Abstract
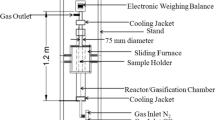
A wire mesh reactor was used to investigate the devolatilization process of coal particle during entrained flow gasification. Coal from Indonesia East Kalimantan mine, which has high moisture and high volatile matter, was chosen as a sample. Experiments were carried out at the heating rate of 1,000 °C/s and isothermal condition was kept at peak temperature under atmospheric pressure. The char, tar and gas formation characteristics of the coal as well as the composition of the gas components at peak temperatures were determined. The experimental results showed that devolatilization process terminated when temperature reached above 1,100 °C. Most of tar was formed at about 800 °C, while the rate of tar formation decreased gradually as the temperature increased. CH4 was observed at temperatures above 600 °C, whereas H2 was detected above 1,000 °C. The amount of formed gases such as H2, CO, CH4 and C n H m increased as the temperature increased. From the characteristics of devolatilization with residence time, it was concluded that devolatilization terminated within about 0.7 second when the temperature reached 1,000 °C. As the operating temperature in an entrained flow gasifier is higher than ash melting temperature, it is expected that the devolatilization time of high volatile coal should be less than one second in an entrained flow gasifier.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Tremel and H. Spliethoff, Fuel, 103, 663 (2013).
A. Tremel, T. Haselsteiner, C. Kunze and H. Spliethoff, Appl. Energy, 92, 279 (2012).
L. Chen, C. Zeng, X. Guo, Y. Mao, Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, W. Li, Y. Long, H. Zhu, B. Eiteneer and V. Zamansky, Fuel Process Technol., 91, 848 (2010).
M. S. Masnadi, R. Habibi, J Kopyscinski, J. M. Hill, X. Bi and C. J. Lim, Fuel, 117, 1204 (2014)
K. Jamil, J. I. Hayashi and C. Z. Li, Fuel, 83, 833 (2004).
G. D. Nola, W. D. Jong and H. Spliethoff, Fuel Process Technol., 90, 388 (2009).
R. Loison and R. Chauvin, Chim. Ind., 91, 269 (1964).
D. B. Anthony, J. B. Howard, H. C. Hottel and H. P. Meissner, Fuel, 55, 121 (1976).
M. R. Khan, Fuel, 68, 1522 (1989).
S. Niksa, W. B. Russel and D. A. Saville, Fuel, 61, 1207 (1982).
S. Niksa, W. B. Russel and D. A. Saville, Nineteenth Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1151 (1982).
J. R. Gibbins and R. Kandiyoti, Fuel, 68, 895 (1989).
C. J. Hindmarsh, K. M. Thomas, W. X. Wang, H.Y. Cai, A. J. Güell, D. R. Dugwell and R. Kandiyoti, Fuel, 74, 1185 (1995).
C. Sathe, J.-I. Hayashi and C. Z. Li, Fuel, 81, 1171 (2002).
C. Zeng, H. Wu, J.-I. Hayashi and C.-Z. Li, Fuel, 84, 1586 (2005).
J. R. Gibbins, R. A.V. King, R. J. Woods and R. Kandiyoti, Review of Scientific Instruments, 60, 1129 (1989).
C. Zeng, L. Chen, G. Liu, W. Li and B. Huang, Review of Scientific Instruments, 79, 084102 (2008).
E. B. H. Quah and C.-Z. Li, Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 258, 63 (2004).
J.Y. Lim, I. N. Chatzakis, A. Magaritis, H.Y. Cai, D. R. Dugwell and R. Kandiyoti, Fuel, 76, 1327 (1997).
Z. S. Gonenc, J. R. Gibbins, L. E. Katheklakis and R. Kandiyoti, Fuel, 69, 383 (1990).
M. A. Serio, D.G. Hamblen, J. R. Markham and P.R. Solomon, Energy Fuels, 1, 138 (1987).
D.-W. Lee, J.-S. Bae, S.-J. Park, Y. J. Lee, J.-C. Hong and Y.-C. Choi, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 51, 13580 (2012).
H. Shui, M. Zheng, Z. Wang and X. Li, Fuel, 86, 1396 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ra, H.W., Seo, M.W., Yoon, S.J. et al. Devolatilization characteristics of high volatile coal in a wire mesh reactor. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 31, 1570–1576 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0061-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0061-z