Abstract
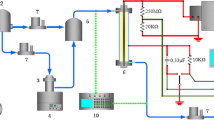
For the treatment of gaseous ozone emission, this study investigated the adsorption and enrichment of ozone and the destruction of the adsorbed ozone by nonthermal plasma. A nonthermal plasma reactor with adsorbent pellets in it was operated in two sequential modes, adsorption and decomposition of ozone. First, the ozone-containing gas was flowed through the reactor for a given period, in which the ozone was adsorbed and concentrated. In the next step, the gas was switched to argon or nitrogen, bypassing the ozone-containing gas, and AC high voltage was applied to the reactor to produce nonthermal plasma for the decomposition of the adsorbed ozone. By this method, the gaseous ozone was effectively treated with reasonable electrical energy consumption. The adsorbed ozone was converted into molecular oxygen when argon was used as the ozone decomposition gas, whereas a small amount of nitrogen oxides was formed with nitrogen. The energy consumed to decompose the adsorbed ozone was found to be 540 and 795 kJ/g-O3 decomposed with argon and nitrogen, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Demirev and V. Nenov, Ozone: Sci. Eng., 27, 475 (2005).
J.W. Choi, H.K. Song, W. Lee, K.-K. Koo, C. Han and B.-K. Na, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 21, 398 (2004).
T. Oda, T. Takahashi and K. Yamaji, IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 40, 1249 (2004).
S.H. Kong, C. I. Kwon and M.H. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 20, 293 (2003).
E. J. Rosenfeldt, K. G. Linden, S. Canonica and U. von Gunten, Water Res., 40, 3695 (2006).
Y. Sun, Y. Qiu, A. Nie and X. Wang, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 35, 1496 (2007).
S. J. Yoa, Y. S. Cho and J. H. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 22, 364 (2005).
G.-B. Zhao, S. V. B. J. Garikipati, X. Hu, M. D. Argyle and M. Radosz, AIChE J., 51, 1800 (2005).
Z. Hao, D. Cheng, Y. Guo and Y. Liang, Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 33, 217 (2001).
B. Dhandapani and S. T. Oyama, Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 11, 129 (1997).
R. Radhakrishnan and S. T. Oyama, J. Catal., 199, 282 (2001).
R. C. Sullivan, T. Thornberry and J. P. D. Abbatt, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 4, 1301 (2004).
C. Subrahmanyam, D. A. Bulushev and L. Kiwi-Minsker, Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 61, 98 (2005).
Y. C. Lin, C. L. Chang, T. S. Lin, H. Bai, M. Yan, F. Ko, C. Wu and C. Huang, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 25, 446 (2008).
O.R. Wulf and R. C. Tolman, The thermal decomposition of ozone, in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 13, 272 (1927).
U. Kogelschatz, Plasma Chem. Plasma Proc., 23, 1 (2003).
L. A. Rosocha, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 33, 129 (2005).
C. Lee, D.B. Graves, M. A. Lieberman and D.W. Hess, J. Electrochem. Soc., 141, 1546 (1994).
J. Kitayama and M. Kuzumoto, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 30, 2453 (1997).
I. Stefanoviæ, N.K. Bibinov, A.A. Deryugin, I. P. Vinogradov, A. P. Napartovich and K. Wiesemann, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 10, 406 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mok, Y.S., Koh, D.J., Shin, D.N. et al. Gaseous ozone decomposition using a nonthermal plasma reactor with adsorbent and dielectric pellets. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 26, 1613–1619 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0248-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0248-x