Abstract
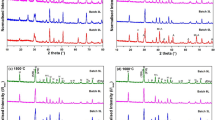
The thermal behavior of Illitic-kaolinitic clay for manufacturing of low porosity ceramic Raschig rings was characterized during the sintering process. The samples were shaped by extrusion method and fired at different temperatures from 1,100 to 1,300 °C. The main physical-chemical transformations were studied by evaluating changes in shrinkage, water absorption, porosity, mechanical strength, microstructure and mineralogical compositions. The optimum sintering condition was found to obtain maximum mechanical strength. Chemical resistance of ceramic Raschig rings also was determined according standard method. It was shown that the better chemical resistance could be attributed to the different mineralogical compositions, in particular with presence of mullite phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. L. Bravo and J. R. Fair, Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev., 21, 162 (1982).
I. R. Billet and I. M. Schultes, Chem. Eng. Tech., 16, 1 (1993).
A. F. Seibert and J. R. Fair, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 32, 2213 (1993).
F. Strigle, Jr., Random packing and packed tower, Huston TX; Gulf Publication Co. (1987).
J. S. Reed, Introduction to principles of ceramic processing, John Wiley & Sons, 2nd ed. New York (1995).
C. M. F. Vieira, P. R. N. Silva, F. T. Silva, J. L. Capitaneo and S. N. Monteiro, Revista Matéria, 10, 526 (2005).
J. M. Villora, P. Callejas, M. F. Barba and C. Baudín, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 24, 589 (2004).
W. M. Carty and U. Senapati, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 81, 3 (1998).
S. Lee, Y. J. Kim, H. J. Lee and H. S. Moon, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 82, 2096 (2001).
W. E. Lee and Y. Iqbal, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 21, 2583 (2001).
ASTM-C21: Standard test method for water absorption, bulk density, apparent porosity of fired ceramic, Annual book of ASTM Standards (1995).
ASTM C329-88: Standard test method for specific gravity of fired ceramic whiteware materials, Annual Book of ASTM Standards (1988).
ASTM-C515: Standard specification for chemical-resistant ceramic tower packing, Annual Book of ASTM Standards (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salehi, M., Salem, A. Influence of sintering temperature on microstructural changes of ceramic Raschig ring. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 26, 500–505 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0085-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-009-0085-y