Abstract
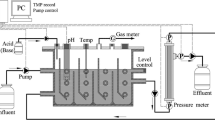
We investigated the effect of organic or inorganic materials on membrane fouling in advanced drinking water treatment by hybrid module packed with granular activated carbon (GAC) outside a tubular ceramic microfiltration membrane. Instead of natural organic matters (NOM) and fine inorganic particles in the natural water source, synthetic water was prepared with humic acid and kaolin. Concentrations of kaolin or humic acid were changed to see effects of inorganic or organic matter. And periodic water-back-flushing using permeate water was performed during 10 sec per filtration of 10 min. As a result, both the resistance of membrane fouling (R f ) and permeate flux (J) were influenced higher by concentration of humic acid rather than kaolin. It was proved that NOM like humic acid could be a more important factor on membrane fouling in drinking water treatment than fine inorganic particles. Treatment efficiencies of turbidity and UV254 absorbance were very high above 97.4% and 92.0%, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. R. Costa and M. N. Pinho, Desalination, 196, 55 (2006).
L. Fiksdal and T. O. Leiknes, J. Membr. Sci., 279, 364 (2006).
Y. T. Lee and J. K. Oh, Membrane Journal, 9, 193 (1999).
T. Leiknes, H. Ødegaard and H. Myklebust, J. Membr. Sci., 242, 47 (2004).
J. I. Oh and S. H. Lee, J. Membr. Sci., 254, 39 (2005).
M. H. Kim and J. Y. Park, Membrane Journal, 11, 190 (2001).
M. H. Cho, C. H. Lee and S. H. Lee, Desalination, 191, 386 (2006).
S. Gur-Reznik, I. Katz and C. G. Dosoretz, Water Res., 42, 1595 (2008).
H. S. Kim, S. Takizawa and S. Ohgaki, Desalination, 202, 271 (2007).
S. Mozia and M. Tomaszewska, Desalination, 162, 23 (2004).
H.K. Oh, S. Takizawa, S. Ohgaki, H. Katayama, K. Oguma and M. J. Yu, Desalination, 202, 191 (2007).
Y. T. Lee and J. K. Oh, Membrane Journal, 13, 219 (2003).
D. B. Mosqueda-Jimenez and P. M. Huck, Desalination, 198, 173 (2006).
W. Yuan, A. Kocic and A. L. Zydney, J. Membr. Sci., 198, 51 (2002).
M. Heran and S. Elmaleh, J. Membr. Sci., 188, 181 (2001).
S. K. Karode, J. Membr. Sci., 188, 9 (2001).
P. Rai, C. Rai, G. C. Majumdara, S. D. Gupta and S. De, J. Membr. Sci., 283, 116 (2006).
E. O. Kim, Membrane Journal, 3, 12 (1993).
Y. T. Lee and M. H. Song, Membrane Journal, 14, 192 (2004).
M. Cheryan, Technomic Publishing Company, Lancaster, Pennsylvania (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is dedicated to Professor Chang Kyun Choi for celebrating his retirement from the School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Seoul National University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H.C., Park, J.Y. & Yoon, DY. Advanced water treatment of high turbid source by hybrid module of ceramic microfiltration and activated carbon adsorption: Effect of organic/inorganic materials. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 26, 697–701 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0116-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0116-8