Abstract
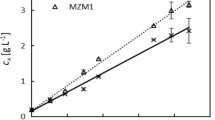
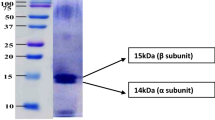
Spirulina is one of the promising photosynthetic microorganisms as the source for food, cosmetic, and other value-added products such as phycocyanin. However, its production cost associated with cultivation is expensive because of high concentration of bicarbonate (76wt%) in standard Zarrouk medium for Spirulina. Bicarbonate not only acts as a carbon source but also helps maintaining culture medium in alkaline condition, which is essential for growth of Spirulina. The present study demonstrates that bicarbonate (16.8 g/L) in standard Zarrouk medium was completely replaceable by chemical CO2 absorption using 0.2M NaOH and 154.2 mmol CO2 gas could be absorbed in the form of NaHCO3/Na2CO3 into 1 L medium during the process. This process was incorporated into Spirulina cultivation, which enabled us to reduce the total cost of preparation of Zarrouk medium by 34.3% without sacrificing biomass and pigments production. In addition, another important use of NaOH is achievement of cost-efficient and ecofriendly sanitization of culture medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Belay, Y. Ota, K. Miyakawa and H. Shimamatsu, J. Appl. Phycol., 5, 235 (1993).
D. White, A. Pagarette, P. Rooks and S. Ali, J. Appl. Phycol., 25, 153 (2013).
S.-H. Ho, C.-Y. Chen, D.-J. Lee and J.-S. Chang, Biotechnol. Adv., 29, 189 (2011).
C. Stewart and M.-A. Hessami, Energy Convers. Manage., 46, 403 (2005).
C. González-López, F. Acién Fernández, J. Fernández-Sevilla, J. Sánchez Fernández and E. Molina Grima, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 109, 1637 (2012).
Y. Peng, B. Zhao and L. Li, Energy Procedia, 14, 1515 (2012).
C.-H. Yu, C.-H. Huang and C.-S. Tan, Aerosol Air Qual. Res., 12, 745 (2012).
R. Moran, Plant Physiology, 69, 1376 (1982).
A. Patel, S. Mishra, R. Pawar and P. Ghosh, Protein Expression and Purification, 40, 248 (2005).
K. H. Ogbonda, R. E. Aminigo and G.O. Abu, Bioresour. Technol., 98, 2207 (2007).
A. Kumari, A. Kumar, A.K. Pathak and C. Guria, J. CO2 Util., 8, 49 (2014).
M. Kanniche, R. Gros-Bonnivard, P. Jaud, J. Valle-Marcos, J.-M. Amann and C. Bouallou, Appl. Therm. Eng., 30, 53 (2010).
J. D. Figueroa, T. Fout, S. Plasynski, H. McIlvried and R.D. Srivastava, Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control, 2, 9 (2008).
R. Thiruvenkatachari, S. Su, H. An and X.X. Yu, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., 35, 438 (2009).
J. Pires, F. Martins, M. Alvim-Ferraz and M. Simões, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 89, 1446 (2011).
D.W. Keith, M. Ha-Duong and J. K. Stolaroff, Clim. Change, 74, 17 (2006).
B. P. Spigarelli and S.K. Kawatra, J. CO2 Util., 1, 69 (2013).
O. Pulz and W. Gross, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 65, 635 (2004).
G. Healthcare, Appl. Note, 18, 1124 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, JY., Yang, JW., Kim, K. et al. Cost-efficient cultivation of Spirulina platensis by chemical absorption of CO2 into medium containing NaOH. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 32, 2285–2289 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-015-0073-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-015-0073-3