Abstract
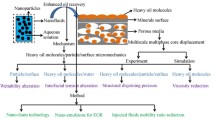
We experimentally investigated nanoparticle-stabilized emulsions for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) applications. The emulsions were injected into a silica bead column containing mineral oil, and the oil recovery was calculated using a mass-balance approach. The experiments were carried out as follows: 1) The emulsions were injected into a column with 100% water saturation to investigate the mobility of the water and emulsions, 2) Water flooding was then carried out at initial oil and water saturation, and the emulsion flooding was injected to calculate the enhancement in the oil recovery rate. The results indicate that the nanoparticle-stabilized emulsions increased the oil recovery rate by 11% after water flooding. The mechanism for this is attributed to a greater pressure difference across the porous medium, leading to oil remaining in the pores being produced via a piston effect. These results indicate that nanoparticle-stabilized emulsions may be effective EOR agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Fu and D. Mamora, The 2010 SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, USA (2010).
X. Fu, R. H. Lane and D. Mamora, The SPE Canadian Unconventional Resources Conference, Calgary, Canada (2012).
T. Zhang, M. R. Roberts, S. L. Bryant and C. Huh, The 2009 SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry, The Woodlands, USA (2009).
T. Zhang, A. Davidson, S. L. Bryant and C. Huh, The 2010 SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, USA (2010).
P. McElfresh, M. Wood and D. Ector, The SPE International Oilfield Nanotechnology Conference, Noordwijk, The Netherlands (2012).
B. P. Brinks and S. O. Lumdson, Phys. Chem Chem. Phys., 2, 2959 (2000a).
B. P. Brinks and S. O. Lumdson, Langmuir, 16, 8622 (2000b).
B. P. Brinks, J. Philip and J. A. Rodrigues, Langmuir, 21, 3296 (2005).
B. P. Brinks and J. A. Rodrigues, Angew. Chem., 117, 445 (2005).
T. S. Horozov, B. P. Brinks and T. Gottschalk-Gaudig, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 9, 6389 (2007).
F. Qiu and D. Mamora, The Canadian Unconventional Resources & International Petroleum Conference, Calgary, Canada (2010).
R. D. Kaminsky, R. C. Wattenbarger, J. P. Lederhos and S. A. Leonardi, The SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Florence, Italy (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, H., Kim, H., Lee, G. et al. Enhanced oil recovery using nanoparticle-stabilized oil/water emulsions. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 31, 338–342 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0214-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0214-5