Abstract
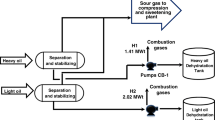
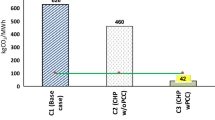
Over the past few decades, reducing CO2 emissions has attracted attention at an industrial level worldwide. This study focuses on utilizing both the byproduct gas, including CO2, and waste heat produced from the steel-making process to produce synthetic fuel by integrating solid oxide electrolyzer cell (SOEC) technology with downstream Fischer-Tropsch and hydrocracking processes. CO2 can be collected from the byproduct gas and used as a feed for the SOEC, and waste heat from the steel-making process can be utilized as the main heat source for operation of the SOEC at high temperatures and to generate electrical power through heat recovery and steam generation (HRSG) as an energy source for the SOEC. The syngas (H2 and CO) produced from the SOEC is then converted to synthetic oil through the FT process, and the yield of the synthetic oil is increased via the hydrocracking process by converting heavy oil to lighter fractions. The entire process was modeled using Aspen HYSYS software, and pinch technology was adopted to maximize the energy efficiency of the process. As a result, CO2 release was reduced by 452 tons/day and syngas was produced by 336.8 tons/day. The syngas produced was then converted to synthetic oil (306.7 tons/day) and light gas (44.24 tons/day). Economic assessment was completed based on the discounted cash flow method for two cases: electricity tariffs and new renewable energy prices. When the electricity tariff is implemented, profit is achieved in seven years, whereas the system becomes profitable in four years when newly regenerated surplus energy is utilized. If the price of renewable energy is reduced, profits may be achieved earlier.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Holappa, Metals, 10, 1117 (2020).
V. Dieterich, A. Buttler, A. Hanel, H. Spliethoff and S. Fendt, Energy Environ. Sci., 13, 3207 (2020).
J. K. Lee, S. Shin, G. J. Kwak, M. K. Lee, I. B. Lee and Y. S. Yoon, Energy Convers. Manag., 224, 113316 (2020).
H. Xi, X. Wu, X. Chen and P. Sha, Appl. Energy, 295, 117069 (2021).
R. Gao, C. Zhang, G. Kwak, Y. J. Lee, S. C. Kang and G. Guan, Energy Convers. Manag., 213, 112819 (2020).
Y. Zeng, X. Xiao, J. Li, L, Sun, C. A. Floudas and H. Li, Energy, 143, 881 (2018).
K. D. Ras, R. V. D. Vijver, V. V. Galvita, G. B. Marin and K. M. V. Geem, Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng., 26, 81 (2019).
M. Czachor, C. J. Laycock, S. J. W. Carr, J. Maddy, G. Lloyd and A. J. Guwy, Energy Convers. Manag., 225, 113455 (2020).
Q. Fu, C. Mabilat, M. Zahid, A. Brisse and L. Gautier, Energy Environ. Sci., 3, 1382 (2010).
J. E. O’Brien, M. G. McKellar, C. M. Stoots, J. S. Herring and G. L. Hawkes, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 34, 4216 (2009).
W. L. Becker, R. J. Braun, M. Penev and M. Melain, Energy, 47, 99 (2012).
F. Salomone, E. Giglioa, D. Ferrero, M. Santarelli, R. Pirone and S. Bensaid, Chem. Eng. J., 377, 120233 (2019).
J. H. Kim, NICE (News & Information for Chemical Engineers), 36, 171 (2018).
R. Q. Wang, L. Jing, Y. D. Wang and A. P. Roskilly, J. Clean. Prod., 274, 122997 (2020).
M. Martin, Industrial chemical process analysis and design, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2016).
T. S. Lee, Numerical modeling and simulation of fischer-tropsch packed-bed reactor and its thermal management, Ph. D Thesis, University of Florida (2011).
J. W. Ward, Fuel Process. Technol., 35, 55 (1993).
C. Gambaro, V. Calemma, D. Molinari and J. Denayer, AIChE J., 57, 711 (2011).
B. S. Lee, M. J. Park, Y. A. Kim, E. D. Park, J. S. Han, K. E. Jeong, C. U. Kim and S. Y. Jeong, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 31, 419 (2014).
L. Pellegrini, S. Bonomi, S. Gamba, V. Calemma and D. Molinari, Chem. Eng. Sci., 62, 5013 (2007).
G. F. Froment, Catal. Today, 1, 455 (1987).
K. Abhinanyu and S. Shishir, Pet. Coal, 54, 59 (2012).
J. L. Hodala, J. S. Jung, E. H. Yang, G. H. Hong, Y. S. Noh and D. J. Moon, Fuel, 185, 339 (2016).
I. C. Kemp, Pinch analysis and process integration: a user guide on process integration for the efficient use of energy, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2007).
S. Y. Im, J. J. Lee, Y. S. Jeon and H. T. Kim, KSFM, 19, 26 (2016).
J. Nyári, M. Magdeldin, M. Larmi, M. Järvinen and A. Santasalo-Aarnio, J. CO2 Util., 39, 101166 (2020).
W. L. Becker, M. Penev and R. J. Braun, J. Energy Resour. Technol., 141, 021901 (2019).
R. Junsittiwate, T. R. Srinophakun and S. Sukpancharoen, Energy Sustain Dev., 66, 140 (2022).
O. Schmidt, A. Gambhir, I. Staffell, A. Hawkes, J. Nelson and S. Few, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 42, 30470 (2017).
L. Bertuccioli, A. Chan, D. Hart, F. Lehner, B. Madden and E. Standen, Study on Development of Water Electrolysis in the EU, E4tech Sàrl with Element Energy Ltd, Lousanne, Switzerland (2014).
J. S. Kim, H. J. Lee, B. R. Lee, J. I. Kim, H. M. Oh, I. B. Lee, Y. S. Yoon and H. K. Lim, Energy Convers. Manag., 250, 114922 (2021).
P. Spath, A. Aden, T. Eggeman, M. Ringer, B. Wallace and J. Jechura, Technical Report, NREL/TP-510-37408 (2005).
A. Mivechian and M. Pakizeh, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 30, 937 (2013).
G. Zang, P. Sun, A. A. Elgowainy, A. Bafana and M. Wang, J. CO2 Utill., 46, 101459 (2021).
R. M. Swanson, A. Platon, J. A. Satrio, R. C. Brown and D. D. Hsu, Technical Report, NREL/TP-6A20-46587 (2010).
A. Dutta, A. H. Sahir, E. Tan, D. Humbird, L. J. Snowden-Swan, P. A. Meyer, J. Ross, D. Sexton, R. Yap and J. Lukas, Technical Report, PNNL-23823 (2015).
S. B. Jones, C. Valkenburt, C. W. Christie, D. C. Elliott, J. E. Holladay, D. J. Stevens, C. Kinchin and S. Czernik, Technical Report, PNNL-18284 Rev. 1 (2009).
R. Davis, L. Tao, E. C. D. Tan, M. J. Biddy, G. T. Scarlata, J. Jacobson, K. Cafferty, J. Ross, J. Lukas, D. Knorr and P. Schoen, Technical Report, NREL/TP-5100-60223 (2013).
M. M. Faruque, R. C. Baliban, J. A. Elia and C. A. Floudas, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 51, 15665 (2012).
South Korea: General Guidelines for Preliminary Feasibility Study, Article 50 (1), Directive No. 436, April 25, 2019 enacted.
L. March, Introduction to pinch technology, Targeting House, Gadbrook Park, Northwich, Cheshire, CW9 7UZ, England (1998).
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), FUTURE OF SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC Deployment, investment, technology, grid integration and socio-economic aspects, A Global Energy Transformation paper (2019).
Acknowledgement
This study was funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE) and supported by the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP), Republic of Korea (Project No. 20182010600400). This work was also supported by Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE) (P0008475, Development Program for Smart Digital Engineering Specialist).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Declaration of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, G.H., Lee, J., Cho, Y. et al. Techno-economic analysis of CO2/steam co-electrolysis process and synfuel production process coupled with steel manufacturing process. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 40, 740–753 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-022-1331-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-022-1331-9