Abstract
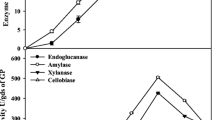
For saccharifying food wastes, cellulolytic enzymes were produced using Trichoderma inhamatum KSJ1 in modified Mandel’s medium. In a previous study, 0.1% bacto peptone in Mandel’s medium was established as the best organic nitrogen source for the production of cellulolytic enzymes using strain KSJ1. However, economically, peptone was too expensive. Therefore, soybean, yeast and Chunggookjang (fermented soybean paste) were substituted for peptone in this research. Also, yeast or ground soybean hydrolyzed by sulfuric acid or from a culture broth of Bacillus alcalophilus, a strain producing protease, was added to the medium as the nitrogen source to the production of cellulolytic enzyme. In the cultivation using 0.5% yeast hydrolyzed with a culture solution of B. alcalophilus as the nitrogen source, the activities of FPase and amylase were 0.20 and 2.17 U/mL in a 100 mL flask, compared to 0.35 and 1.24 U/mL with the 0.1% peptone as control, respectively. In a 10 L jar fermenter, the activities of FPase and amylase were improved to 0.40 and 4.82 U/mL in the cultivation, respectively, using 0.5% yeast hydrolyzed with the culture broth, compared with 0.38 and 3.79 U/mL, respectively, for the 0.1% peptone as control. Therefore, hydrolyzed yeast was established as an available nitrogen source for the industrial scale production of cellulolytic enzymes by strain KSJ1, resulting in a 52.3% cost reduction in the production of cellulolytic enzyme by substitution of the expensive nitrogen sources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. J. Song, J. H. Seo, G. S. Cha and S. J. Kim, Korean J. Soc. Urb. Environ., 6, 21 (2006).
H. J. Han and S. J. Kim, Korean J. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 21, 267 (2006).
H. J. Han, H. X. Li and S. J. Kim, Korean J. Biotechnol. Bioeng., 21, 474 (2006).
K. C. Kim, S. W. Kim, M. J. Kim and S. J. Kim, Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng., 10, 52 (2005).
S. S. Yoo, K. C. Kim, Y. A. Oh, S. Y. Chung and S. J. Kim, Kor. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 30, 172 (2002).
G. E. Ji, H. K. Han, S. W. Yun and S. L. Rhim, J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2, 85 (1992).
M. W. Thomas and K. M. Bhat, Method Enzymol., 160, 87 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Kim, MJ. & Kim, SJ. Cost-cutting of nitrogen source for economical production of cellulolytic enzymes by Trichoderma inhamatum KSJ1. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 26, 1070–1074 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0178-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0178-7