Abstract
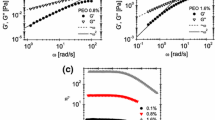
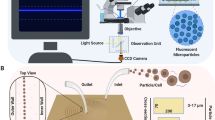
The relaxation time of a viscoelastic fluid is an essential parameter for characterizing the degree of elasticity. However, measuring the relaxation time of dilute polymer solutions with low viscosity using conventional rotational rheometers remains challenging because of the low instrument sensitivity. In this study, we demonstrate an efficient microfluidic method for measuring the relaxation time of a dilute polymer solution by utilizing elasticity-driven lateral particle migration in a microchannel. First, the previous theoretical model was refined, based on the Oldroyd-B constitutive equation, in order to predict lateral particle migration in a viscoelastic fluid with constant shear viscosity, considering the inlet and finite particle size effects. This model was utilized to determine the relaxation times of dilute poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) aqueous solutions. Direct comparison of the measured relaxation times with those obtained from Zimm theory verified the reliability of the proposed method. The current approach is expected to be useful in characterizing the relaxation times of a wide range of polymer solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. B. Bird, R. C. Armstrong and O. Hassager, Dynamics of polymeric liquids, Wiley Interscience, New York (1987).
R. G. Larson, The structure and rheology of complex fluids, Oxford University Press, New York (1999).
K. Kang, S. S. Lee, K. Hyun, S. J. Lee and J. M. Kim, Nat. Commun., 4, 2567 (2013).
J. Zilz, C. Schafer, C. Wagner, R. J. Poole, M. A. Alves and A. Lindner, Lab Chip, 14, 351 (2014).
C. W. Macosko, Rheology: principles, measurements, and applications, Wiley-VCH (1994).
L. E. Rodd, T. P. Scott, J. J. Cooper-White and G. H. McKinley, Appl. Rheol., 15, 12 (2004).
F. Del Giudice, G. D’Avino, F. Greco, I. De Santo, P. A. Netti and P. L. Maffettone, Lab Chip, 15, 783 (2015).
F. D. Giudice, S. J. Haward and A. Q. Shen, J. Rheol., 61, 327 (2017).
C. Clasen, J. P. Plog, W.-M. Kulicke, M. Owens, C. Macosko, L. E. Scriven, M. Verani and G. H. McKinley, J. Rheol., 50, 849 (2006).
J. M. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 32, 2406 (2015).
D. Y. Kim and J. M. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 36, 837 (2019).
A. Shiriny, M. Bayareh and A. A. Nadooshan, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 38, 1686 (2021).
B. Kim, S. S. Lee, T. H. Yoo, S. Kim, S. Y. Kim, S.-H. Choi and J. M. Kim, Sci. Adv., 5, eaav4819 (2019).
É. Guazzelli and J. F. Morris, A physical introduction to suspension dynamics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012).
B. P. Ho and L. G. Leal, J. Fluid Mech., 76, 783 (1976).
A. Karnis, S. G. Mason and H. L. Goldsmith, Nature, 200, 159 (1963).
A. M. Leshansky, A. Bransky, N. Korin and U. Dinnar, Phys. Rev. Lett., 98, 234501 (2007).
G. D’Avino, G. Romeo, M. M. Villone, F. Greco, P. A. Netti and P. L. Maffettone, Lab Chip, 12, 1638 (2012).
G. Romeo, G. D’Avino, F. Greco, P. A. Netti and P. L. Maffettone, Lab Chip, 13, 2802 (2013).
G. D’Avino, F. Greco and P. L. Maffettone, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech., 49, 341 (2017).
D. F. James, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech., 41, 129 (2009).
W. W. Graessley, Polymer, 21, 258 (1980).
V. Tirtaatmadja, G. H. McKinley and J. J. Cooper-White, Phys. Fluids, 18, 043101 (2006).
M. Rubinstein and R. H. Colby, Polymer physics, Oxford University Press, Oxford (2003).
S. Yang, J. Y. Kim, S. J. Lee, S. S. Lee and J. M. Kim, Lab Chip, 11, 266 (2011).
L. E. Rodd, T. P. Scott, D. V. Boger, J. J. Cooper-White and G. H. McKinley, J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech., 129, 1 (2005).
L. E. Rodd, J. J. Cooper-White, D. V. Boger and G. H. McKinley, J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech., 143, 170 (2007).
L. Casanellas, M. A. Alves, R. J. Poole, S. Lerouge and A. Lindner, Soft Matter, 12, 6167 (2016).
Y. G. Liu, Y. G. Jun and V. Steinberg, J. Rheol., 53, 1069 (2009).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Ajou University Research Fund, grant number [S-2019-G0001-00498].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, Y., Shim, T.S. & Kim, J.M. Facile microfluidic method for measuring the relaxation time of dilute polymer solution based on viscoelastic particle focusing. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 39, 2318–2323 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-022-1152-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-022-1152-x