Abstract
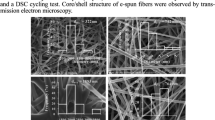
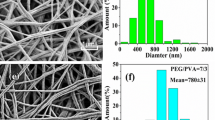
We fabricated eicosane/poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) core/shell nanofibers by melt coaxial electrospinning as potential heat-storage applications. Eicosane, a hydrocarbon with melting point near the human body temperature and high latent heat, was chosen as the core material. Melted eicosane and PVDF solutions were coaxially electrospun using a double spinneret, in which melted eicosane was fed at 0.090–0.210 mL/h while the feeding rate of PVDF solution was maintained constant at 1.500 mL/h. The applied voltage and working distance were maintained constant at 12 kV and 17 cm, respectively. Good core/shell structure of nanofibers was observed at core feed rates of 0.090–0.180mL/h by transmission electron microscopy. Differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis values indicated good thermal stability and high energy-storage capacity of the obtained nanofibers. The highest amount of eicosane encapsulated in the electrospun core/shell nanofibers reached 32.5 wt% at core feed rate 0.180 mL/h and had a latent heat of 77 J/g at melting point 39.2 °C. These shape-stabilized core/shell composite nanofibers showed good thermoregulating properties and had sufficiently high tensile strength for potential energy-storage applications, especially in smart textiles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. F. Mohammed, M. K. Amar, K.R. Siddique Ali and A. H. Said, Energy Convers. Manage., 45, 1597 (2004).
Z. Belen, M.M. Jose, F. C. Luisa and M. Harald, Appl. Therm. Eng., 23, 251 (2003).
K. Ravindra, K. M. Manoj, K. Rohitash, G. Deepak, P. K. Sharma, B. B. Tak and S. R. Meena, Def. Sci. J., 61, 576 (2011).
S. Mondal, Appl. Therm. Eng., 28, 1536 (2008).
M. F. Demirbas, Energy Source, Part B, 1, 85 (2006).
C.C. Chang, Y. L. Tsai, J. J. Chiu and H. Chen, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 112, 1850 (2009).
A. Sari, C. Alkan, A. Karaipekli and O. Uzun, Sol. Energy, 83, 1757 (2009).
L. S. Silva, J. Tsavalas, D. Sundberg, P. SaÌnchez and J. F. Rodriguez, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 49(23), 12204 (2010).
Z. Yang, Z. Wei, L. Leping, L. Wujun and X. Yi, Adv. Sci. Lett., 4(3), 933 (2011).
L. Sánchez, P. Sánchez, A. Lucas, M. Carmona and J. F. Rodríguez, Colloid. Polym. Sci., 285(12), 1377 (2007).
P. Sánchez, M.V. Sánchez-Fernandez, A. Romero, J. F. Rodríguez and L. Sánchez-Silva, Thermochim. Acta, 498(1–2), 16 (2010).
L. X. Zheng, T. Z. Cheng, Z.G. Long, S. L. Xian and Z. Tao, Chinese J. Chem., 22, 411 (2004).
Y. Shin, D. Yoo and K. Son, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 96(5), 2005 (2005).
Y. Shin, D. Yoo and K. Son, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 97(3), 910 (2005).
H. Shim, E. A. McCullough and B.W. Jones, Text. Res. J., 71(6), 495 (2001).
C. Chen, L. Wang and Y. Huang, Mater. Lett., 62, 3515 (2008).
C. Chen, L. Wang and Y. Huang, Chem. Eng. J., 150, 269 (2009).
C. Chen, L. Wang and Y. Huang, Polymer, 48, 5202 (2007).
S. Alay, F. Göde and C. Alkan, Fibers and Polymers, 11(8), 1089 (2010).
T. T. T. Nguyen, J.G. Lee and J. S. Park, Macromol. Res., 19, 370 (2011).
C. V. Do, T. T. T. Nguyen and J. S. Park, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 104, 131 (2012).
J. T. McCann, M. Marquez and Y. Xia, Nano Lett., 6, 2868 (2006).
F. Salaün, E. Devaux, S. Bourbigot and P. Rumeau, Text. Res. J., 80(3), 195 (2010).
S. S. Deveci and G. Basal, Colloid. Polym. Sci., 287(12), 1455 (2009).
G. Basal, S. S. Deveci1, D. Yalcin and O. Bayraktar, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 121(4), 1885 (2011).
L. X. Zheng, T. Z. Cheng, Z.G. Long, S. L. Xian and Z. Tao, Chinese J. Chem., 22, 411 (2004).
J. E. Díaz, A. Barrero, M. Márquez and I.G. Loscertales, Adv. Funct. Mater., 16, 2110 (2006).
C. Alkan, A. Sar, A. Karaipekli and O. Uzun, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 93(1), 143 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Do, C.V., Nguyen, T.T.T. & Park, J.S. Phase-change core/shell structured nanofibers based on eicosane/poly(vinylidene fluoride) for thermal storage applications. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 30, 1403–1409 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0046-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0046-3