) Estimation of genetic relatedness among cultivated and wild lens based on morphological and molecular markers. Plant Gene Trait 6:1–8
Toklu F, Karaköy T, Haklı E, Bicer T, Brandolini A, Kilian B, Özkan H (2009) Genetic variation among lentil (Lens culinaris Medik) landraces from Southeast Turkey. Plant Breed 128(2):178–186
Zaccardelli M, Lupo F, Piergiovanni AR, Laghetti G, Sonnante G, Daminati MG, Sparvoli F, Lioi L (2012) Characterization of Italian lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) germplasm by agronomic traits, biochemical and molecular markers. Genet Resourc Crop Evolut 59(5):727–738
Zagorcheva T, Stanev S, Rusanov K, Atanassov I (2020) SRAP markers for genetic diversity assessment of lavender (Lavandula angustifolia mill.) varieties and breeding lines. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 34(1):303–308
Zohary D, Hopf M (2000) Domestication of plants in the Old World: the origin and spread of cultivated plants in West Asia, Europe and the Nile Valley, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Deanship of Scientific Research, College of Food and Agricultural Sciences, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia for support and cooperation during the completion of the present research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammed, N.A., Afzal, M., Al-Faifi, S.A. et al. Effectiveness of sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers to assess the geographical origin and genetic diversity of collected lentil genotypes. Plant Biotechnol Rep 17, 519–530 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-023-00842-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-023-00842-9