Abstract
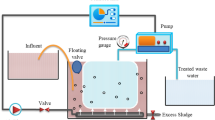
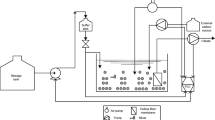
Water shortages and strict environmental provisions necessitate wastewater renovation using various wastewater treatment methods, among which applications of submerged membrane bioreactors (SMBRs) are rapidly increasing due to their advantages such as high loading capacity and quality of effluent. In this work, the effect of hydraulic retention time (HRT 8, 10 and 12 h) and temperature (25, 30 and 35°C) on membrane fouling and sludge production was investigated in a 5-Liter SMBR equipped with immersed PVDF hollow fiber membrane module. Phenolic synthetic wastewater and acclimatized activated sludge with phenol during a 2-month period were used as toxic and microbial sources, respectively. Results showed that by increasing HRT membrane fouling decreases, while excellent treatment performance of over 99.5% phenol and 95% COD removals was achieved at all HRTs. Therefore, HRT=8 h corresponding to the highest effluent flow rate of 12 L/m2·h was used to investigate the effect of temperature, resulting in phenol and COD removals of higher than 99 and 96%, respectively, at all temperatures. Membrane fouling occurred at 12, 5 and 3 days for 25, 30 and 35 °C, respectively. Additionally, the effect of HRT and temperature on mixed liquor volatile suspended solid (MLVSS) as a measure of biomass was examined. MLVSS concentration showed decreases with increasing HRT and temperature. Overall, it was shown that SMBR can be used to efficiently treat phenolic wastewater at a range of flow rates and temperatures, among which HRT=8 h and T=25 °C are the preferred operating conditions, resulting in high flow rate and low membrane fouling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Judd, The MBR Book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors in Water and Wastewater Treatment, Elsevier, Oxford (2006).
G. Traegardh and D. Johansson, Desalination, 119, 21 (1998).
Y.-C. Juang, D.-J. Lee and J.-Y. Lai, J. Chin. Ins. Chem. Eng., 39, 657 (2008).
S. Delgado, F. Díaz, R. Villarroel, L. Vera, R. Díaz and S. Elmaleh, Desalination, 146, 445 ( 2002).
H. S. Shin and S. T. Kang, Water Res., 37, 121 (2003).
F. Zhang, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1, 2859 (2009).
A. F. Viero, G. L. Sant and A. Jr, J. Hazard. Mater., 150, 185 (2008).
F. Meng and F. Yang, J. Membr. Sci., 305, 48 (2007).
S. Zhang, F. Yang, Y. Liu, X. Zhang, Y. Yamad and K. Furukaw, Desalination, 194, 146 (2006).
W. Lee, S. Kang and H. Shin, J. Membr. Sci., 216, 217 (2003).
B. Jefferson, P. Le-Clech and S. J. Judd, J. Membr. Sci., 218, 117 (2003).
F. Wicaksana, A. G. Fane and V. Chen, J. Membr. Sci., 271, 186 (2006).
A. Al-Amri, M.R. Salim and A. Aris, Desalination, 259, 111 (2010).
A. P. Le-Clech, B. S.B. Jefferson and B. J. Judd, Desalination, 173, 113 (2005).
E. S. Tarleton and R. J. Wakeman, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 71399–410 (1993).
Laure Defrance, Michel Y. Ja€rin, Bharat Gupta, Patrick Paullier and Valery Geaugey, Bioresur. Technol., 105 (2000).
W. Lee, S. K. Kang and H. S. Shin, J. Membr. Sci., 217 (2003).
Y. Magara and M. Itoh, Water Sci. Technol., 23, 1583 (1991).
J. Lee, W.Y. Ahn and C. H. Lee, Water Res., 35(10), 2435 (2001).
S. R. Chae and Y. Watanabe, J. Water Environ. Technol., 5, 45 (2007).
S. P. Hong, T. H. Bae, T.M. Tak, S. Hongb and A. Randall, Desalination, 143, 219 (2002).
S. R. Chae, Y. T. Ahn, S. T. Kang and H. S. Shin, J. Member. Sci., 280, 16 (2006).
Zhi Huang, Say L. Ong and How Y. Ng, Water Res., 1 (2010).
S. P. Hong, T. H. Bae, T.M. Tak, S. Hong and A. Randall, Desalination, 143, 219 (2002).
O. Tardiff and E. R. Hall, Water Sci. Technol., 35, 57 (1997).
T. Huuhilo, J. Suvilampi, L. Puro, J. Rintala, M. Mänttäri, J. Nuortila, Jokinen and M. Nyström, Paper and Timber, 84, 50 (2002).
S. Ahn, S. Congeevaram, Y. K. Choung and J. Park, Desalination, 494 (2008).
A. B. Martinez, E. Barbot, B. Marrot, P. Moulin and N. Roche, J. Membr. Sci., 288 (2006).
M. Maghami, Membrane bioreactor design for synthetic wastewater treatment, Master of Science Thesis in Chemical Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology (2010).
American Public Health Association and American Water Works Association and Water Pollution Control Federation, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th Ed., Washington DC (1998).
A. E. Greenberg, R. R. Trussell and L. S. Clesceri, Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 16th Ed., 556–567 (1985).
N. P. Cheremisinoff, The Biochemical Book: Biotechnology for Water and Wastewater Treatment (2001).
A. B. Martinez, E. Barbot, B. Marrot, P. Moulin and N. Roche, J. Membr. Sci., 281, 288 (2006).
F. Meng, S.R. Chae, A. Drews, M. Kraume, H. S. Shin and F. Yang, Water Res., 1489 (2009).
N. Ren, Z. Chen, A. Wanga and D. Hu, International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 55, 279 (2005).
F. Kargi and I. Konya, J. Environ. Manage., 84, 20 (2007).
K.G. Song, J. Cho and K. H Ahn, Bioprocess Biosystem Eng., 32, 135 (2009).
Z. Wang, Z. Wu and S. Tang, Water Res., 43, 2504 (2009).
Suvilampi and JAerobic, wastewater treatment under high and varying temperature-thermophilic process performance and effluent quality, Doctoral Thesis, University of Jyväskylä, 59 p (2003).
A. B. Martinez, E. Barbot, B. Marrot, P. Moulin and N. Roche, J. Membr. Sci., 288 (2006).
C.T. Joõ, P.R. Rachel, M. S. Cláudio and R. L. Valter, Process Biochem., 40, 1125 (2005).
S. Ahn, S. Congeevaram, Y. K. Choung and J. Park, Desalination, 494 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemmati, A., Dolatabad, M.M., Naeimpoor, F. et al. Effect of hydraulic retention time and temperature on submerged membrane bioreactor (SMBR) performance. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 29, 369–376 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0180-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0180-8