Abstract
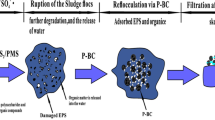
Enhancement of sludge dewaterability is key for sludge management and disposal of wastewater treatment plants (WWTP). In this study, the Fe2+-peroxymonosulfate (PMS) conditioning approach was first used to oxidize the primary sludge from the primary sedimentation tank of a full scale WWTP. The combination of Fe2+ (0.05–0.5 g/g TSS) and PMS (0.05–0.5 g/g TSS) could significantly improve the dewaterability of primary sludge. The optimal addition amount of Fe2+ and PMS was 0.1 g/g TSS and 0.25 g/g TSS, respectively, under which the capillary suction time (CST) and specific resistance to filtration (SRF) of the sludge was reduced by 79% and 95%. The physicochemical properties (particle size, zeta potential, EPS composition) of the primary sludge before and after oxidative conditioning were measured. Results showed that sulfate radicals generated from Fe2+-PMS system effectively reduced organic matter in different EPS fractions, further destroying sludge floc cells. Then the bound water in the sludge flocs was released, thereby improving the sludge dewaterability. The microscopic morphology also indicated that the sludge flocs have a blocky structure with tight texture before conditioning. After conditioning, the sludge flocs become smaller, and many irregular pores are formed on the surface, which facilitates the passage of internal moisture. Economic analysis showed that Fe2++PMS conditioning is more economical than the traditional Fenton method.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADS:
-
anaerobic digested sludge
- AOPs:
-
advanced oxidation processes
- COD:
-
chemical oxygen demand
- CST:
-
capillary suction time
- DOC:
-
dissolved organic carbon
- EPS:
-
extracellular polymeric substances
- EZP:
-
electrolysis/electrocoagulation and zero-valent iron activated persulfate oxidation
- HP:
-
hydrogen peroxide, H2O2
- LB-EPS:
-
loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances
- MW:
-
microwave
- Mw:
-
weight-average molecular weight
- Mn:
-
number-average molecular weight
- ·OH:
-
hydrogen radical
- OPC:
-
quick lime and 42.5 ordinary portland cement
- PDS:
-
peroxydisulfate, S2O2−8
- PMS:
-
peroxymonosulfate, HSO−5
- PMS-EDTA-Fe2+ :
-
peroxymonosulfate activated by EDTA chelated-Fe2+ process
- SB-EPS:
-
soluble extracellular polymeric substances
- SEM:
-
scanning electron microscope
- SO·−4 :
-
sulfate radical
- SRF:
-
specific resistance to filtration
- TB-EPS:
-
tightly bound extracellular polymeric substances
- TOC:
-
total organic carbon
- TS:
-
total solids
- TSS:
-
total suspended solids
- VS:
-
volatile solids
- VSS:
-
volatile suspended solids
- VTM-PMS-RH:
-
natural vanadium-titanium magnetite-activated peroxymonosulfate oxidation coupled with rice husk as skeleton builder
- WAS:
-
waste activated sludge
- ZVI:
-
zero-valent iron
References
Q. Wang, W. Wei, Y. Gong, Q. Yu, Q. Li, J. Sun and Z. Yuan, Sci. Total Environ., 587–588, 510 (2017).
W. Wei, X. Zhou, D. Wang, J. Sun and Q. Wang, Water Res., 118, 12 (2017).
X. Zhou, G. Jiang, Q. Wang and Z. Yuan, Rsc Adv., 4, 50644 (2014).
K. Xiao, Y. Chen, X. Jiang, Q. Yang, W. Y. Seow, W. Zhu and Y. Zhou, Water Res., 109, 13 (2017).
B. Cao, W. Zhang, Y. Du, R. Wang, S. P. Usher, P. J. Scales and D. Wang, Water Res., 130, 363 (2018).
W. Gao, Desalination, 268, 170 (2011).
S. Guo, F. Qu, A. Ding, J. He, H. Yu, L. Bai, G. Li and H. Liang, Rsc Adv., 5, 43065 (2015).
L. Wang, C. Qian, J. Jiang, X. Ye and H. Yu, Environ. Pollut., 231, 1388 (2017).
G. Q. Su, M. X. Huo, Z. G. Yuan, S. Y. Wang and Y. Z. Peng, Bioresour. Technol., 136, 237 (2013).
M. B. Kurade, K. Murugesan, A. Selvam, S. Yu and J. W. C. Wong, Bioresour. Technol., 217, 179 (2016).
W. Zhang, P. Xiao, Y. Liu, S. Xu, F. Xiao, D. Wang and C. W. K. Chow, Sep. Purif. Technol., 132, 430 (2014).
H. Liu, J. Yang, N. Zhu, H. Zhang, Y. Li, S. He, C. Yang and H. Yao, J. Hazard. Mater., 258, 144 (2013).
X. Zhou, Q. Wang, G. Jiang, P. Liu and Z. Yuan, Bioresour. Technol., 185, 416 (2015).
X. Zhou, H. Chen, S. Gao, S. Han, R. Tu, W. Wei, C. Cai, P. Liu, W. Jin and Q. Wang, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 34, 2672 (2017).
G. Zhen, X. Lu, Y. Li, Y. Zhao, B. Wang, Y. Song, X. Chai, D. Niu and X. Cao, Bioresour. Technol., 119, 7 (2012).
R. Dewil, J. Baeyens and E. Neyens, J. Hazard. Mater., 117, 161 (2005).
E. Neyens, J. Baeyens, M. Weemaes and B. De Heyder, J. Hazard. Mater., 98, 91 (2003).
M. S. Kim, K. Lee, H. Kim, H. Lee, C. Lee and C. Lee, Environ. Sci. Technol., 50, 7106 (2016).
W. Ren, Z. Zhou, Y. Zhu, L. Jiang, H. Wei, T. Niu, P. Fu and Z. Qiu, Int. Biodeter. Biodegr., 104, 384 (2015).
C. Liu, B. Wu and X. Chen, Chem. Eng. J., 335, 865 (2018).
S. Wacławek, H. V. Lutze, K. Grübel, V. V. T. Padil, M. Černík and D. D. Dionysiou, Chem. Eng. J., 330, 44 (2017).
C. Liu, Chem. Eng. J., 359, 217 (2019).
A. Rastogi, S. R. Al-Abed and D. D. Dionysiou, Water Res., 43, 684 (2009).
C. Cai, H. Zhang, X. Zhong and L. Hou, J. Hazard. Mater., 283, 70 (2015).
J. Liu, Q. Yang, D. Wang, X. Li, Y. Zhong, X. Li, Y. Deng, L. Wang, K. Yi and G. Zeng, Bioresour. Technol., 206, 134 (2016).
K. Song, X. Zhou, Y. Liu, Y. Gong, B. Zhou, D. Wang and Q. Wang, Sci. Rep-Uk., 6, 24800 (2016).
R. Canziani and L. Spinosa Sludge from wastewater treatment plants, Elsevier, The Netherlands (2019).
V. K. Tyagi and S. Lo, Renew. Sust. Energy Rev., 25, 708 (2013).
H. Carrère, C. Dumas, A. Battimelli, D. J. Batstone, J. P. Delgenès, J. P. Steyer and I. Ferrer, J. Hazard. Mater., 183, 1 (2010).
P. Devi and A. K. Saroha, Sci. Total Environ., 578, 16 (2017).
T. Meyer, P. Amin, D. G. Allen and H. Tran, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 6, 6317 (2018).
J. Benítez, A. Rodríguez and A. Suárez, Water Res., 28, 2067 (1994).
J. Diak and B. Örmeci, J. Environ. Manage., 216, 406 (2018).
J. Lu, S. Rao, T. Le, S. Mora and S. Banerjee, Process Biochem., 46, 353 (2011).
K. Xiao, Y. Chen, X. Jiang, V. K. Tyagi and Y. Zhou, Water Res., 105, 470 (2016).
X. Zhou, W. Jin, H. Chen, C. Chen, S. Han, R. Tu, W. Wei, S. Gao, G. Xie and Q. Wang, Water Sci. Technol., 76, 2427 (2017).
F. Sun, K. Xiao, W. Zhu, N. Withanage and Y. Zhou, Water Res., 130, 208 (2018).
X. Zhou, G. Jiang, T. Zhang, Q. Wang, G. Xie and Z. Yuan, Bioresour. Technol., 192, 817 (2015).
G. Zhen, X. Lu, Y. Zhao, X. Chai and D. Niu, Bioresour. Technol., 116, 259 (2012).
G. Zhen, X. Lu, B. Wang, Y. Zhao, X. Chai, D. Niu, A. Zhao, Y. Li, Y. Song and X. Cao, Bioresour. Technol., 124, 29 (2012).
Y. Li, X. Yuan, D. Wang, H. Wang, Z. Wu, L. Jiang, D. Mo, G. Yang, R. Guan and G. Zeng, Bioresour. Technol., 262, 294 (2018).
F. Liu, L. Zhou, J. Zhou, X. Song and D. Wang, J. Hazard. Mater., 221–222, 170 (2012).
K. B. Thapa, Y. Qi and A. F. A. Hoadley, Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 334, 66 (2009).
Q. Yu, H. Lei, G. Yu, X. Feng, Z. Li and Z. Wu, Chem. Eng. J., 155, 88 (2009).
G. Zhen, X. Lu, Y. Li and Y. Zhao, Bioresour. Technol., 136, 654 (2013).
G. Sheng, H. Yu and X. Li, Biotechnol. Adv., 28, 882 (2010).
X. Qian, Y. Wang and H. Zheng, Water Res., 88, 93 (2016).
B. Wilén, K. Keiding and P. H. Nielsen, Water Res., 34, 3933 (2000).
G. Zhen, J. Wang, X. Lu, L. Su, X. Zhu, T. Zhou and Y. Zhao, Chemosphere, 221, 141 (2019).
J. Wang, M. Yang, R. Liu, C. Hu, H. Liu and J. Qu, Water Res., 160, 454 (2019).
N. Buyukkamaci, Process Biochem., 39, 1503 (2004).
G. Zhen, X. Lu, J. Niu, L. Su, X. Chai, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, Y. Song and D. Niu, Chem. Eng. J., 233, 274 (2013).
K. Song, X. Zhou, Y. Liu, G. Xie, D. Wang, T. Zhang, C. Liu, P. Liu, B. Zhou and Q. Wang, Chem. Eng. J., 295, 436 (2016).
Q. Wang, J. Sun, K. Song, X. Zhou, W. Wei, D. Wang, G. Xie, Y. Gong and B. Zhou, J. Environ. Sci.-China, 67, 378 (2018).
Y. Li, X. Yuan, Z. Wu, H. Wang, Z. Xiao, Y. Wu, X. Chen and G. Zeng, Chem. Eng. J., 303, 636 (2016).
C. Liu, B. Wu, X. E. Chen and S. Xie, Chem. Pap., 71, 2343 (2017).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51878215), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M661265), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2018A030313185) and Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Project (KJYY20171011144235970, JCYJ 20170307150223308).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Jin, W., Wang, L. et al. Improving primary sludge dewaterability by oxidative conditioning process with ferrous ion-activated peroxymonosulfate. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 37, 1498–1506 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-020-0517-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-020-0517-2