Abstract
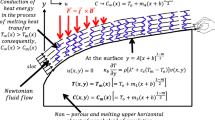
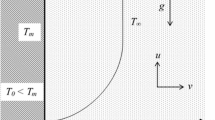
When a horizontal homogeneous solid is melted from below, convection can be induced in a thermally unstable melt layer. In this study the onset of buoyancy-driven convection during time-dependent melting is investigated by using similarly transformed disturbance equations. The critical Rayleigh numbers based on the melt-layer thickness are found numerically for various conditions. For small superheats, the present predictions approach the well known results of classical Rayleigh-Bénard problems, that is, critical Rayleigh numbers are located between 1,296 and 1,708, regardless of the Prandtl number. However, for high superheats the critical Rayleigh number increases with an increase in phase change rate but with decrease in Prandtl number.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.M. Sparrow, L. Lee and N. Shamsundar, J. Heat Transfer, 98, 88 (1976).
C. Gau and R. Viskanta, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 28, 573 (1985).
C. F. Chen and F. Chen, J. Fluid Mech., 227, 567 (1991).
I.G. Hwang and C.K. Choi, J. Crystal Growth, 267, 714 (2004).
R. J. Goldstein and J.W. Ramsey, in Studies in heat transfer, A. Festschrift, E. R.G. Eckert, J. P. Hartnet Eds., McGraw-Hill, Washington DC, pp. 199–208 (1978).
S. Ostrach, Trans. ASME: J. Fluids Eng., 105, 5 (1983).
D. Feldman, M. M. Shapiro, D. Banu and C. J. Fuks, Solar Energy Mater., 18, 201 (1989).
M. K. Smith, J.Fluid Mech., 188, 547 (1988).
H. S. Carslaw and J. C. Jaeger, Conduction of heat in solids, 2nd ed., Oxford Univ. Press (1959).
I. G. Hwang, AIChE J., 47, 1698 (2001).
D.V. Boger and J.W. Westwater, Trans. ASME: J. Heat Transfer, 89, 81 (1967).
R. P. Lowell, J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., 26, 1 (1985).
M. C. Kim, T. J. Chung and C.K. Choi, Kor. J. Chem. Eng., 21, 69 (2004).
J. Mathews and R. L. Walker, Mathematical methods of physics, 2nd ed., W.A. Benjamin Inc. (1970).
E.M. Sparrow, R. J. Goldsetin and V.K. Jonsson, J. Fluid Mech., 18, 513 (1964).
M. C. Kim, H. K. Park and C. K. Choi, Theoret. Comput. Fluid Mech., 16, 49 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.C., Lee, D.W. & Choi, C.K. Onset of buoyancy-driven convection in melting from below. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 25, 1239–1244 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-008-0205-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-008-0205-0