Abstract
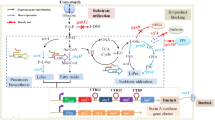
Effects of different ammonium sulfate concentrations on meilingmycin biosynthesis were studied in this research. The results show that a lower concentration of ammonium ions stimulates the biosynthesis of meilingmycin, while a concentration higher than 5 mmol/L inhibits the mycelial growth and the biosynthesis of the products. However, increased sugar consumption rate with the elevated concentration of ammonium sulfate was observed during the fermentation process. On this basis, six enzymes, which are responsible for the meilingmycin biosynthesis and the glucose metabolism, were measured and analyzed during the bioprocess. The results suggest that glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, citrate synthase, succinate dehydrogenase and fatty acid synthase are stimulated by higher concentration of ammonium ions, while valine dehydrogenase and methylmalonyl-CoA carboxyltransferase are inhibited. From the results it follows that the precursor supply was restricted with the higher concentration of ammonium ions, which results in the lower production of meilingmycin. Thus, the strategy of maintaining a low level of FAS activity is a critical factor for high yield of meilingmycin.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
S. Takahashi, H. Miyaoka, K. Tanaka, R. Enokita and T. Okazaki, J. Antibiot., 46(9), 1364 (1993).
L. Ouyang, J. Microbiol., (Chinese), 24, 195 (1984).
H. Ikeda and S. Omura, J. Antibiot., 48(7), 549 (1995).
J. Novák, P. Hájek, T. Rezanka, et al., FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 93, 57 (1992).
S. Omura, Y. Tanaka, H. Mamada and R. Masuma, J. Antibiot., 37(5), 494 (1984).
Y. P. Zhuang, B. Chen, J. Chu and S. L. Zhang, Process Biochem., 41(2), 405 (2006).
S. R. Li, X. Z. Xie, Z. Z. Hu, Q. P. Jin and B. J. Cai, J. East China Inst. Chem. Eng., 2, 177 (1982).
L.X. Zhang, T. F. Zhang and L.Y. Li, The method and technology of biochemical experiment (Second edition), High Education Publishing Company, Beijing, China (1997).
A. Vancura, I. Vancurová, J. Volc, S. P. Fussey, M. Flieger, J. Neuzil, J. Marsálek and V. Bhal, J. Gen. Microbiol., 134(12), 3213 (1988).
K. Vu-Trong, S. Bhuwapathanapun and P. P. Gray, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 17, 519 (1980).
H.U. Bergmeyer, Methods of enzymatic analysis, 3rd Ed., Florida· Basel, Verlag Chemie (Vol. III), 190 (1983).
Z. T. Ding, Y. P. Jiang and H. M. Ren, Chin. J. Clin Neurosci, 11(3), 243 (2003).
P. Dickie and J. H. Weiner, Can. J. Biochem., 57, 813 (1979).
W.X. Tian, Y.Q. Dong, C. Hu and F. Wen, Chin. Biochem. J., 12(2), 234 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhuang, Yp., Wang, P. et al. Regulation of meilingmycin in Streptomyces nanchangensis: Effect of ammonium ion. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 27, 910–914 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0150-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0150-6