Abstract
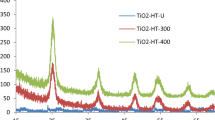
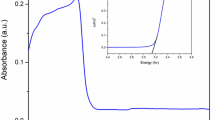
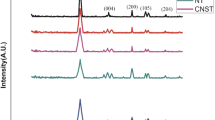
Photocatalytic degradation (PCD) of polyphenols (gallic acid) from E. camaldulensis leaves on TiO2/MCM-41 was investigated in order to get rid of substances harmful to aquatic life. The TiO2/MCM-41 catalysts with titania loading of 2–40% were synthesized by hydrothermal method using rice husk silica and tetraethyl orthotitanate as silica and titania sources, respectively. The obtained catalysts were characterized by XRD, TEM, Zeta potential analyzer, N2 adsorption-desorption and diffuse reflectance UV spectroscopy. Hexagonal array of MCM-41 was confirmed, but its crystallinity decreased dramatically with titania loading. Zeta potential of TiO2/MCM-41s surface varied from 2.11 to 6.00 with the increase of TiO2 from 0 to 100 wt%. Band gap energy of TiO2 shifted from 394.1 to 425.1 nm after adding 60%MCM-41 (40%TiO2/MCM-41), facilitating the ease of OH establishment. Gallic acid - a weak acid solution (pKa=4.0) around 27 ppm was favorable to dissolve in water. PCD of gallic acid was carried out on irradiating of 400W of mercury lamp. The results showed gallic acid solution about 10 wt% properly adsorbed on 10%TiO2/MCM-41 and effectively degraded at pH solution of 9.0. PCD completed at 60 minutes of irradiation time through catalyst concentration of 0.17 g/L and obeyed pseudo-first order. Intermediate products were formic, oxalic, pyruvic, malanic and maleic acids that finally mineralized to CO2 and H2O as downstream products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Bravo, Nutr. Rev., 56, 317 (1998).
R. Ahmed, A. T.M. R. Hoque and M. K. Hossain, J. Forest Res., 19, 19 (2008).
P. C. Gehrke, M. B. Revell and A.W. Philbey, J. Fish Biol., 43, 265 (1993).
M. Abelho and M. A. S. Graça, Hydrobiologia, 324, 195 (1996).
A. Molina, M. J. Reigosa and A. Carballeira, J. Chem. Ecol., 17, 147 (1991).
S. Azabou, W. Najjar, A. Gargoubi, A. Ghorbel and S. Sayadi, Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 77, 166 (2007).
R. Capasso, A. Evidente, L. Schivo, G. Orru, M. A. Marcialis and G. Cristinzio, J. Appl. Bacter., 79, 393 (1995).
R. Borja, J. Alba and C. J. Banks, Process Boichem., 32, 121 (1997).
S. Kim and W. Choi, Environ. Sci. Technol., 36, 2019 (2002).
M. S. Vohra, J. Lee and W. Choi, J. Appl. Electrochem., 35, 757 (2005).
S. Artkla, W. Kim, W. Choi and J. Wittayakun, Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 91, 157 (2009).
S. Artkla, K. Wantala, B.-O. Srinameb, N. Grisdanurak, W. Klysubun and J. Wittayakun, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 26, 1556 (2009).
S. Artkla, W. Choi and J. Wittayakun, Adv. Mater. Res., 93, 22 (2010).
M. A. Zanjanchi, H. Golmojdeh and M. Arvand, J. Hazard. Mater., 169, 233 (2009).
G.A. Eimer, S.G. Casuscelli, G. E. Ghione, M. E. Crivello and E. Herrero, Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 298, 232 (2006).
M.V. Landau, L. Vradman, X.G. Wang and L. Titelman, Micropor. Mesopor. Mater., 78, 117 (2005).
O. Carp, C. L. Huisman and A. Reller, Prog. Solid State Chem., 32, 33 (2004).
S. Artkla, W. Choi and J. Wittayakun, Environment Asia, 2, 41 (2009).
M. R. Hoffmann, S. T. Martin, W. Choi and D.W. Bahnemann, Chem. Rev., 95, 69 (1995).
I. K. Konstantinou and T.A. Albanis, Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 49, 1 (2004).
B. Neppolian, H.C. Choi, S. Sakthivel, B. Arabindoo and V. Murugesan, Chemosphere, 46, 1173 (2002).
J. X. Mai, W. L. Sun, L. Xiong, Y. Liu and J. R. Ni, Chemosphere, 73, 600 (2008).
A. C. Eslami, W. Pasanphan, B. A. Wagner and G.R. Buettner, Chem. Cent. J., 4, 15 (2010).
S. Kim and W. Choi, J. Phy. Chem: B, 109, 5143 (2005).
N. Nishiyama, H. Saputra, D.H. Park, Y. Egashira and K. Ueyamaet, J. Membr. Sci., 218, 165 (2003).
D.-H. Park, H. Saputra, N. Nishiyama, Y. Egashira and K. Ueyamaet, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 34, 1321 (2001).
S. Kim and W. Choi, Environ. Sci. Technol., 36, 2019 (2002).
A. Maira, K. L. Yeung, C.Y. Yan, P. L. Yue and C.K. Chan, J. Catal., 192, 185 (2000).
F. J. Beltrá, O. Gimeno, F. J. Rivas and M. Carbajo, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 81, 1787 (2006).
J.-C. Lee, M.-S. Kim, C. K. Kim, C.-H. Chung, S.M. Cho, G.Y. Han, K. J. Yoon and B.-W. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 20, 862 (2003).
H.-J. Lee, D.-W. Kang, J. Chi and D. H. Lee, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 20, 503 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Artkla, S. Photodecomposition of polyphenols in E. camaldulensis leaves in the presence of hybrid catalyst of titania and MCM-41 synthesized from rice husk silica. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 29, 555–562 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0230-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0230-2