Abstract
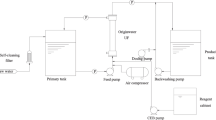
It is believed that rapid membrane fouling generally occurs at early-stage of filtration. The operating parameters have great effects on membrane performance. As a result, conducting filtration with appropriate conditions in initial stage may improve membrane efficiency. Therefore, we propose the idea of improving membrane performance by controlling initial operating parameters. Two strategies are employed for this purpose: enhanced backwash and inclining filtration. During initial period of operation, backwash frequency is increased (enhanced backwash) or/and flux is increased from the sub-critical flux to the critical or the supra-critical flux (inclining filtration). To evaluate the effects of these strategies, synthetic water simulating a river is treated through microfiltration (MF) of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane at dead-end mode. The study results showed that initial enhanced backwash causes more fouling than normal backwash. Instead, filtration without initial backwash successfully reduces fouling. Inclining filtration is found effective in fouling reduction. Rapid fouling progress is successfully suppressed by employing filtration at low flux during initial operation.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
P. Le-Clech, V. Chen and T. A. G. Fane, J. Membr. Sci., 284, 17 (2006).
S. G. J. Heijman, M. Vantieghem, S. Raktoe, J. Q. J. C. Verberk and J. C. van Dijk, J. Membr. Sci., 287, 119 (2007).
A. W. Zularisam, A. F. Ismail and R. Salim, Desalination, 194, 211 (2006).
J. D. Lee, S. H. Lee, M. H. Jo, P. K. Park and J. W. Kwak, Environ. Sci. Technol., 34, 3780 (2000).
A. T. Pikkarainen, S. J. Judd, J. Jokela and L. Gillberg, Water Res., 38, 455 (2004).
K. Katsoufidou, S. G. Yiantsios and A. J. Karabelas, J. Membr. Sci., 266, 40 (2005).
P. J. Smith, S. Vigneswaran, H. H. Ngo, R. B. Aim and H. Nguyen, J. Membr. Sci., 278, 381 (2006).
N. M. Mostefa, O. Akoum, M. Nedjihoui, L. Ding and M. Y. Jaffrin, Desalination, 206, 494 (2007).
Z. F. Cui and K. I. T. Wright, J. Membr. Sci., 117, 109 (1996).
L. Defrance and M. Y. Jaffrin, J. Membr. Sci., 152, 203 (1999).
R. W. Field, D. Wu, J. A. Howell and B. B. Gupta, J. Membr. Sci., 100, 259 (1995).
C. C. Ho and A. L. Zydney, J. Colloid. Interf. Sci., 232, 389 (2000).
E. Iritani, Y. Mukai, Y. Tanaka and T. Murase, J. Membr. Sci., 103, 181 (1995).
P. Bacchin, P. Aimar and R. W. Field, J. Membr. Sci., 281, 42 (2006).
K. Y. J. Choi and B. A. Dempsey, J. AWWA, 97(7), 134 (2005).
R. Chan, V. Chen and M. P. Bucknall, Desalination, 146(1–3), 83 (2002).
I.H. Huisman, E. Vellenga, G. Trägårdh and C. Trägårdh, J. Membr. Sci., 156, 153 (1999).
B. O. Cho and A. G. Fane, J. Membr. Sci., 209, 391 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, QF., Kim, SH. Inclining filtration and enhanced backwash for initial fouling control in microfiltration. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 27, 1565–1569 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0241-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0241-4