Abstract
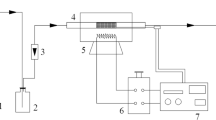
We used commercial activated coke (AC) as adsorbent and fixed-bed, FTIR, N2 adsorption, ion chromatograph as research methods to study the SO2 removal mechanism in the presence of O2 and H2O and adsorbate (H2SO4) desorption mechanism by combined regeneration. The results showed that AC saturation sulfur retention (52.6 mg/g) in SO2+O2+H2O atmosphere was 4.6 times as much as that (11.4 mg/g) in SO2+O2 atmosphere and 5.0 times as much as that (10.6 mg/g) in SO2+O2 atmosphere at 90 °C. O2 and H2O were necessary in AC desulfurization process. Reaction of SO3 and H2O (g) and condensation of sulfuric acid vapor were the dynamic of AC desulfurization process. Water vapor blowing in combined regeneration inhibited the reaction between H2SO4 and carbon, and consequently reduced the chemical lost of carbon. AC cumulative quality loss (53.6%) of five-times in C-R was still less than that (62.4%) of three-times in H-R. Water vapor blowing inhibited reactivation effect, as a result reducing the changes of AC pore structure and surface functional groups. Adsorbate H2SO4 generated in desulfurization evaporated to sulfuric acid vapor due to the high temperature in regeneration and was carried out by water vapor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Energy Strategy Study Group and Chinese Academy of Translation, 1st Ed. Science Press, Beijing, In Chinese (2006).
Y.-W. Nam and K.-S. Park, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 21, 370 (2004).
J. J. L and N. Kobayashi, Chem. Eng. Process., 47, 118 (2007).
K.-S. Kim, S. H. Park, K. T. Park, B.-H. Chun and S. H. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27, 624 (2010).
E. Richer, Catal. Today, 7, 93 (1990).
I. Mochida, K. Kuroda, S. Kawano, Y. Matsumura and M. Yoshikawa, Fuel, 76, 533 (1997).
E. Raymundo-Pinero, D. Cazorla-Amoro and A. Linares-Solano, Carbon, 39, 231 (2001).
A. A. Lizzio and J. A. De Barr, Fuel, 75, 1515 (1996).
E. Raymundo-Pinero, D. Cazorla-Amoro, C. S. M de Lecea and A. Linares-Solano, Carbon, 38, 335 (2000).
B. Rubio and M. T. Izquierdo, Fuel, 77, 631 (1998).
V. Gaur, R. Asthana and N. Verma, Carbon, 44, 26 (2006).
X. L. Zhang, H.X. Reng, K. Li and S. L. Han, Journal of China Mining University, 36, 210, In Chinese (2007).
A. A. Lizzio and J. A. Debarr, Energy Fuel, 11, 284 (1997).
J. Zawadzki, Carbon, 25, 431 (1987).
S.Y. Zhang, T.Y. Zhu, Y. Wang, J. F. Lu and G. X. Yue, Power System Engineering, 20, 47, In Chinese (2004).
J. Zawadzki, Carbon, 25, 495 (1987).
I. Mochida, Y. Kora and M. Shirahama, Carbon, 38, 227 (2000).
Z. Y. Feng, Active coke preparation and application technology, Dalian University of Technology Press, Dalian, In Chinese (2007).
X. M. Fei, Y. C. Zhang and J. X. Zhou, Chem. Environ., 26, 378, In Chinese (2000).
M. S. Jia and C. M. Ling, Industrial Boiler, 82, 31 (2003). (In Chinese).
G. J. Shang, Mechanism of physical structure and surface functional groups of activated semi-cokes used in SO 2 removal from flue gas, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, In Chinese (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, F., Gao, J., Zhu, Y. et al. Mechanism of SO2 adsorption and desorption on commercial activated coke. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 28, 2218–2225 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0078-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0078-5