Abstract
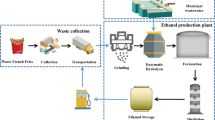
The synchronous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) by continuous fill and draw method was investigated in order to develop a continuous ethanol fermentation process using the food wastes (FW) available among Korea’s organic wastes. The activity of the hydrolytic enzymes was maintained constantly in the continuous culture by their intermittent addition together with medium exchange. The concentrations of reducing sugar in the culture were maintained at a steady state by regulating supplemented enzyme concentration and exchange rate of medium, reflecting on the consumption rate of reducing sugar caused by the fermentation. When the temperature of the SSF was maintained at the fixation of 35 °C, which enabled us to perform both enzymatic hydrolysis and enzyme fermentation simultaneously, the rate of reducing sugar consumption was 3.61 g/L-hr. For the enzymatic saccharification of FW, when 0.01 BGU as Viscozyme/g-FW and 0.05 AGU as Spirizyme Plus/g-FW were used, the production rate of reducing sugar was 3.93 g/L-hr, indicating a little higher rate of production than that of consumption. A decompression device with ethanol condensing ability was used to continuously pull out ethanol from the culture broth at −600 mmHg, where the ethanol evaporation ability would be maximized and the water evaporation minimized during the process. As a result of the continuous SSF performance, the reducing sugar concentration was maintained at around 30 g/L. The amylase activity was maintained at 8.93±2.17 U/mL. During a 352 hour culture, the whole ethanol productivity was 2.24 g/L-hr, indicating a considerable productivity compared with the other result reported in the continuous SSF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. S. Lee and Y. J. Lee, Current aspects and future prospects of bioethanol as a motor fuel, Special Edition (2006).
The national waste statistics survey in Korea, Ministry of environment republic of Korea & National Institute of Environmental Research (2009).
G. Shama, Proc. Biochem., 23, 138 (1988).
A. K. Chandel, E. S. Chan, R. Rudravaram, M. L. Narasu, L.V. Rao and P. Ravindra, Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2(1), 14 (2007).
M. Takagi, S. Abe, S. Suzuki, G. H. Emert and N. Yata, Chem. Microbial Protein, IIT, Delhi, 554 (1977).
J. D. Wright, Energy Prog., 84, 71 (1988).
M. E. Hong, K. S. Lee, B. J. Yu, Y. J. Sung, S. M. Park, H. M. Koo, D. H. Kweon, J. C. Park and Y. S. Jin, J. Biotechnol., 149(1–2), 52 (2010).
I. Holzberg, R. K. Finn and K. H. Steinbraus, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 9, 413 (1967).
H. J. Han, H. X. Li and S. J. Kim, Korean J. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 21(6), 474 (2006).
G.W. Choi, M. H. Han and Y. Kim, Korean J. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 23(3), 276 (2008).
M.W. Thomas and K.M. Bhat, Method Enzym., 160, 87 (1998).
N. Svetlana, M. Ljilana, R. Marica and P. Dusanka, Fuel, 88, 1602 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Yang, L., Kim, YJ. et al. Continuous ethanol production by the synchronous saccharification and fermentation using food wastes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 28, 1085–1089 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0465-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0465-3