Abstract
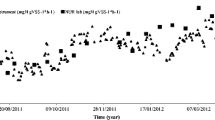
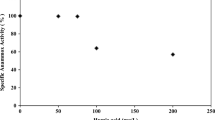
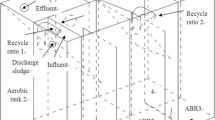
To assess the effect of DO concentration in aerobic biofilm reactor, we investigated the bacterial communities and their activity utilizing the combination of two methods, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and INTdehydrogenase activity test. D-1, D-2, D-3 and D-4 reactor with different DO concentrations (1, 3, 5 and 7 mg/L, respectively) were set up in the thermostat and acclimated. The optimal DO concentration with stable nitrification efficiency in aerobic biofilm reactor was above 5.0 mg/L. FISH method showed us that higher DO concentration led to the increase of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria ratios and the decrease of heterotrophs ratio. The INT-DHA activities of each reactor were 203, 153, 36 and 45 mgO2*/g VSS/day, respectively. The INT-DHA activities in D-1 and D-2 reactors were higher than those of D-3 and D-4 reactors, which indicates that filamentous microorganisms affected the INT-DHA activity. In the case of D-3 and D-4 reactors, as nitrification efficiency increased, INT-DHA activity also increased. In the relationship between the attached biomass and nitrification efficiency, only active biomass influenced the nitrification efficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hur, S., Park, J., Kim, Y. et al. Fluorescence in situ hybridization and INT-dehydrogenase activity test to assess the effect of DO concentration in aerobic biofilm reactor. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 24, 93–98 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-5015-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-007-5015-2