Abstract
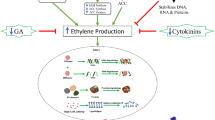
We investigated whether ethylene is involved in the stem-bending mechanism of the two different gerberas [long-lived cultivar ‘Mary Queen’ and short-lived cultivar ‘Harmony’] by pretreating the stems with an ethylene-releasing compound (Ethephon), an ethylene-action inhibitor [silver thiosulfate (STS)], or Ethephon in combination with STS (Ethephon + STS), using distilled water as the control. In the cv. ‘Mary Queen,’ the control stems did not show stem bending, while the treatment groups showed bending at 6 and 9 days after treatment (DAT). In the cv. ‘Harmony,’ the bending rate observed in the Ethephon-treated stems was lower than the other treatments at 9 DAT. However, a lower bending rate in the Ethephon group relative to the other treatments is unlikely to be associated with ethylene action, because the bending rate observed in the Ethephon + STS group was significantly higher than the STS group. In addition, the bending rates of both cultivars were not associated with lignin contents or the expression of lignin biosynthesis genes in the stems. As it is complicated to conclude the role of Ethephon in stem bending of the gerberas, these results suggest that the use of Ethephon to delay stem bending in cut gerberas is not warranted.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown GE (1990) Changes in phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, soluble phenolics and lignin in injured orange exocarp. Proc Fla State Hort Soc 103:234–237
Cheng G, Wang L, He S, Liu J, Huang H (2020) Involvement of pectin and hemicellulose depolymerization in cut gerbera flower stem bending during vase life. Postharv Biol Technol 167:111231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111231
Cinotti A, Ferrante A, Tognoni F, Serra G (2005) Piegatura dello stelo nei fiori. Gartenbauwissenschaft 47:77–81
De Jong J, Garretsen F (1985) Genetic analysis of cut flower longevity in gerbera. Euphytica 34:779–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035416
Dubuc-Lebreux MA, Vieth J (1985) Histologie du pédoncule inflorientiel de Gerbera jamesonii. Acta Bot Neerl 34:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.1985.tb01877.x
Ezhilmathi K, Singh VP, Arora A, Sairam RK (2007) Effect of 5-sulfosalicylic acid on antioxidant activity in relation to vase life of Gladiolus cut flowers. Plant Growth Regul 51:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-006-9142-2
Ferrante A, Alberici A, Antonacci S, Serra G (2007) Effect of promoter and inhibitors of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase enzyme on stem bending of cut gerbera flowers. Acta Hortic 775:471–476. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2007.755.64
Ferrante A, Serra G (2009) Lignin content and stem bending incidence on cut gerbera flowers. Acta Hortic 847:377–384. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2009.847.52
Ge Y, Lai Q, Luo P, Liu X, Chen W (2019) Transcriptome profiling of Gerbera hybrida reveals that stem bending is caused by water stress and regulation of abscisic acid. BMC Genomics 20:600. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5961-1
Gerabeygi K, Roein Z, Rezvanipour S (2021) Control of stem bending in cut gerbera flowers through application of dithiothreitol and thioglycolic acid as wound reaction inhibitors. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2021.1887768
Hamedan JH, Sohani MM, Aalami A, Nazarideljou MJ (2019) Genetic engineering of lignin biosynthesis pathway improved stem bending disorder in cut gerbera (Gerbera jamesonii) flowers. Sci Hortic 245:274–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.10.013
Huang WN, Liu HK, Zhang HH, Chen Z, Guo YD, Kang YF (2013) Ethylene-induced changes in lignification and cell wall-degrading enzymes in the roots of mungbean (Vigna radiata) sprouts. Plant Physiol Biochem 73:412–419
Kumar N, Srivastava GC, Dixit K (2008) Flower bud opening and senescence in roses (Rosa hybrida L.). Plant Growth Regul 55:81–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-008-9263-x
Li C, Fan Y, Luan W, Dai Y, Wang M, Wei C, Ma X (2020) Titanium ions inhibit the bacteria in vase solutions of freshly cut Gerbera jamesonii and extend the flower longevity. Microbiol Ecol 77:967–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-020-01572-
Liu J, He S, Zhang Z, Cao J, Lv P, He S, Joyce DC (2009) Nano-silver pulse treatments inhibit stem-end bacteria on cut Gerbera cv. Ruikou flowers. Postharv Biol Technol 54:59–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2009.05.004
Liu J, Lai L, Liu H, Li H, Yu G, Sun Y, He S (2021) Nano-silver treatment reduces bacterial proliferation and stem bending in cut gerbera flowers: an in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Postharv Biol Technol 180:111595
Luo ZS, Xu XL, Cai ZZ, Yan M (2007) Effects of ethylene and 1-methylcyclopropene (1-MCP) on lignification of postharvest bamboo shoot. Food Chem 105:521–527
Mangieri MA, Mantese AI, Alvarez Schurmann A, Chimenti CA (2016) Effects of ethephon on anatomical changes in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) stems associated with lodging. Crop Pasture Sci 67:988–999
Marousky FJ (1986) Vascular structure of the Gerbera scape. Acta Hortic 181:399–406. https://doi.org/10.17660/ACTAHORTIC.1986.181.54
Meman MA, Dabhi KM (2006) Effects of different stalk lengths and certain chemical substances on vase life of gerbera (Gerbera jamesonii Hook.) cv. ‘Savana Red.’ J Appl Hortic 8:147–150
Mencarelli F, Agostini R, Rotondi R, Massantini R (1995) Ethylene production, ACC content, PAL and POD activities in excised sections of straight and bent gerbera scapes. J Hortic Sci 70:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.1995.11515310
Naing AH, Lee K, Kim KO, Ai TN, Kim CK (2017) Involvement of sodium nitroprusside (SNP) in the mechanism that delays stem bending of different gerbera cultivars. Front Plant Sci 8:2045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.02045
Naing AH, Soe MT, Yeum JH, Kim CK (2021) Ethylene acts as a negative regulator of the stembending mechanism of different cut snapdragon cultivars. Front Plant Sci 12:745038. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.745038
Nair SA, Singh V, Sharma TV (2003) Effect of chemical preservatives on enhancing vase-life of gerbera flowers. J Trop Agric 41:56–58
Perik RRJ, Razé D, Harkema H, Zhong Y, van Doorn WG (2012) Bending in cut Gerbera jamesonii flowers relates to adverse water relations and lack of stem sclerenchyma development, not to expansion of the stem central cavity or stem elongation. Postharv Biol Technol 74:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2012.06.009
Perik RRJ, Razé D, Ferrante A, Van Doorn WG (2014) Stem bending in cut Gerbera jamesonii flowers: effects of a pulse treatment with sucrose and calcium ions. Postharv Biol Technol 98:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2014.06.008
Prashanth P, Chandrasekhar R (2007) Studies on postharvest application of mineral salts on scape bending, peroxidase activity and biochemical components of cut gerbera. Asian J Hortic 2:239–244
Reid MS (1989) The role of ethylene in flower senescence. Acta Hort 261:157–169. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.1989.261.20
Sitbon F, Hennion S, Little CHA, Sundberg B (1999) Enhanced ethylene production and peroxidase activity in IAA-overproducing transgenic tobacco plants is associated with increased lignin content and altered lignin composition. Plant Sci 141:165–173
Solgi M, Kafi M, Taghavi TS, Naderi R (2009) Essential oils and silver nanoparticles (SNP) as novel agents to extend vase-life of gerbera (Gerbera jamesonii cv. ‘Dune’) flowers. Postharv. Biol. Technol. 53:155–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2009.04.003
Steinitz B (1983) The influence of sucrose and silver ions on dry weight, fiber and lignin content, and stability of cut Gerbera flower stalks. Gartenbauwissenschaft 48:821–837
Syros T, Yupsanis T, Zafiriadis H, Economou AS (2004) Activity and isoforms of peroxidases, lignin and anatomy, during adventitious rooting in cuttings of Ebenus cretica L. J Plant Physiol 161:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00938
Van Doorn WG, de Witte Y (1994) Effect of bacteria on scape bending in cut Gerbera jamesonii flowers. J Am Soc Hort Sci 119:568–571
Van Doorn WG, Perik PRJ, Abadie P, Harkeme H (2011) A treatment to improve the vase life of cut tulips: effects on tepal senescence, tepal abscission, leaf yellowing and stem elongation. Postharv Biol Technol 61:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2011.02.003
Werett HC, Sheehan TJ, Wilfret GJ, Marousky FJ, Lyrene PM, Knauff AD (1996) Postharvest longevity of cut gerbera. Response to selection for vase life components. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 121:216–221
Ye ZH (1997) Association of caffeoyl coenzyme A 3-O-methyltransferase expression with lignifying tissues in several dicot plants. Plant Physiol 115:1341–1350. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.115.4.1341
Ye DL, Zhang YS, Al-Kaisi MM, Duan LS, Zhang MC, Li ZH (2016) Ethephon improved stalk strength associated with summer maize adaptations to environments differing in nitrogen availability in the North China Plain. J Agric Sci 154:960–977. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859615000829
Zhao HY, Sheng QX, Lv SY (2004) Characterization of three rice CCoAOMT genes. Chin Sci Bull 49:1602–1606. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184129
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2021R1A2C2008951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AHN designed the study and wrote and revised the manuscript. MTS conducted the experiments. NMW analyzed the data and made the graphs. HK and MYC assisted in the experiments. CKK supervised the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Naing, A.H., Soe, M.T., Win, N.M. et al. Investigating the role of Ethephon in the stem-bending mechanism and petal senescence of two different gerbera flowers. Plant Biotechnol Rep 16, 645–654 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-022-00791-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-022-00791-9