Abstract
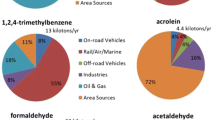
We compiled contour maps of the concentrations of major volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and corresponding chronic inhalation and carcinogenic risks in South Korea for the year 2004. We used the CALPUFF modeling system, an atmospheric dispersion model, to calculate the concentrations of five species of VOCs (benzene, ethylbenzene, styrene, toluene, and xylene). This modeling approach was used to validate the emission rates estimated in Part I of this study. The predicted concentrations show good overall agreement with the observed concentrations. In terms of risk assessment, we studied the chronic and carcinogenic effects on human health based on toxicity data and predicted concentrations of VOCs in ambient air. Risk levels were influenced by regional characteristics and spatial emission patterns. The results of such risk assessments could be used in support of air quality management in South Korea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. C. Edwards and E. M. Kenyon, Air toxics and risk assessment, Lewis Publishers, USA, 256 (1991).
B. J. Finlayson-Pitts and J. N. Jr. Pitts, Science, 276, 1045 (1997).
T. Elbir, Atmos. Environ., 38, 4509 (2004).
M. Caputo, M. Giménez and M. Schlamp, Atmos. Environ., 37, 2435 (2003).
N. S. Homes and L. Morawska, Atmos. Environ., 40, 5902 (2006).
J. S. Scire, D. G. Strimaitis and R. J. Yamartino, A User’s Guide for the CALPUFF Dispersion Model (Version 5). Earth Tech, Inc. (2000).
L. Wang, D. B. Parker, C. B. Parnell, R. E. Lacey and B. W. Shaw, Atmos. Environ., 40, 4663 (2006).
Ministry of Environment in Korea (MOE), Monthly report of air quality (2004).
R. Heinrich-ramm, M. Jakubowski, B. Heinzow, J. M. Christensen, E. Olsen and O. Hertel, Pure Appl. Chem., 72, 385 (2000).
Integrated risk information system, USEPA (The United States Environmental Protection Agency), (2007).
Guidelines for carcinogen risk assessment, USEPA (The United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2005).
F. Cangialosi, G. Intini, L. Liberti, M. Notarnicola and P. Stellacci, Waste Manag., 28, 885 (2008).
T. Ohura, T. Amagai and M. Fusaya, Atmos. Environ., 40, 238 (2006).
Human health risk assessment Protocol for hazardous waste combustion facilities, USEPA (The United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1998).
C. J. Willmott, Phys. Geogr., 2. 185 (1981).
P. Z. Reza, S. Kingham and J. Pearce, Sci. Total Environ., 349. 249 (2005).
Role of the baseline risk assessment in superfund remedy selection decisions, USEPA (The United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwak, B.K., Kim, J.H., Park, HS. et al. A GIS-based national emission inventory of major VOCs and risk assessment modeling: Part II — quantitative verification and risk assessment using an air dispersion model. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 27, 121–128 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0306-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0306-4